The US Air Force B-1B bomber, also known as the Lancer, is a strategic bomber used by the United States Air Force. With a rich history dating back to the 1970s, the B-1B has undergone significant transformations to become one of the most advanced bombers in the world. The aircraft's development was initially driven by the need for a supersonic, variable-sweep wing bomber that could penetrate Soviet airspace and deliver nuclear weapons. Although the program faced significant challenges and controversies, the B-1B has proven to be a reliable and versatile asset for the US military.
Design and Development
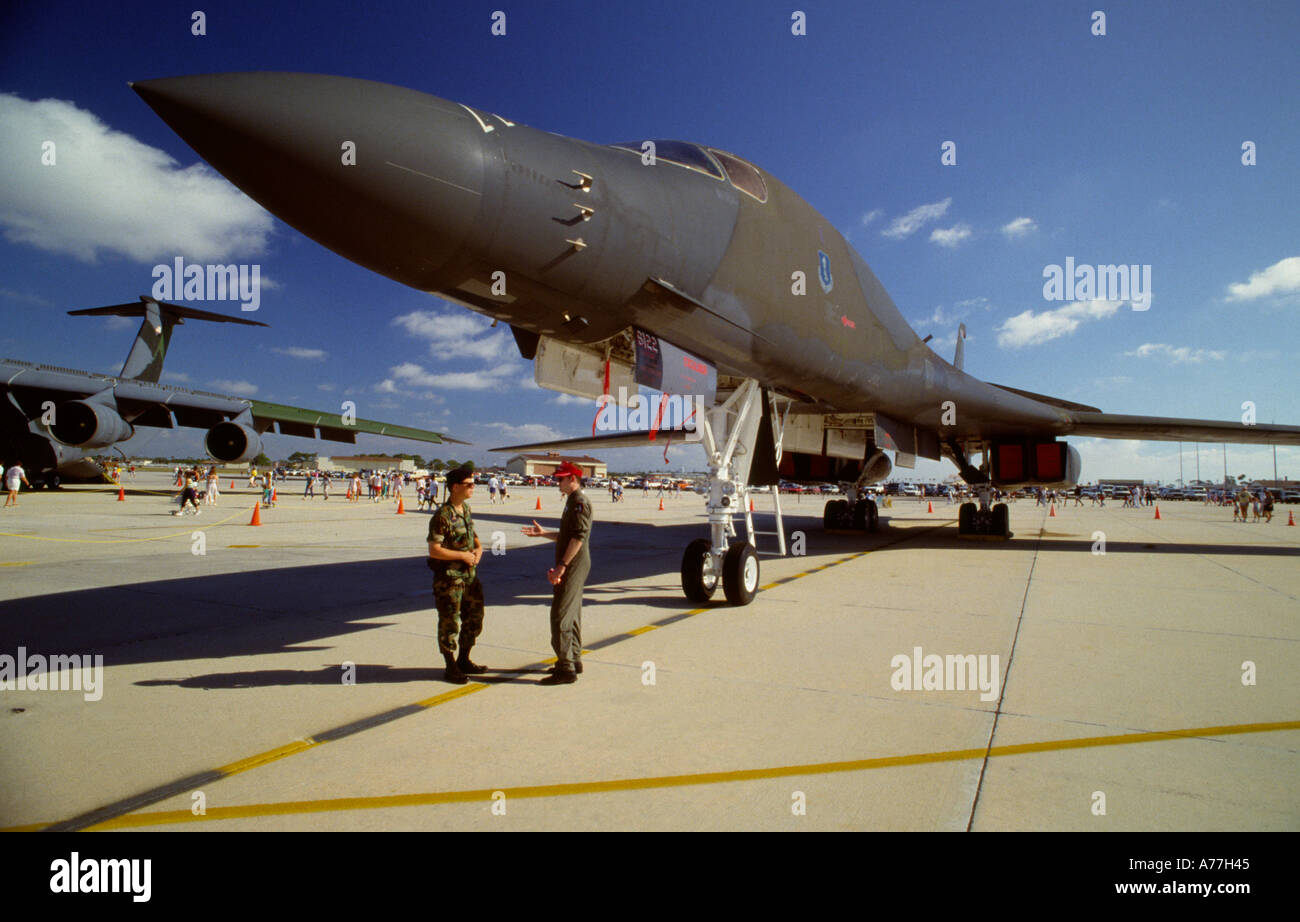

