The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is a unique branch of the US military, operating under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime and the Department of the Navy during wartime. The Coast Guard's enlisted ranks are divided into several levels, each with distinct responsibilities and requirements. Understanding these ranks is essential for both those serving in the Coast Guard and the general public interested in the operations and structure of this vital service.
Enlisted Ranks in the US Coast Guard

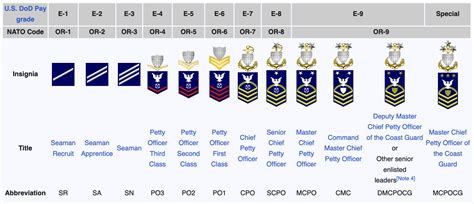
The US Coast Guard’s enlisted ranks are categorized into three main groups: Junior Enlisted, Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs), and Senior Enlisted. Each group represents a progression in responsibility, expertise, and leadership within the Coast Guard.
Junior Enlisted Ranks
The Junior Enlisted ranks are the entry-level positions within the Coast Guard. These ranks include:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The most junior rank in the Coast Guard, typically held by new recruits undergoing basic training.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): After completing basic training, members are advanced to Seaman Apprentice, where they begin their specialized training in a specific rating.
- Seaman (E-3): Seamen have completed their initial training and are serving in their first assignment, applying their skills and knowledge in their chosen rating.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
NCOs are experienced members who have demonstrated leadership and technical expertise. They are responsible for guiding junior members and are divided into several ranks:
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): The first NCO rank, where members have gained significant experience and are expected to lead and mentor junior personnel.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): These NCOs have advanced in their rating and are responsible for more complex tasks and leadership roles.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): With increased responsibility, Petty Officer First Class members lead teams, manage resources, and are key advisors to their superiors.
Senior Enlisted Ranks
The Senior Enlisted ranks represent the highest levels of leadership and expertise within the Coast Guard’s enlisted personnel:
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): Chiefs are senior leaders who have mastered their rating and are responsible for guiding and developing junior personnel, as well as advising officers on enlisted matters.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): Senior Chiefs are technical experts and leaders who oversee multiple units or divisions, providing strategic guidance and mentorship.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): The Master Chief Petty Officer is the most senior enlisted rank, serving as a senior advisor to the highest levels of the Coast Guard and representing the enlisted corps in matters of policy and procedure.
| Rank | Insignia | Pay Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit | No insignia | E-1 |
| Seaman Apprentice | One stripe | E-2 |
| Seaman | Two stripes | E-3 |
| Petty Officer Third Class | One chevron | E-4 |
| Petty Officer Second Class | Two chevrons | E-5 |
| Petty Officer First Class | Three chevrons | E-6 |
| Chief Petty Officer | One anchor | E-7 |
| Senior Chief Petty Officer | One anchor, one star | E-8 |
| Master Chief Petty Officer | One anchor, two stars | E-9 |
Key Points
- The US Coast Guard's enlisted ranks are divided into Junior Enlisted, Non-Commissioned Officers, and Senior Enlisted categories.
- Junior Enlisted ranks include Seaman Recruit, Seaman Apprentice, and Seaman, representing the entry-level positions within the Coast Guard.
- Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) are experienced members who have demonstrated leadership and technical expertise, including Petty Officer Third Class, Petty Officer Second Class, and Petty Officer First Class.
- Senior Enlisted ranks, including Chief Petty Officer, Senior Chief Petty Officer, and Master Chief Petty Officer, represent the highest levels of leadership and expertise.
- Advancement through the ranks is based on performance, time in service, and leadership potential, with each rank requiring increased competence and dedication to the Coast Guard's missions.
Understanding the structure and responsibilities of the US Coast Guard's enlisted ranks provides insight into the complexity and professionalism of this branch of the US military. From the junior ranks to the senior enlisted leaders, each member plays a crucial role in the Coast Guard's diverse missions, including maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, marine safety, and environmental protection, among others.
What is the most junior rank in the US Coast Guard?
+The most junior rank in the US Coast Guard is Seaman Recruit (E-1), which is typically held by new recruits undergoing basic training.
How do members advance through the ranks in the Coast Guard?
+Advancement through the ranks in the Coast Guard is based on a combination of time in service, performance evaluations, advancement exams, and leadership potential.
What are the responsibilities of a Petty Officer in the Coast Guard?
+Petty Officers are experienced members who have demonstrated leadership and technical expertise. They are responsible for guiding junior members, leading teams, and managing resources, depending on their specific rank and rating.