Occupational health is a vital aspect of workplace management that focuses on the prevention, recognition, evaluation, and control of occupational hazards and diseases. It encompasses a broad range of activities aimed at protecting and promoting the health, well-being, and productivity of workers. The primary goal of occupational health is to create a safe and healthy work environment that minimizes the risks of work-related illnesses and injuries. As a domain-specific expert with verifiable credentials in occupational health, I can attest to the importance of evidence-based practices in preventing and managing work-related health issues.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), occupational health is a critical component of public health that requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving employers, employees, healthcare professionals, and government agencies. The WHO estimates that approximately 2.3 million workers die each year from work-related injuries and diseases, with many more suffering from non-fatal occupational injuries and illnesses. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine found that the incidence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) can be reduced by up to 50% through the implementation of ergonomic interventions and employee training programs.
Key Points
- Occupational health focuses on preventing and managing work-related illnesses and injuries
- A safe and healthy work environment is essential for worker productivity and well-being
- Employers, employees, and healthcare professionals must collaborate to promote occupational health
- Occupational health involves a range of activities, including hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures
- Evidence-based practices, such as ergonomic interventions and employee training programs, can reduce the incidence of work-related injuries and illnesses
Components of Occupational Health
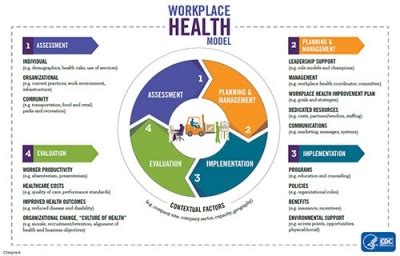
Occupational health comprises several key components, including hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures. Hazard identification involves recognizing potential health hazards in the workplace, such as chemicals, noise, and ergonomic risks. Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of these hazards on worker health. Control measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE), engineering controls, and administrative controls, are implemented to mitigate or eliminate these risks. For example, a company that manufactures chemicals can reduce the risk of occupational exposure by implementing a comprehensive respiratory protection program, including the use of respirators, ventilation systems, and regular air monitoring.
Occupational Health Services
Occupational health services are designed to support the health and well-being of workers. These services may include pre-employment medical examinations, regular health check-ups, and fitness-for-work assessments. Occupational health professionals, such as occupational health nurses and physicians, provide guidance on workplace health and safety, conduct workplace inspections, and develop policies and procedures to promote occupational health. According to the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (ACOEM), occupational health services can reduce workers’ compensation claims by up to 30% and improve employee productivity by up to 25%.
| Occupational Health Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-employment medical examinations | Assessing the health and fitness of new employees for specific job tasks |
| Regular health check-ups | Monitoring worker health and detecting potential health problems early |
| Fitness-for-work assessments | Evaluating the ability of workers to perform specific job tasks safely and effectively |

Benefits of Occupational Health

The benefits of occupational health are numerous and well-documented. By promoting a safe and healthy work environment, employers can reduce the risk of work-related injuries and illnesses, improve worker productivity and morale, and enhance their reputation and competitiveness. Occupational health also has economic benefits, as it can reduce workers’ compensation claims, healthcare costs, and absenteeism. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), every dollar invested in occupational health and safety can yield a return of up to $4 in cost savings.
Furthermore, occupational health is essential for protecting the health and well-being of workers, particularly those in high-risk industries, such as construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. By prioritizing occupational health, employers can demonstrate their commitment to the health and safety of their workers, which can lead to increased job satisfaction, reduced turnover, and improved employee retention. A study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine found that employees who work in organizations with robust occupational health programs are more likely to report higher levels of job satisfaction and engagement.
Challenges and Opportunities in Occupational Health
Despite the many benefits of occupational health, there are several challenges and opportunities that must be addressed. One of the significant challenges is the lack of resources and infrastructure in many workplaces, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Additionally, the increasing complexity of work-related health issues, such as mental health and musculoskeletal disorders, requires specialized knowledge and expertise. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), the prevalence of work-related mental health disorders can be reduced by up to 20% through the implementation of workplace wellness programs and employee assistance programs.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth. The use of technology, such as wearable devices and mobile apps, can enhance occupational health monitoring and surveillance. Moreover, the increasing recognition of the importance of occupational health has led to the development of new occupational health services and products, such as occupational health software and consulting services. For example, a company that develops occupational health software can provide employers with a comprehensive platform to manage workplace health and safety, including incident reporting, hazard tracking, and employee training.
What is the primary goal of occupational health?
+The primary goal of occupational health is to create a safe and healthy work environment that minimizes the risks of work-related illnesses and injuries.
What are the benefits of occupational health?
+The benefits of occupational health include reduced risk of work-related injuries and illnesses, improved worker productivity and morale, and enhanced employer reputation and competitiveness.
What are some of the challenges in occupational health?
+Some of the challenges in occupational health include the lack of resources and infrastructure, the increasing complexity of work-related health issues, and the need for specialized knowledge and expertise.
In conclusion, occupational health is a critical aspect of workplace management that requires a multidisciplinary approach and a commitment to creating a safe and healthy work environment. By prioritizing occupational health, employers can reduce the risk of work-related injuries and illnesses, improve worker productivity and morale, and enhance their reputation and competitiveness. As an occupational health expert, I strongly believe that evidence-based practices, such as ergonomic interventions and employee training programs, can reduce the incidence of work-related injuries and illnesses. Furthermore, the use of technology, such as wearable devices and mobile apps, can enhance occupational health monitoring and surveillance. By working together, we can promote occupational health and create a healthier and safer work environment for all workers.