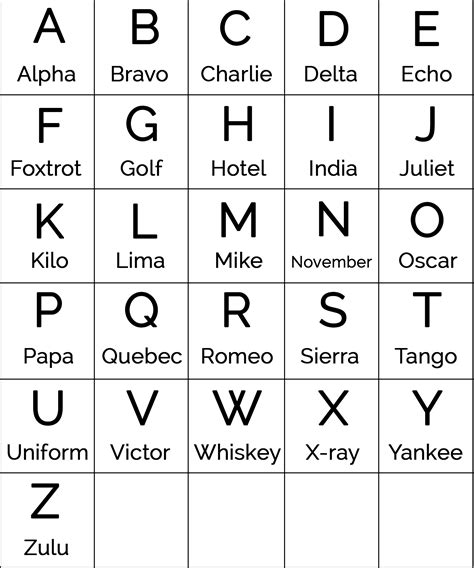
The military alphabet, also known as the NATO phonetic alphabet, is a standardized system used to clearly communicate letters and numbers over radio and phone communications, particularly in situations where standard letter pronunciation may be unclear. This system is crucial for avoiding confusion between similar-sounding letters, thereby ensuring accuracy and safety in military, aviation, and maritime communications.
Understanding the Military Alphabet
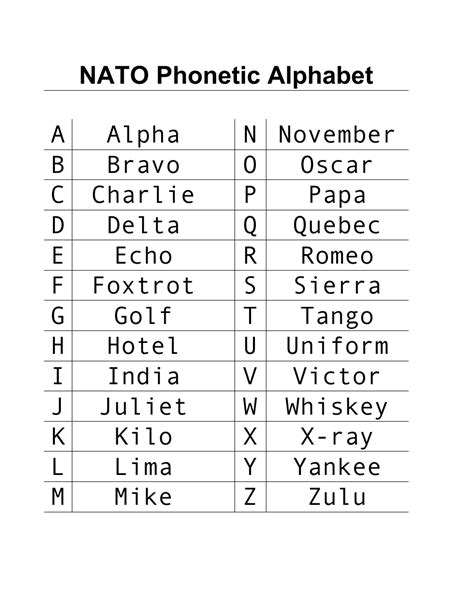
The military alphabet consists of 26 code words, each corresponding to a letter of the English alphabet. These code words are chosen to be distinct and easy to understand, even in environments with high levels of background noise or when communication quality is poor. For example, the letter “V” is represented by the code word “Victor” in the military alphabet.
Origin and Evolution
The use of a phonetic alphabet dates back to the early 20th century, with various organizations developing their own systems. However, it wasn’t until after World War II that the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) developed a standardized phonetic alphabet for global use. This standardization led to the adoption of the NATO phonetic alphabet by military forces around the world, ensuring consistent communication practices across different countries and organizations.
| Letter | Military Alphabet Code Word |
|---|---|
| A | Alpha |
| B | Bravo |
| C | Charlie |
| D | Delta |
| E | Echo |
| F | Foxtrot |
| G | Golf |
| H | Hotel |
| I | India |
| J | Juliet |
| K | Kilo |
| L | Lima |
| M | Mike |
| N | November |
| O | Oscar |
| P | Papa |
| Q | Quebec |
| R | Romeo |
| S | Sierra |
| T | Tango |
| U | Uniform |
| V | Victor |
| W | Whiskey |
| X | X-ray |
| Y | Yankee |
| Z | Zulu |
Practical Applications and Training

Training in the use of the military alphabet is an integral part of military and aviation education, emphasizing the importance of clear and precise communication. This training often includes practice exercises where individuals spell out words and phrases using the phonetic alphabet, helping to build muscle memory and improve communication speed and accuracy.
Benefits of Standardization
The standardization of the phonetic alphabet has significantly reduced communication errors in high-stakes environments. By providing a universally recognized and accepted method of clarifying letter pronunciation, the military alphabet has become an indispensable tool in global communication, facilitating cooperation and safety across linguistic and cultural barriers.
Key Points
- The military alphabet, or NATO phonetic alphabet, is a standardized system for clearly communicating letters and numbers.
- Each letter of the alphabet is assigned a unique code word to avoid confusion.
- The letter "V" is represented by the code word "Victor" in the military alphabet.
- Standardization of the phonetic alphabet has improved communication safety and efficiency in military, aviation, and other critical fields.
- Training in the use of the military alphabet is essential for personnel in these fields to ensure accurate and clear communication.
In conclusion, the military alphabet plays a vital role in ensuring clear and effective communication in situations where accuracy is paramount. The code word for the letter "V", Victor, is just one part of this comprehensive system designed to minimize errors and maximize understanding. As technology continues to evolve and global communication becomes increasingly complex, the importance of standardized communication tools like the military alphabet will only continue to grow.
What is the purpose of the military alphabet?
+The military alphabet is used to clearly communicate letters and numbers, especially in situations where standard pronunciation may be unclear or confusing.
How is the letter “V” represented in the military alphabet?
+The letter “V” is represented by the code word “Victor” in the military alphabet.
Why is standardization of the phonetic alphabet important?
+Standardization ensures that there is a universally recognized method for clarifying letter pronunciation, reducing communication errors and enhancing safety and cooperation across different countries and organizations.