The B-1B’s design is characterized by its unique variable-sweep wing, which allows the aircraft to adjust its wing angle to optimize performance during different phases of flight. The bomber’s wings can sweep back to 67.5 degrees, reducing drag and increasing speed, or sweep forward to 15 degrees, increasing lift and reducing landing speed. This feature enables the B-1B to achieve high speeds, exceeding Mach 1.2, while also maintaining a relatively low landing speed. The aircraft’s airframe is made of a combination of aluminum, titanium, and composite materials, providing a strong and lightweight structure.
Avionics and Electronics
The B-1B is equipped with advanced avionics and electronics, including a AN/APQ-164 passive, phased-array radar system, which provides the aircraft with a high degree of situational awareness. The radar system allows the B-1B to detect and track multiple targets, including air defenses and enemy aircraft. The bomber also features a AN/ALQ-161 electronic countermeasures system, which helps to detect and neutralize enemy radar and missile systems. Additionally, the B-1B is equipped with a advanced communication system, including satellite communication and data links, enabling real-time communication with command centers and other aircraft.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Length | 146 feet (44.5 meters) |
| Wingspan | 136 feet (41.5 meters) |
| Height | 34 feet (10.4 meters) |
| Empty Weight | 192,000 pounds (87,090 kilograms) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 477,000 pounds (216,635 kilograms) |
| Engines | 4 x General Electric F101-GE-102 turbofan engines |
| Thrust | 30,000 pounds-force (133.4 kilonewtons) each |

Operational History

The B-1B has been involved in several military operations, including the Gulf War, the Kosovo War, and the War in Afghanistan. The bomber has proven to be an effective asset, providing close air support and conducting strategic bombing missions. The B-1B has also been used in various exercises and training missions, demonstrating its ability to operate in a variety of environments and scenarios.
Upgrades and Modernization
The B-1B has undergone several upgrades and modernization programs, including the installation of new avionics and electronics systems, as well as the integration of new munitions and sensors. The aircraft’s engines have also been upgraded, improving its range and endurance. Additionally, the B-1B has been equipped with advanced communications systems, enabling real-time communication with command centers and other aircraft.
Key Points
- The B-1B is a strategic bomber with a variable-sweep wing design, allowing it to achieve high speeds and maneuverability.
- The aircraft is equipped with advanced avionics and electronics, including a phased-array radar system and electronic countermeasures.
- The B-1B has been involved in several military operations, including the Gulf War and the War in Afghanistan.
- The aircraft has undergone several upgrades and modernization programs, including the installation of new avionics and electronics systems.
- The B-1B is capable of carrying a variety of munitions, including precision-guided bombs and missiles.
Munitions and Sensors
The B-1B is capable of carrying a variety of munitions, including precision-guided bombs, such as the Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) and the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser (WCMD). The aircraft is also equipped with advanced sensors, including a AN/AAQ-33 Sniper Advanced Targeting Pod, which provides high-resolution imaging and targeting capabilities. The B-1B’s sensor systems enable the aircraft to detect and engage targets in a variety of environments, including urban and mountainous terrain.
Crew and Training
The B-1B has a crew of four, including a pilot, co-pilot, and two weapon systems officers. The crew undergoes extensive training, including simulator training and live-fly exercises, to prepare for a variety of missions. The B-1B’s advanced avionics and electronics systems require a high degree of proficiency, and the crew must be able to operate the aircraft’s systems effectively in a variety of scenarios.
What is the primary mission of the B-1B bomber?
+The primary mission of the B-1B bomber is to provide strategic bombing capabilities, including the delivery of nuclear and conventional munitions.
What is the top speed of the B-1B bomber?
+The top speed of the B-1B bomber is over Mach 1.2, or approximately 900 miles per hour.
How many B-1B bombers are in service with the US Air Force?
+There are currently 62 B-1B bombers in service with the US Air Force.
The B-1B bomber is a highly capable and versatile aircraft, with a rich history and a wide range of capabilities. With its advanced avionics and electronics systems, the B-1B is able to perform a variety of missions, from strategic bombing to close air support. The aircraft’s variable-sweep wing design and advanced sensors make it an extremely effective asset, capable of operating in a variety of environments and scenarios.