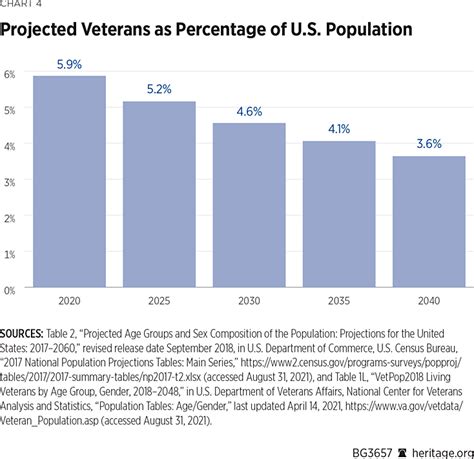
The United States Army has consistently faced challenges in meeting its recruiting goals, a situation that has been exacerbated by various factors including demographic changes, increasing competition from civilian employers, and evolving societal values. The Army's recruiting mission is to identify, recruit, and retain high-quality volunteers who can meet the service's manpower needs, ensuring the force remains capable of executing its full range of military operations. To achieve this, the Army sets annual recruiting goals that are based on a variety of factors, including personnel strength requirements, retention rates, and projected losses due to separations and retirements.
Historical Context and Challenges

Historically, the Army has adapted its recruiting strategies to respond to changing environments and challenges. For instance, during the height of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, the Army faced significant recruiting challenges due to the dangers and uncertainties of military service. In response, the Army implemented a range of initiatives, including enhanced recruiting bonuses, expanded enlistment opportunities for non-citizens, and improved marketing campaigns to appeal to a broader demographic. Despite these efforts, the Army has continued to face difficulties in meeting its recruiting goals, particularly in certain specialties and for high-quality recruits who meet stringent educational and aptitude standards.
Key Points
- The US Army faces persistent challenges in meeting its annual recruiting goals due to demographic shifts, competition from civilian employers, and evolving societal attitudes towards military service.
- Recruiting strategies have evolved over time, incorporating new technologies, marketing approaches, and incentives to attract a diverse pool of high-quality recruits.
- The Army's ability to meet its recruiting goals has significant implications for its operational capacity, force readiness, and ability to execute its missions effectively.
- Strategic partnerships with educational institutions, community organizations, and employers are critical for expanding the Army's reach and appeal to potential recruits.
- Efforts to enhance the recruiting process, including the use of data analytics and personalized outreach, aim to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recruiting operations.
Current Recruiting Environment and Strategies
The current recruiting environment is characterized by intense competition for top talent, with the Army competing against not only other military branches but also civilian employers offering competitive salaries, benefits, and career advancement opportunities. In response, the Army has implemented a range of strategies aimed at enhancing its appeal to potential recruits. These include the development of more sophisticated marketing campaigns that leverage social media and other digital platforms, the expansion of enlistment bonuses and other incentives, and efforts to improve the recruiting process itself, making it more efficient, personalized, and responsive to the needs and preferences of potential recruits.
| Recruiting Metric | FY 2020 | FY 2021 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Component Enlistments | 62,150 | 57,714 | 60,398 |
| Reserve Component Enlistments | 39,024 | 36,219 | 38,502 |
| High-Quality Recruits (AFQT 50+) | 73.1% | 71.5% | 74.2% |
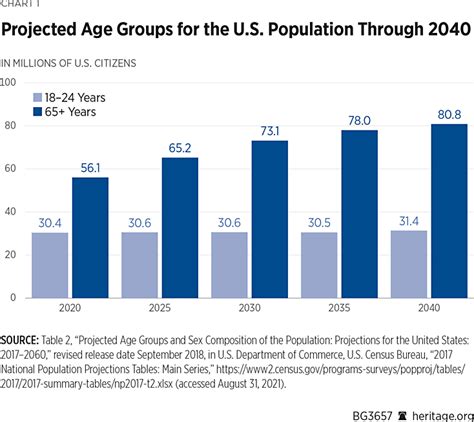
Future Directions and Implications

Looking ahead, the Army’s recruiting efforts will need to be responsive to emerging trends and challenges, including changes in the labor market, shifts in societal attitudes towards military service, and the evolving nature of conflict and military operations. This will require continued innovation in recruiting strategies, investments in digital technologies and data analytics, and a sustained focus on enhancing the Army’s appeal and value proposition to potential recruits. Furthermore, strategic partnerships with educational institutions, community organizations, and employers will be essential for expanding the Army’s reach and attracting a diverse pool of high-quality recruits.
The implications of failing to meet recruiting goals are significant, with potential impacts on force readiness, operational capacity, and the Army's ability to execute its missions effectively. Therefore, it is critical that the Army continues to evolve and improve its recruiting strategies, ensuring that it can attract and retain the talent needed to meet the challenges of the 21st century.
What are the primary challenges facing the US Army in terms of meeting its recruiting goals?
+The US Army faces several challenges, including demographic shifts, competition from civilian employers, and evolving societal attitudes towards military service. These factors make it difficult for the Army to attract and retain high-quality recruits who meet its manpower needs.
How is the Army adapting its recruiting strategies to address these challenges?
+The Army is implementing a range of strategies, including the use of digital technologies, enhanced marketing campaigns, and personalized outreach to potential recruits. Additionally, the Army is offering competitive incentives and improving the recruiting process to make it more efficient and responsive to the needs of recruits.
What are the implications of the Army failing to meet its recruiting goals?
+Failing to meet recruiting goals could have significant implications for the Army’s operational capacity, force readiness, and ability to execute its missions effectively. It is critical that the Army continues to evolve and improve its recruiting strategies to attract and retain the talent needed to meet the challenges of the 21st century.