The Air Force Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) community plays a vital role in supporting national security objectives by providing timely and accurate geospatial information to decision-makers. As a domain-specific expert with a background in geospatial analysis and a deep understanding of the Air Force's GEOINT capabilities, I will delve into the complexities of this field, exploring its evolution, current state, and future directions. With a focus on technical accuracy and accessibility, this article aims to provide an authoritative perspective on the critical role of GEOINT in modern military operations.
Key Points
- The Air Force GEOINT community utilizes a range of sensors and platforms to collect and analyze geospatial data, providing critical support to military operations and national security decision-making.
- Advances in remote sensing technologies, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and hyperspectral imaging, have significantly enhanced the accuracy and resolution of geospatial data, enabling more effective targeting and battle damage assessment.
- The integration of GEOINT with other intelligence disciplines, such as signals intelligence (SIGINT) and human intelligence (HUMINT), has improved the overall effectiveness of intelligence operations, enabling more comprehensive and accurate assessments of adversary capabilities and intentions.
- The Air Force is investing in new technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of GEOINT analysis, and to improve the dissemination of geospatial information to decision-makers.
- The increasing use of commercial satellite imagery and other non-traditional sources of geospatial data is expanding the scope and accessibility of GEOINT, enabling more widespread use of geospatial information across the military and intelligence communities.
Evolution of Air Force Geospatial Intelligence
The Air Force GEOINT community has undergone significant transformation over the past few decades, driven by advances in technology, changes in the global security environment, and evolving military doctrine. The advent of satellite-based remote sensing in the 1960s marked the beginning of a new era in geospatial intelligence, enabling the collection of high-resolution imagery and other geospatial data from space. The development of digital imaging technologies in the 1980s further enhanced the accuracy and resolution of geospatial data, paving the way for the widespread adoption of GEOINT across the military and intelligence communities.
Remote Sensing Technologies
Remote sensing technologies have played a critical role in the evolution of Air Force GEOINT, enabling the collection of geospatial data from a range of sensors and platforms. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and hyperspectral imaging are two examples of advanced remote sensing technologies that have significantly enhanced the accuracy and resolution of geospatial data. SAR, which uses radar pulses to generate high-resolution images, has proven particularly effective in penetrating cloud cover and collecting data in low-light conditions, making it an essential tool for military operations in a range of environments.
| Remote Sensing Technology | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) | Uses radar pulses to generate high-resolution images | Penetrates cloud cover, effective in low-light conditions |
| Hyperspectral Imaging | Collects data across a range of spectral bands | Enables detailed analysis of terrain and target characteristics |
| Multispectral Imaging | Collects data across a limited range of spectral bands | Provides basic terrain and target characterization |

Current State of Air Force Geospatial Intelligence
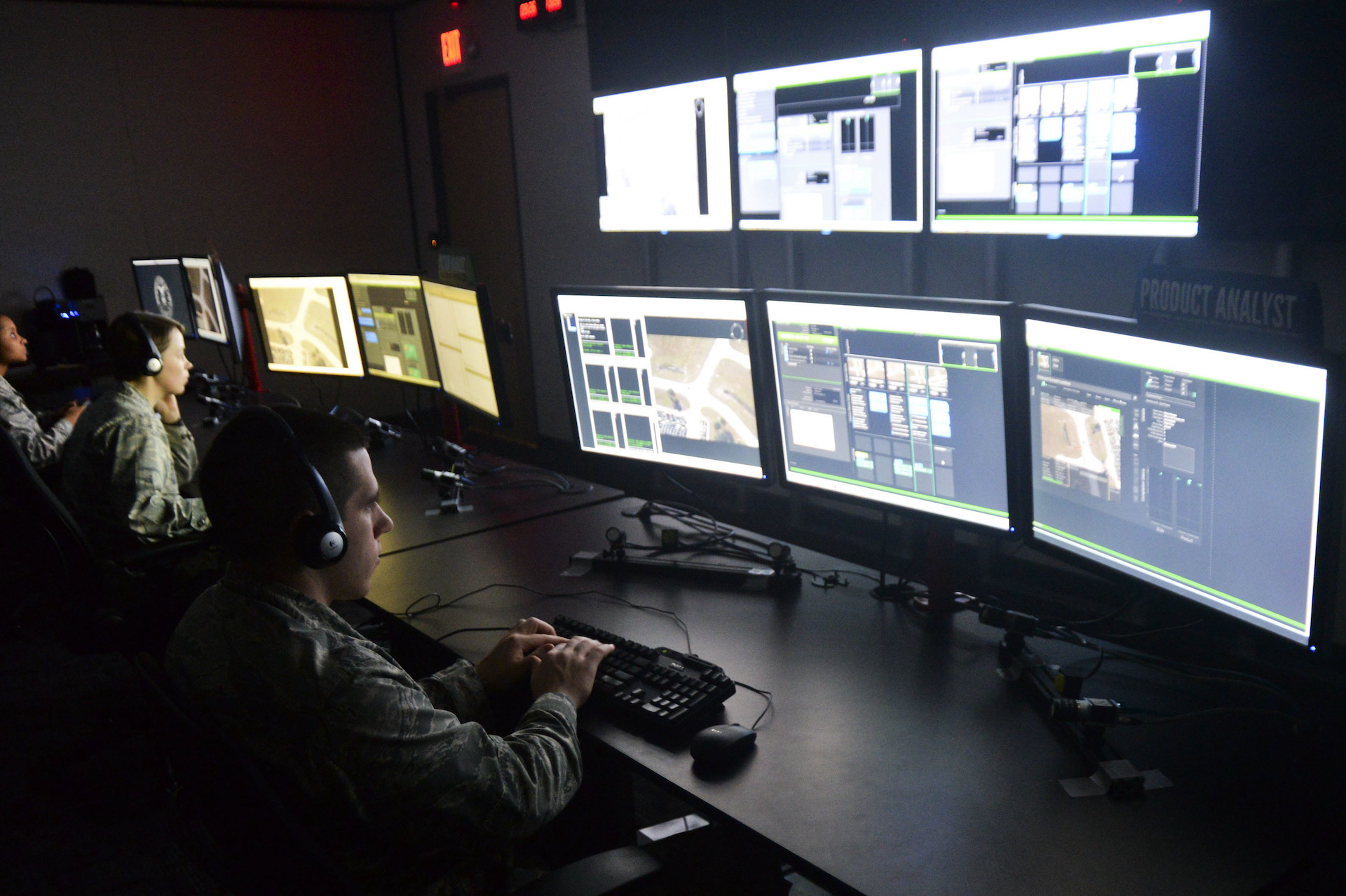

