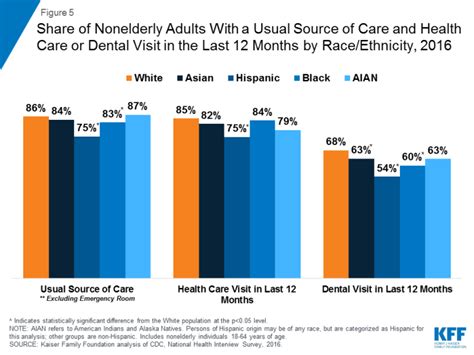
The city of San Bernardino, located in San Bernardino County, California, faces significant health disparities that affect the quality of life and life expectancy of its residents. As the largest city in the county, San Bernardino's health disparities are a major concern for public health officials, policymakers, and community leaders. The city's diverse population, with a mix of racial and ethnic groups, socioeconomic statuses, and access to healthcare, contributes to the complexity of these disparities.
According to the California Department of Public Health, San Bernardino County has some of the worst health outcomes in the state. The county ranks 45th out of 58 counties in terms of overall health outcomes, with high rates of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The city of San Bernardino specifically faces challenges related to access to healthcare, with many residents lacking health insurance or facing barriers to accessing healthcare services. This can lead to delayed diagnoses, inadequate treatment, and poor health outcomes.
Demographic Factors Contributing to Health Disparities
Demographic factors, such as race and ethnicity, play a significant role in health disparities in San Bernardino. The city's population is predominantly Latino (63.3%), followed by African American (15.6%), and White (14.9%). These populations often face systemic barriers to healthcare, including language barriers, cultural incompetence, and discrimination. Additionally, socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and education level, also contribute to health disparities. San Bernardino has a poverty rate of 28.1%, which is higher than the state average, and only 12.1% of residents have a bachelor's degree or higher.
Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment, also play a crucial role in health disparities. San Bernardino faces challenges related to affordable housing, with many residents experiencing housing insecurity or living in overcrowded conditions. This can lead to increased stress, poor living conditions, and limited access to healthy food and physical activity opportunities. Furthermore, education and employment opportunities are also limited in San Bernardino, with only 64.1% of residents having a high school diploma or equivalent, and unemployment rates higher than the state average.
| Health Indicator | San Bernardino County | California State Average |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity Rate | 34.1% | 25.2% |
| Diabetes Rate | 12.1% | 9.5% |
| Heart Disease Rate | 4.3% | 3.4% |
Key Points
- San Bernardino faces significant health disparities, with high rates of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Demographic factors, such as race and ethnicity, contribute to health disparities, with Latino and African American populations facing systemic barriers to healthcare.
- Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and education level, also play a crucial role in health disparities.
- Social determinants of health, including housing, education, and employment, are essential to addressing health disparities.
- Addressing health disparities in San Bernardino requires a comprehensive approach that involves community-based initiatives, policy changes, and systemic reforms.
Addressing Health Disparities in San Bernardino

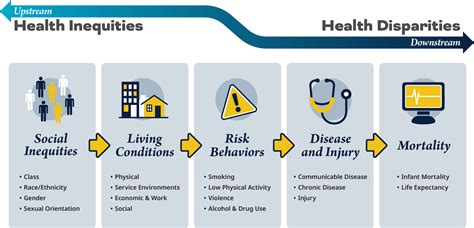
Addressing health disparities in San Bernardino requires a multifaceted approach that involves community-based initiatives, policy changes, and systemic reforms. Community-based initiatives, such as health education programs, community gardens, and physical activity initiatives, can help to promote healthy behaviors and improve access to healthcare. Policy changes, such as increasing funding for healthcare programs, implementing policies to reduce tobacco use, and promoting affordable housing, can also help to address health disparities. Additionally, systemic reforms, such as increasing diversity in the healthcare workforce, improving cultural competence, and addressing systemic racism, are essential to addressing the root causes of health disparities.
Collaborative Efforts
Collaborative efforts between community organizations, healthcare providers, and policymakers are essential to addressing health disparities in San Bernardino. Partnerships between community organizations and healthcare providers can help to increase access to healthcare, promote health education, and provide culturally competent care. Policy advocacy efforts can also help to promote policy changes that address health disparities, such as increasing funding for healthcare programs and implementing policies to reduce tobacco use.
In conclusion, health disparities in San Bernardino are a complex issue that requires a comprehensive approach to address. By recognizing the systemic and structural factors that contribute to health disparities, and by working together to implement community-based initiatives, policy changes, and systemic reforms, we can help to promote health equity and improve the health outcomes of San Bernardino residents.
What are the primary causes of health disparities in San Bernardino?
+The primary causes of health disparities in San Bernardino are complex and multifaceted, involving demographic factors, such as race and ethnicity, socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and education level, and social determinants of health, including housing, education, and employment.
How can community-based initiatives help to address health disparities in San Bernardino?
+Community-based initiatives, such as health education programs, community gardens, and physical activity initiatives, can help to promote healthy behaviors, improve access to healthcare, and address social determinants of health.
What role do policymakers play in addressing health disparities in San Bernardino?
+Policymakers play a crucial role in addressing health disparities in San Bernardino by implementing policies that promote health equity, increase funding for healthcare programs, and address systemic barriers to healthcare.