Teen dating violence is a pervasive issue affecting millions of adolescents worldwide. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 11 female and 1 in 14 male high school students in the United States experience physical dating violence each year. This translates to around 12% of female and 7% of male high school students, highlighting the significance of addressing this critical issue. The statistics are alarming, with 21% of female and 10% of male high school students reporting experiencing physical or sexual dating violence.
The consequences of teen dating violence are far-reaching and can have a lasting impact on the victim's physical, emotional, and mental well-being. Victims of dating violence are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and substance abuse, as well as engage in risky behaviors such as unprotected sex and self-harm. Furthermore, teen dating violence can lead to long-term consequences, including increased risk of intimate partner violence in adulthood, chronic health problems, and even mortality. It is essential to acknowledge the complexity of this issue and address it through a comprehensive approach that involves education, awareness, and community engagement.
Key Points
- About 1 in 11 female and 1 in 14 male high school students experience physical dating violence each year.
- 21% of female and 10% of male high school students report experiencing physical or sexual dating violence.
- Teen dating violence can lead to depression, anxiety, substance abuse, and risky behaviors.
- Victims of teen dating violence are at increased risk of intimate partner violence in adulthood and chronic health problems.
- Education, awareness, and community engagement are crucial in addressing and preventing teen dating violence.
Prevalence and Characteristics of Teen Dating Violence
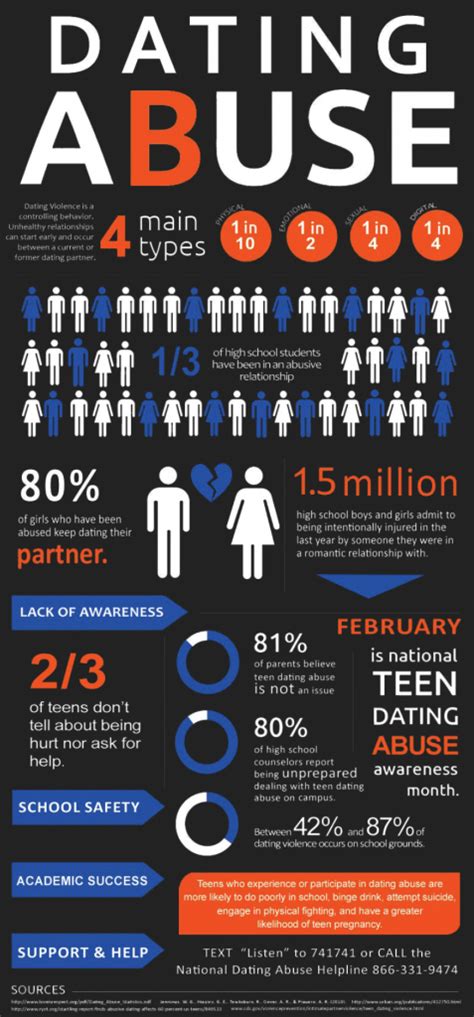
Research has shown that teen dating violence can take many forms, including physical, emotional, and sexual abuse. Physical abuse is the most commonly reported form, with 12% of female and 7% of male high school students experiencing physical dating violence. Emotional abuse, which includes behaviors such as isolation, humiliation, and threats, is also prevalent, with 23% of female and 14% of male high school students reporting emotional dating violence. Sexual abuse, including forced sex and sexual coercion, affects around 10% of female and 3% of male high school students.
Risk Factors and Correlates of Teen Dating Violence
Certain risk factors and correlates have been identified as increasing the likelihood of experiencing teen dating violence. These include having a history of child abuse, experiencing family violence, and engaging in substance use. Additionally, adolescents who exhibit aggressive behaviors, such as bullying or fighting, are more likely to be involved in violent dating relationships. The presence of mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, can also increase the risk of experiencing dating violence. Understanding these risk factors is essential in developing targeted prevention and intervention strategies.
| Type of Abuse | Prevalence Among Female High School Students | Prevalence Among Male High School Students |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Abuse | 12% | 7% |
| Emotional Abuse | 23% | 14% |
| Sexual Abuse | 10% | 3% |

Consequences and Long-Term Effects of Teen Dating Violence
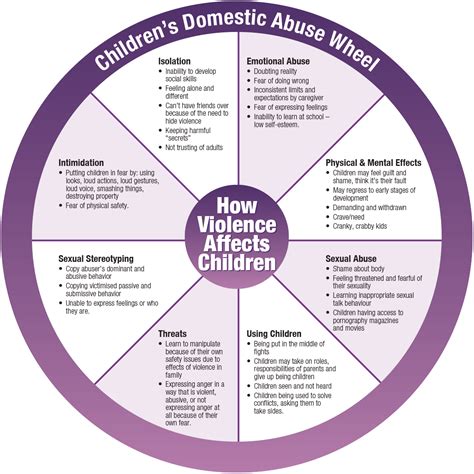
The consequences of teen dating violence can be severe and long-lasting, affecting not only the individual but also their families and communities. Victims of dating violence are more likely to experience academic difficulties, social isolation, and mental health problems. Furthermore, the experience of dating violence can increase the risk of revictimization, with some studies suggesting that up to 50% of women who experience dating violence in adolescence will experience intimate partner violence in adulthood. It is essential to provide support and resources to victims of teen dating violence, including counseling, advocacy, and education on healthy relationships.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Preventing teen dating violence requires a multi-faceted approach that involves education, awareness, and community engagement. Schools can play a critical role in prevention by implementing evidence-based programs that teach healthy relationship skills, such as communication, empathy, and conflict resolution. Additionally, parents, caregivers, and community leaders can help by modeling healthy relationships, providing supportive environments, and engaging in open conversations about dating violence. By working together, we can promote a culture of respect, empathy, and nonviolence, ultimately reducing the prevalence of teen dating violence.
What is the most common form of teen dating violence?
+Physical abuse is the most commonly reported form of teen dating violence, affecting around 12% of female and 7% of male high school students.
What are some risk factors for experiencing teen dating violence?
+Risk factors for experiencing teen dating violence include having a history of child abuse, experiencing family violence, and engaging in substance use. Additionally, adolescents who exhibit aggressive behaviors or have mental health issues are more likely to be involved in violent dating relationships.
How can we prevent teen dating violence?
+Preventing teen dating violence requires a multi-faceted approach that involves education, awareness, and community engagement. This can include implementing evidence-based programs in schools, modeling healthy relationships, and engaging in open conversations about dating violence.