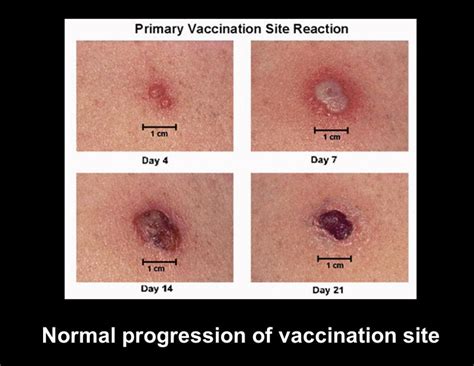
The quest for effective tuberculosis (TB) vaccines has been ongoing for decades, with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine being the most widely used. However, the BCG vaccine has several limitations, including variable efficacy in different regions and a significant drawback: it often leaves a visible scar at the injection site. This has led researchers to explore alternative vaccines that can provide improved protection without the scarring. One such approach is the development of TB vaccines that do not cause scarring, offering a more acceptable and cosmetic option for vaccine recipients.
Understanding the Need for Scar-Free TB Vaccines
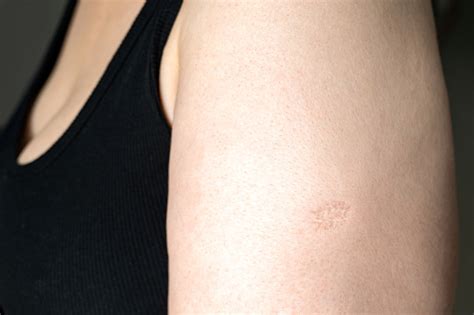
The BCG vaccine is administered via an intradermal injection, typically on the forearm or upper arm, and the resulting scar is considered a sign of successful vaccination. However, in many cultures, scars are viewed negatively, and the presence of a visible scar can lead to social stigma, especially among women. This stigma can discourage people from getting vaccinated, undermining efforts to control and prevent TB. A scar-free TB vaccine would not only improve the acceptability of vaccination but also enhance the overall effectiveness of TB control programs.
Approaches to Developing Scar-Free TB Vaccines
Several strategies are being explored to develop TB vaccines that do not cause scarring. One approach involves the use of different delivery methods, such as oral or nasal administration, which could potentially eliminate the need for injections and thereby reduce the risk of scarring. Another strategy focuses on developing vaccines that can be administered via a patch or a microneedle device, which would cause minimal trauma to the skin and result in less noticeable or no scarring.
| Vaccine Type | Delivery Method | Potential for Scarring |
|---|---|---|
| BCG | Intradermal Injection | High |
| Oral TB Vaccines | Oral Administration | None |
| Nasal TB Vaccines | Nasal Spray | None |
| Patch or Microneedle TB Vaccines | Transdermal | Low to None |
Key Considerations in TB Vaccine Development

Beyond the issue of scarring, several key considerations must be taken into account when developing new TB vaccines. These include ensuring high efficacy across different populations, particularly in regions with high TB prevalence; enhancing safety to minimize adverse reactions; and improving durability of protection to reduce the need for booster shots. Additionally, the development of TB vaccines must be guided by a thorough understanding of the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes TB, and how this response can be effectively harnessed to provide long-term protection.
Future Directions and Challenges
The road to developing effective, scar-free TB vaccines is fraught with challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the complex nature of the immune response to M. tuberculosis, which involves multiple cell types and pathways. Moreover, TB is a disease that affects people differently, depending on factors such as age, nutritional status, and the presence of co-infections like HIV. Therefore, any new vaccine must demonstrate efficacy and safety across a diverse range of populations. Despite these challenges, researchers remain optimistic, driven by advances in vaccine technology, a deeper understanding of the immune system, and the urgent need for better TB control tools.
Key Points
- The BCG vaccine, while effective, has limitations, including variable efficacy and the formation of a scar at the injection site.
- There is a need for TB vaccines that do not cause scarring to improve vaccine acceptance and reduce social stigma associated with vaccination scars.
- Researchers are exploring alternative delivery methods, such as oral, nasal, and transdermal routes, to develop scar-free TB vaccines.
- The development of new TB vaccines must consider efficacy, safety, durability of protection, and cultural acceptability.
- Understanding the immune response to M. tuberculosis and addressing the complexity of TB disease are crucial for the development of effective vaccines.
In conclusion, the development of TB vaccines that do not cause scarring represents a significant step forward in the fight against tuberculosis. By addressing the limitations of current vaccines and developing new technologies that are more acceptable and effective, researchers aim to enhance TB control efforts worldwide. As science continues to advance and our understanding of the immune system and vaccine technologies deepens, the prospect of scar-free, highly effective TB vaccines becomes increasingly promising.
What are the main limitations of the BCG vaccine?
+The BCG vaccine has variable efficacy in different regions and leaves a visible scar at the injection site, which can be a deterrent for some individuals due to social stigma.
How are researchers developing scar-free TB vaccines?
+Researchers are exploring alternative delivery methods such as oral, nasal, and transdermal administration to reduce or eliminate scarring. They are also working on vaccines that can be administered via patches or microneedle devices.
What factors are crucial for the development of effective TB vaccines?
+Ensuring high efficacy, safety, and durability of protection, as well as considering cultural and social factors that influence vaccine acceptance, are crucial for the development of effective TB vaccines.