The United States Battleships of World War II were a formidable force, playing a crucial role in the Allied victory. With their powerful guns, robust armor, and advanced propulsion systems, these battleships were the epitome of naval warfare during that era. The U.S. Navy's battleship fleet was comprised of several classes, each with its unique characteristics and strengths. This article will delve into the history, design, and operations of the U.S. battleships during World War II, highlighting their significance and impact on the war.
Key Points
- The U.S. Navy had 18 battleships in commission at the start of World War II, with 11 more under construction.
- The USS American battleships, including the Washington and South Dakota classes, were the most advanced and heavily armed of their time.
- Battleships played a crucial role in the Pacific Theater, providing gunfire support for amphibious landings and engaging enemy ships in surface battles.
- The USS Missouri (BB-63) was the site of the formal Japanese surrender on September 2, 1945, marking the end of World War II.
- The U.S. battleship fleet suffered significant losses during the war, including the USS Arizona (BB-39) and USS Oklahoma (BB-37) at Pearl Harbor.
Design and Construction
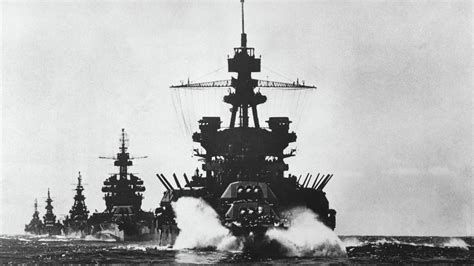
The U.S. battleships of World War II were designed to be fast, heavily armed, and well-armored. The Washington class, for example, had a top speed of over 28 knots (52 km/h) and was equipped with nine 16-inch (406mm) guns. The South Dakota class, on the other hand, had a slightly slower top speed but featured a more advanced armor layout and improved fire control systems. The U.S. Navy’s battleship design philosophy emphasized the importance of a strong, balanced fleet, with each ship capable of operating independently or as part of a larger task force.
Battleship Classes
The U.S. Navy had several battleship classes during World War II, each with its unique characteristics and strengths. The Colorado class, for example, was known for its powerful armament and robust armor, while the North Carolina class was recognized for its speed and agility. The Iowa class, which included the USS Iowa (BB-61), USS New Jersey (BB-62), USS Missouri (BB-63), and USS Wisconsin (BB-64), was the most advanced and heavily armed of all, with nine 16-inch (406mm) guns and a top speed of over 30 knots (56 km/h).
| Class | Ships | Armament | Armor | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 4 | 8 x 16-inch (406mm) guns | 13.5 inches (343mm) belt armor | 21 knots (39 km/h) |
| North Carolina | 2 | 9 x 16-inch (406mm) guns | 12 inches (305mm) belt armor | 28 knots (52 km/h) |
| South Dakota | 4 | 9 x 16-inch (406mm) guns | 12 inches (305mm) belt armor | 27 knots (50 km/h) |
| Iowa | 4 | 9 x 16-inch (406mm) guns | 12 inches (305mm) belt armor | 30 knots (56 km/h) |
Operations and Engagements

The U.S. battleships played a significant role in the Pacific Theater, providing gunfire support for amphibious landings and engaging enemy ships in surface battles. The USS California (BB-44), for example, participated in the Battle of Surigao Strait, where it helped sink the Japanese battleship Yamashiro. The USS Washington (BB-56) engaged the Japanese battleship Kirishima in the Battle of Guadalcanal, while the USS South Dakota (BB-57) fought against the Japanese battleship Yamato in the Battle of the Philippine Sea.
Pacific Theater Engagements
The U.S. battleships were involved in several key engagements in the Pacific Theater, including the Battle of Midway, the Battle of Guadalcanal, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. These battles showcased the U.S. battleships’ ability to operate effectively in a variety of environments, from the open ocean to coastal waters. The U.S. battleships’ gunfire support was instrumental in the success of Allied amphibious landings, such as the invasion of Tarawa and the invasion of Iwo Jima.
What was the primary role of U.S. battleships in World War II?
+The primary role of U.S. battleships in World War II was to provide gunfire support for amphibious landings and engage enemy ships in surface battles.
Which U.S. battleship class was the most advanced and heavily armed?
+The Iowa class was the most advanced and heavily armed U.S. battleship class, with nine 16-inch (406mm) guns and a top speed of over 30 knots (56 km/h).
What was the significance of the USS Missouri (BB-63) in World War II?
+The USS Missouri (BB-63) was the site of the formal Japanese surrender on September 2, 1945, marking the end of World War II.
Meta Description: Discover the history and significance of the United States Battleships in World War II, including their design, operations, and key engagements in the Pacific Theater. Learn about the different battleship classes and their roles in the war.



