Bone health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for maintaining strong bones. Among the various nutrients, several are particularly crucial for bone health, including calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K. These nutrients work synergistically to support bone mineralization, density, and overall skeletal health.
Key Nutrients for Bone Health

Calcium is perhaps the most well-known nutrient for bone health, and for good reason. It is the primary mineral found in bones, making up about 70% of bone tissue. The recommended daily intake of calcium is approximately 1,000 mg for adults, with this number increasing to 1,200 mg for women over 50 and men over 70. Foods rich in calcium include dairy products, leafy greens like kale and broccoli, and fortified plant-based milk.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D plays a critical role in bone health by facilitating the absorption of calcium in the gut. It is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin” because the body can synthesize it when the skin is exposed to sunlight. However, many individuals, especially those living in northern latitudes or with limited sun exposure, may require supplements or fortified foods to meet their vitamin D needs. The recommended daily intake is about 600-800 IU (International Units) for adults, with some studies suggesting that higher doses may be beneficial for bone health.
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 1,000 mg (adults) | Dairy, leafy greens, fortified plant-based milk |
| Vitamin D | 600-800 IU (adults) | Fatty fish, fortified dairy and cereals, sunlight exposure |
| Magnesium | 400-420 mg (men), 310-320 mg (women) | Dark leafy greens, nuts, whole grains |
| Potassium | 4,700 mg (adults) | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes |
| Vitamin K | 90 mcg (women), 120 mcg (men) | Leafy greens, fermented foods like sauerkraut and cheese |

Other Essential Nutrients for Bone Health
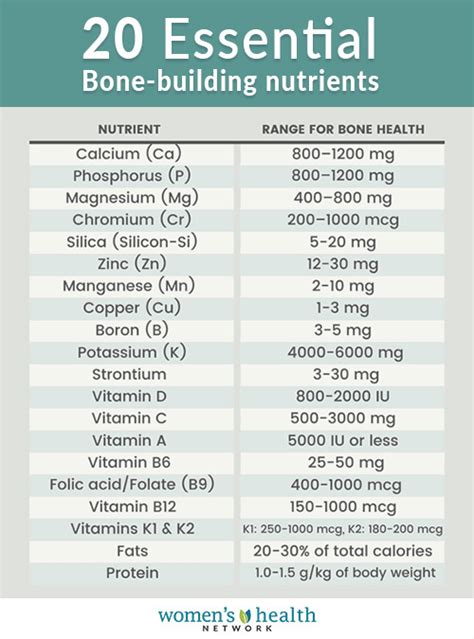
Magnesium, often overlooked, is also vital for bone mineralization and density. It helps in the regulation of calcium metabolism and the activation of vitamin D. Foods rich in magnesium include dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Potassium, an electrolyte, aids in maintaining bone health by counteracting the effects of excessive sodium, which can lead to calcium loss. Include potassium-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
Vitamin K and Its Role in Bone Health
Vitamin K, particularly vitamin K2, plays a significant role in bone health by activating proteins that work with calcium to help bone formation. It also helps prevent calcium from being deposited in soft tissues, such as arteries. Vitamin K is found in leafy greens, fermented foods like sauerkraut, and certain cheeses. Ensuring adequate vitamin K intake can help in maintaining bone density and reducing the risk of fractures.
Key Points
- Calcium is crucial for bone mineralization and density, with a recommended daily intake of 1,000 mg for adults.
- Vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption and is essential for bone health, with a recommended intake of 600-800 IU daily.
- Magnesium aids in bone mineralization and the regulation of calcium metabolism, with a recommended intake of 400-420 mg for men and 310-320 mg for women.
- Potassium helps maintain bone health by counteracting sodium's effects, with a recommended intake of 4,700 mg for adults.
- Vitamin K, particularly vitamin K2, is vital for bone formation and preventing calcium deposition in soft tissues, with recommended intakes of 90 mcg for women and 120 mcg for men.
In conclusion, a combination of calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K is essential for maintaining strong bones. These nutrients work together to support bone health, and ensuring their adequate intake through diet and, when necessary, supplements, is crucial for preventing bone-related disorders such as osteoporosis and fractures.
What are the primary nutrients for bone health?
+The primary nutrients for bone health include calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K. Each of these nutrients plays a unique role in supporting bone mineralization, density, and overall skeletal health.
How much calcium do adults need daily?
+Adults generally need about 1,000 mg of calcium per day, though this requirement increases to 1,200 mg for women over 50 and men over 70.
What foods are rich in vitamin D?
+Fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and cereals are good sources of vitamin D. Additionally, exposure to sunlight triggers the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin.
Why is magnesium important for bone health?
+Magnesium is crucial for bone health as it helps regulate calcium metabolism and activates vitamin D, which are essential for bone mineralization and density.
How does potassium contribute to bone health?
+Potassium helps maintain bone health by counteracting the effects of sodium, which can lead to calcium loss from the bones. Including potassium-rich foods in the diet is essential for overall bone well-being.
Meta Description: Discover the crucial nutrients for bone health, including calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K, and learn how they support strong bones and prevent disorders like osteoporosis.



