The United States Army Reserve is a vital component of the US Armed Forces, providing critical support to the Active Component and playing a significant role in national defense. As a Reserve Officer, individuals have the opportunity to serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers. The US Army Reserve offers a wide range of officer jobs, each with its unique responsibilities and requirements.
Officer Careers in the US Army Reserve
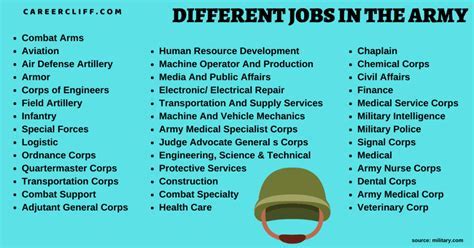
The US Army Reserve has over 150 different officer career fields, known as Military Occupational Specialties (MOS). These careers span various branches, including infantry, engineering, logistics, and medical fields, among others. Some of the most in-demand officer jobs in the US Army Reserve include:
- Infantry Officer (11A): Leads infantry troops in combat and training, responsible for the health, welfare, and safety of their soldiers.
- Signal Officer (25A): Manages the installation, operation, and maintenance of communication systems, ensuring seamless communication between units.
- Logistics Officer (90A): Oversees the planning, coordination, and execution of logistics operations, including supply chain management and transportation.
- Medical Officer (62B): Provides medical care to soldiers, including diagnosing and treating illnesses, injuries, and wounds.
- Cyber Operations Officer (17A): Conducts cyber operations to disrupt, degrade, or destroy enemy command and control systems.
Requirements for US Army Reserve Officer Jobs
To become an officer in the US Army Reserve, individuals must meet specific requirements, including:- Age: Be between 17 and 35 years old (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Education: Hold a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution
- Citizenship: Be a US citizen
- Background: Pass a background check and meet moral and medical standards
- Training: Complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or another approved commissioning program
Key Points
- The US Army Reserve offers over 150 different officer career fields
- Officer jobs range from infantry and engineering to logistics and medical fields
- Requirements for officer jobs include a bachelor's degree, US citizenship, and passing a background check
- Officer candidates must complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or another approved commissioning program
- Reserve Officers serve one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with opportunities for additional training and deployment
Benefits of Serving as a US Army Reserve Officer

Serving as a Reserve Officer offers numerous benefits, including:
- Leadership Opportunities: Develop leadership skills and gain experience in command and staff positions
- Education Benefits: Receive tuition assistance, student loan repayment, and access to graduate education programs
- Career Advancement: Enhance civilian career prospects with skills and experience gained through military service
- Travel and Training: Participate in training exercises and deployments, both domestically and internationally
- Healthcare and Retirement: Receive access to TRICARE healthcare and retirement benefits, including a pension and Thrift Savings Plan matching
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Leadership Opportunities | Develop leadership skills and gain experience in command and staff positions |
| Education Benefits | Receive tuition assistance, student loan repayment, and access to graduate education programs |
| Career Advancement | Enhance civilian career prospects with skills and experience gained through military service |
| Travel and Training | Participate in training exercises and deployments, both domestically and internationally |
| Healthcare and Retirement | Receive access to TRICARE healthcare and retirement benefits, including a pension and Thrift Savings Plan matching |
Pathways to Becoming a US Army Reserve Officer
There are several pathways to becoming a US Army Reserve Officer, including:- Officer Candidate School (OCS): A 12-week training program that teaches leadership, tactics, and military skills
- Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC): A college-based program that combines academic coursework with military training
- Direct Commission: A program that allows individuals with specialized skills or experience to be directly commissioned as officers
- Warrant Officer Candidate School: A program that trains individuals to become warrant officers, technical experts in their field
Conclusion
The US Army Reserve offers a wide range of officer jobs, each with its unique responsibilities and requirements. With benefits including leadership opportunities, education benefits, and career advancement, serving as a Reserve Officer can be a rewarding and challenging experience. Whether through Officer Candidate School, ROTC, or other pathways, individuals can develop valuable skills and serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers.What are the requirements to become a US Army Reserve Officer?
+To become a US Army Reserve Officer, individuals must meet specific requirements, including being between 17 and 35 years old, holding a bachelor’s degree, being a US citizen, passing a background check, and completing Officer Candidate School (OCS) or another approved commissioning program.
What are the benefits of serving as a US Army Reserve Officer?
+Serving as a US Army Reserve Officer offers numerous benefits, including leadership opportunities, education benefits, career advancement, travel and training, and healthcare and retirement benefits.
How do I become a US Army Reserve Officer?
+There are several pathways to becoming a US Army Reserve Officer, including Officer Candidate School (OCS), Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC), Direct Commission, and Warrant Officer Candidate School.



