Tpn Health, also known as Total Parenteral Nutrition, is a method of providing essential nutrients to the body through intravenous (IV) infusion. This medical treatment is designed for individuals who cannot receive nutrition through the traditional oral route, often due to severe gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, or other critical health conditions. The concept of Tpn Health has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in medical technology and a deeper understanding of nutritional requirements. As a domain-specific expert in healthcare, it is crucial to delve into the intricacies of Tpn Health, its benefits, and its potential complications, to provide informed guidance to healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Understanding Tpn Health

Tpn Health involves the administration of a specialized nutrient solution directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. This solution typically contains a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, tailored to meet the individual’s nutritional needs. The primary goal of Tpn Health is to support the body’s metabolic functions, promote healing, and prevent malnutrition. According to the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN), approximately 200,000 to 300,000 patients in the United States receive Tpn Health each year, highlighting the significance of this treatment modality.
Key Points
- Tpn Health is a method of providing essential nutrients through intravenous infusion.
- The treatment is designed for individuals with severe gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, or other critical health conditions.
- The nutrient solution contains a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Tpn Health aims to support metabolic functions, promote healing, and prevent malnutrition.
- Approximately 200,000 to 300,000 patients in the United States receive Tpn Health each year.
Indications and Contraindications
The decision to initiate Tpn Health is typically made by a healthcare provider, taking into account the patient’s medical history, nutritional status, and ability to tolerate oral or enteral nutrition. Indications for Tpn Health include severe gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or short bowel syndrome, as well as cancer, AIDS, or other conditions that impair nutrient absorption. However, Tpn Health is not without risks, and contraindications include stable patients with functional gastrointestinal tracts, those with mild malnutrition, or individuals with a history of Tpn-related complications.
| Indications | Contraindications |
|---|---|
| Severe gastrointestinal disorders | Stable patients with functional gastrointestinal tracts |
| Cancer | Mild malnutrition |
| AIDS | History of Tpn-related complications |

Benefits and Complications of Tpn Health
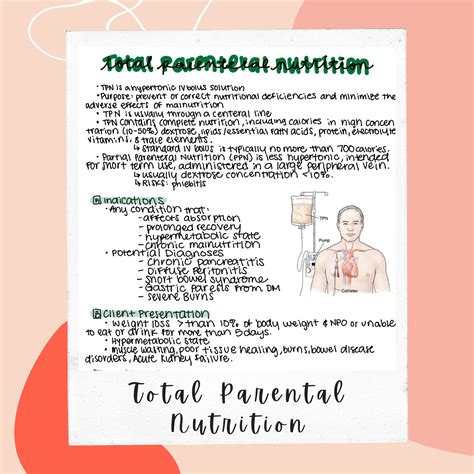
The benefits of Tpn Health are numerous, including improved nutritional status, enhanced wound healing, and reduced morbidity and mortality rates. However, Tpn Health is also associated with potential complications, such as infections, metabolic disturbances, and liver dysfunction. According to a study published in the Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, the incidence of Tpn-related complications can be reduced by implementing evidence-based practices, such as strict asepsis, regular monitoring of laboratory parameters, and timely adjustment of nutrient formulations.
Metabolic Complications
Metabolic complications, such as hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and electrolyte imbalances, are common in patients receiving Tpn Health. These complications can be managed through close monitoring of laboratory parameters, adjustment of nutrient formulations, and implementation of insulin therapy or other pharmacological interventions as needed. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that the use of insulin therapy in patients receiving Tpn Health can reduce the risk of hyperglycemia and related complications.
What are the primary benefits of Tpn Health?
+The primary benefits of Tpn Health include improved nutritional status, enhanced wound healing, and reduced morbidity and mortality rates.
What are the potential complications of Tpn Health?
+The potential complications of Tpn Health include infections, metabolic disturbances, and liver dysfunction.
How can metabolic complications be managed in patients receiving Tpn Health?
+Metabolic complications can be managed through close monitoring of laboratory parameters, adjustment of nutrient formulations, and implementation of insulin therapy or other pharmacological interventions as needed.
In conclusion, Tpn Health is a vital treatment modality for individuals with severe gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, or other critical health conditions. While Tpn Health is associated with potential complications, these can be minimized through evidence-based practices, close monitoring, and timely adjustment of nutrient formulations. As a healthcare expert, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest research and guidelines to provide optimal care for patients receiving Tpn Health.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the benefits and complications of Tpn Health, a method of providing essential nutrients through intravenous infusion, and learn how to manage potential complications.” (149 characters)