The United States Navy has a long history of utilizing helicopter door guns in various military operations, providing suppressive fire and close air support to ground troops. The concept of helicopter door guns emerged during the Vietnam War, where the Navy's helicopter squadrons were tasked with providing medical evacuation, transport, and gunfire support. The door gunner, typically a crew chief or a gunner's mate, was responsible for operating the machine gun mounted on the helicopter's door or window. Over time, the role of door guns has evolved, with advancements in technology and changes in military doctrine.
The most commonly used door guns in the US Navy are the M240 machine gun and the GAU-17/A Minigun. The M240 is a 7.62mm general-purpose machine gun, known for its reliability and versatility, while the GAU-17/A is a 7.62mm six-barrel rotary machine gun, capable of firing up to 3,000 rounds per minute. The choice of door gun often depends on the specific mission requirements and the type of helicopter being used. For example, the MH-60R Seahawk and the MH-60S Knighthawk, both used by the Navy for anti-submarine warfare and search and rescue operations, are typically equipped with the M240 machine gun.
Key Points
- The US Navy uses helicopter door guns for suppressive fire and close air support.
- The M240 machine gun and the GAU-17/A Minigun are the most commonly used door guns in the Navy.
- The choice of door gun depends on the mission requirements and the type of helicopter being used.
- Door guns provide a vital layer of protection for ground troops and are an essential component of naval aviation operations.
- The role of door guns has evolved over time, with advancements in technology and changes in military doctrine.
Evolution of Door Guns in the US Navy

The concept of door guns in the US Navy has undergone significant changes since its inception during the Vietnam War. Initially, door guns were used primarily for self-defense and providing suppressive fire during medical evacuation and transport missions. However, as the military doctrine evolved, the role of door guns expanded to include close air support and anti-personnel missions. The introduction of new helicopter platforms, such as the MH-60R and MH-60S, has also led to the development of more advanced door gun systems, including the use of remote-controlled turret systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Door Guns
Door guns provide a vital layer of protection for ground troops and are an essential component of naval aviation operations. They offer several advantages, including the ability to provide suppressive fire, close air support, and self-defense capabilities. However, door guns also have limitations, such as the risk of friendly fire, the need for careful target identification, and the potential for gun jamming or malfunction. Additionally, the use of door guns can be affected by environmental factors, such as weather conditions and the presence of obstacles or terrain features.
| Type of Door Gun | Caliber | Rate of Fire |
|---|---|---|
| M240 machine gun | 7.62mm | 650-1,000 rounds per minute |
| GAU-17/A Minigun | 7.62mm | 2,000-3,000 rounds per minute |
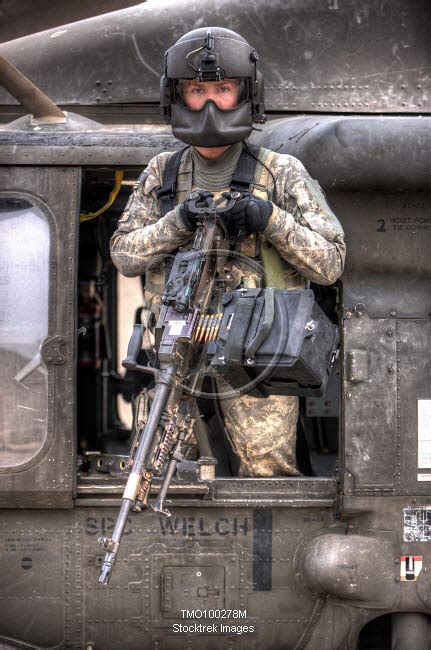

Training and Operations

The US Navy provides extensive training to its door gunners, including instruction on the operation and maintenance of the door gun, as well as training on tactics and procedures for engaging targets. Door gunners must also undergo regular qualification and proficiency training to ensure they are proficient in the use of the door gun. In terms of operations, door guns are typically used in conjunction with other assets, such as fixed-wing aircraft and ground troops, to provide a comprehensive and coordinated response to enemy forces.
Future Developments and Advancements
The future of door guns in the US Navy is likely to be shaped by advancements in technology and changes in military doctrine. The development of new helicopter platforms, such as the MH-60R and MH-60S, has already led to the introduction of more advanced door gun systems, including remote-controlled turret systems. Additionally, the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and other unmanned systems may also impact the role of door guns in future military operations. As the military continues to evolve and adapt to new threats and challenges, it is likely that the use of door guns will also continue to evolve and change.
What is the primary purpose of door guns in the US Navy?
+The primary purpose of door guns in the US Navy is to provide suppressive fire and close air support to ground troops, as well as self-defense capabilities for the helicopter and its crew.
What are the most commonly used door guns in the US Navy?
+The most commonly used door guns in the US Navy are the M240 machine gun and the GAU-17/A Minigun.
What are the limitations of door guns in the US Navy?
+The limitations of door guns in the US Navy include the risk of friendly fire, the need for careful target identification, and the potential for gun jamming or malfunction.