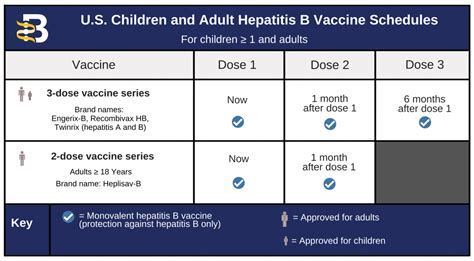
The hepatitis B vaccination schedule is a crucial aspect of preventing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which can lead to severe liver disease, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) recommend a series of vaccinations to provide long-term protection against HBV. In this article, we will delve into the hepatitis B vaccination schedule, its importance, and the various factors that influence its administration.
Primary Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule
The primary hepatitis B vaccination schedule typically consists of three doses of the hepatitis B vaccine, which are administered at specific intervals. The first dose is usually given at birth, followed by a second dose at 1-2 months of age, and a third dose at 6-18 months of age. This schedule is designed to provide optimal protection against HBV infection and is recommended for all individuals, regardless of age or risk factors.
Vaccination Schedule for High-Risk Groups
Certain individuals, such as healthcare workers, injection drug users, and those with multiple sexual partners, are at increased risk of HBV infection. For these high-risk groups, the hepatitis B vaccination schedule may be accelerated or modified to provide more rapid protection. For example, a two-dose schedule with a booster dose at 1-2 years may be recommended for adults who require rapid protection.
| Vaccination Schedule | Age | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Schedule | Birth | 1st dose |
| Primary Schedule | 1-2 months | 2nd dose |
| Primary Schedule | 6-18 months | 3rd dose |
| Accelerated Schedule | 0 months | 1st dose |
| Accelerated Schedule | 1 month | 2nd dose |
| Accelerated Schedule | 2 months | 3rd dose |

Key Points
- The primary hepatitis B vaccination schedule consists of three doses administered at birth, 1-2 months, and 6-18 months of age.
- High-risk groups, such as healthcare workers and injection drug users, may require an accelerated or modified vaccination schedule.
- The hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective in preventing HBV infection, with a success rate of 90-95% after completion of the primary schedule.
- Booster doses may be recommended for certain individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems or who are at increased risk of HBV infection.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the most appropriate hepatitis B vaccination schedule for individual circumstances.
Importance of Hepatitis B Vaccination
Hepatitis B vaccination is crucial in preventing HBV infection, which can lead to severe liver disease and liver cancer. The hepatitis B vaccine has been shown to be highly effective in preventing HBV infection, with a success rate of 90-95% after completion of the primary schedule. Furthermore, vaccination has been associated with a significant reduction in the incidence of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
Global Impact of Hepatitis B Vaccination
The introduction of hepatitis B vaccination has had a significant impact on the global incidence of HBV infection. According to the WHO, the prevalence of HBV infection has decreased by 84% since the introduction of vaccination in 1982. This reduction in incidence has been associated with a significant decrease in the number of cases of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
In conclusion, the hepatitis B vaccination schedule is a critical aspect of preventing HBV infection. The primary schedule consists of three doses administered at birth, 1-2 months, and 6-18 months of age, with modified schedules recommended for high-risk groups. The importance of hepatitis B vaccination cannot be overstated, with a success rate of 90-95% after completion of the primary schedule and a significant reduction in the incidence of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
What is the primary hepatitis B vaccination schedule?
+The primary hepatitis B vaccination schedule consists of three doses administered at birth, 1-2 months, and 6-18 months of age.
Who is at increased risk of HBV infection?
+Certain individuals, such as healthcare workers, injection drug users, and those with multiple sexual partners, are at increased risk of HBV infection.
What is the success rate of the hepatitis B vaccine?
+The hepatitis B vaccine has a success rate of 90-95% after completion of the primary schedule.