The current state of Air Force GEOINT is characterized by a high degree of technological sophistication, with a range of advanced sensors and platforms providing critical support to military operations and national security decision-making. The integration of GEOINT with other intelligence disciplines, such as SIGINT and HUMINT, has improved the overall effectiveness of intelligence operations, enabling more comprehensive and accurate assessments of adversary capabilities and intentions. The Air Force is also investing in new technologies, including AI and ML, to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of GEOINT analysis, and to improve the dissemination of geospatial information to decision-makers.
Geospatial Intelligence Analysis
Geospatial intelligence analysis is a critical component of Air Force GEOINT, involving the interpretation and analysis of geospatial data to extract relevant information and insights. This process typically involves a range of activities, including data collection, data processing, and data analysis, as well as the integration of geospatial data with other sources of intelligence. The use of advanced analytics tools, such as geographic information systems (GIS) and geospatial data bases, has significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of geospatial intelligence analysis, enabling more rapid and effective decision-making.
Future Directions for Air Force Geospatial Intelligence
The future of Air Force GEOINT is likely to be shaped by a range of factors, including advances in technology, changes in the global security environment, and evolving military doctrine. The increasing use of commercial satellite imagery and other non-traditional sources of geospatial data is expected to expand the scope and accessibility of GEOINT, enabling more widespread use of geospatial information across the military and intelligence communities. The Air Force is also likely to continue investing in new technologies, including AI and ML, to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of GEOINT analysis, and to improve the dissemination of geospatial information to decision-makers.
Emerging Technologies
A range of emerging technologies, including small satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and autonomous systems, are likely to play a significant role in the future of Air Force GEOINT. These technologies have the potential to provide more rapid and effective collection of geospatial data, as well as enhanced analytical capabilities, enabling more accurate and timely decision-making. The integration of these technologies with existing GEOINT capabilities will be critical to ensuring the continued effectiveness of Air Force GEOINT in supporting national security objectives.
What is the role of geospatial intelligence in modern military operations?
+Geospatial intelligence plays a critical role in modern military operations, providing timely and accurate information on the location, characteristics, and intentions of adversary forces. This information is used to support a range of military activities, including targeting, battle damage assessment, and situational awareness.
How has the Air Force GEOINT community evolved over time?
+The Air Force GEOINT community has undergone significant transformation over the past few decades, driven by advances in technology, changes in the global security environment, and evolving military doctrine. The advent of satellite-based remote sensing in the 1960s marked the beginning of a new era in geospatial intelligence, enabling the collection of high-resolution imagery and other geospatial data from space.
What are some of the key challenges facing the Air Force GEOINT community?
+The Air Force GEOINT community faces a range of challenges, including the need to integrate GEOINT with other intelligence disciplines, the requirement to provide more rapid and effective decision-making support, and the need to address emerging threats and technologies. The community must also balance the need for advanced technological capabilities with the requirement for trained and experienced analysts to interpret and analyze geospatial data.
Meta Description: Discover the critical role of Air Force Geospatial Intelligence in supporting national security objectives, and explore the evolution, current state, and future directions of this vital intelligence discipline.



