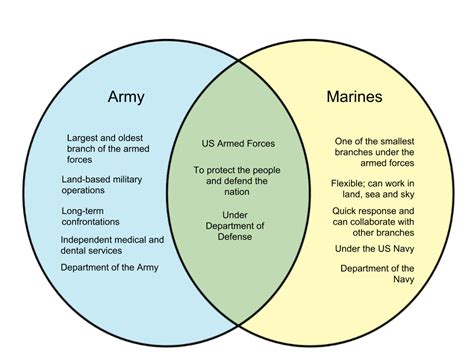
The United States Army's warrant officer ranks are a unique and vital part of the military's structure, providing a blend of technical expertise and leadership that is unparalleled in other branches of the armed forces. With a history dating back to 1918, warrant officers have played a crucial role in the Army's success, serving as specialists in their respective fields and providing guidance to enlisted personnel and commissioned officers alike. To become a warrant officer in the US Army, one must undergo a rigorous selection process, which includes meeting specific eligibility requirements, completing a warrant officer candidate school, and demonstrating a high level of technical proficiency in their chosen specialty.
History and Evolution of Warrant Officers in the US Army

The concept of warrant officers in the US Army has its roots in World War I, when the Army needed experts in specific technical fields to support its operations. The first warrant officers were appointed in 1918, and since then, the ranks have evolved to include a wide range of specialties, from aviation and signal communications to intelligence and cybersecurity. Today, there are over 25,000 warrant officers serving in the US Army, making up about 2.5% of the total officer corps. According to the US Army’s Warrant Officer Career College, the number of warrant officers has increased by 15% over the past five years, reflecting the growing demand for technical expertise in the military.
Key Points
- The US Army's warrant officer ranks were established in 1918 to provide technical expertise in specific fields.
- Warrant officers undergo a rigorous selection process, including meeting eligibility requirements and completing warrant officer candidate school.
- There are over 25,000 warrant officers serving in the US Army, making up about 2.5% of the total officer corps.
- The number of warrant officers has increased by 15% over the past five years, reflecting the growing demand for technical expertise in the military.
- Warrant officers play a critical role in the Army's success, serving as specialists in their respective fields and providing guidance to enlisted personnel and commissioned officers.
Warrant Officer Ranks and Specialties
The US Army has five warrant officer ranks: Warrant Officer 1 (WO1), Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2), Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3), Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4), and Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5). Each rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements, with WO1 being the entry-level rank and CW5 being the most senior. Warrant officers can specialize in a wide range of fields, including aviation, signal communications, intelligence, cybersecurity, and more. According to the US Army’s Warrant Officer Career College, the most in-demand specialties include cybersecurity, data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
| Warrant Officer Rank | Specialty | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| WO1 | Aviation | Conducts flight operations, maintains aircraft, and provides training to junior personnel. |
| CW2 | Signal Communications | Installs, operates, and maintains communications equipment, and provides technical guidance to junior personnel. |
| CW3 | Intelligence | Analyzes and interprets intelligence data, provides tactical support to units, and conducts training exercises. |
| CW4 | Cybersecurity | Develops and implements cybersecurity protocols, conducts risk assessments, and provides technical guidance to junior personnel. |
| CW5 | Artificial Intelligence | Develops and implements AI systems, conducts research and development, and provides strategic guidance to senior leaders. |

Warrant Officer Selection Process

The warrant officer selection process is highly competitive, with only a small percentage of applicants being selected for warrant officer candidate school. To be eligible, candidates must meet specific requirements, including being a US citizen, having a high school diploma or equivalent, and scoring well on the Army’s aptitude tests. They must also have a minimum of two years of service in the Army, and be recommended by their commander. Once selected, candidates undergo a rigorous training program, which includes classroom instruction, hands-on training, and field exercises. According to the US Army’s Warrant Officer Career College, the selection process has a 10% acceptance rate, making it one of the most competitive programs in the military.
Warrant Officer Career Progression
Warrant officers can expect to serve in a variety of roles throughout their careers, from technical specialist to leader and mentor. As they gain experience and complete advanced training, they can move up the ranks, taking on more senior roles and responsibilities. Warrant officers can also pursue advanced degrees and certifications, which can enhance their career prospects and provide opportunities for advancement. According to the US Army’s Warrant Officer Career College, the average warrant officer serves for 20 years, with 75% of warrant officers retiring at the rank of CW4 or higher.
What is the role of a warrant officer in the US Army?
+A warrant officer in the US Army is a technical expert in a specific field, providing guidance and support to enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. They serve as specialists in their respective fields, and are responsible for maintaining and operating complex equipment, analyzing data, and providing tactical support to units.
How do I become a warrant officer in the US Army?
+To become a warrant officer in the US Army, you must meet specific eligibility requirements, including being a US citizen, having a high school diploma or equivalent, and scoring well on the Army's aptitude tests. You must also have a minimum of two years of service in the Army, and be recommended by your commander. Once selected, you will undergo a rigorous training program, which includes classroom instruction, hands-on training, and field exercises.
What are the benefits of being a warrant officer in the US Army?
+The benefits of being a warrant officer in the US Army include the opportunity to serve as a technical expert in a specific field, providing guidance and support to enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. Warrant officers also have the opportunity to pursue advanced degrees and certifications, which can enhance their career prospects and provide opportunities for advancement. Additionally, warrant officers are eligible for special pay and allowances, and have access to a range of benefits, including healthcare, education, and retirement benefits.
In conclusion, warrant officers play a critical role in the US Army’s success, serving as technical experts in their respective fields and providing guidance to enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. The warrant officer selection process is highly competitive, but for those who are selected, the rewards are well worth the challenge. With their unique blend of technical expertise and leadership skills, warrant officers are an essential part of the Army’s structure, and will continue to play a vital role in the military’s operations for years to come. According to the US Army’s Warrant Officer Career College, the demand for warrant officers is expected to increase by 20% over the next five years, making it an exciting and rewarding career path for those who are interested in serving their country and pursuing a challenging and rewarding career.