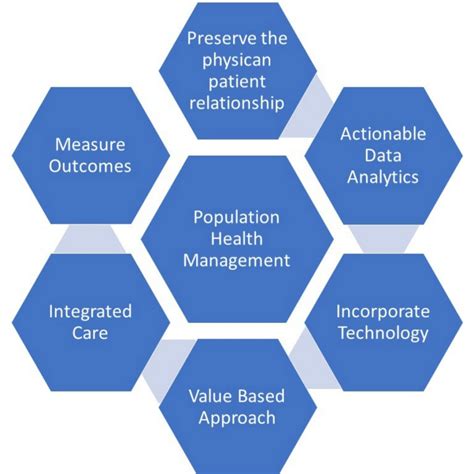
The importance of preventive care in maintaining public health cannot be overstated. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the role of preventive care outreach in addressing population health gaps has become increasingly crucial. Preventive care encompasses a broad range of services and interventions designed to prevent or detect diseases early, reducing the risk of complications and improving health outcomes. However, despite its proven benefits, disparities in access to preventive care persist, contributing to significant gaps in population health.
These disparities are often rooted in socioeconomic factors, geographic location, and access to healthcare services. Populations in rural or underserved areas may face barriers such as lack of healthcare providers, limited access to specialized care, and higher rates of uninsured or underinsured individuals. Moreover, cultural and linguistic barriers can further exacerbate these disparities, making it challenging for certain populations to navigate the healthcare system and access necessary preventive care services.
Key Points
- Preventive care is essential for maintaining public health and reducing healthcare costs in the long term.
- Disparities in access to preventive care contribute to population health gaps, particularly among underserved and rural populations.
- Cultural and linguistic barriers can hinder access to preventive care, emphasizing the need for tailored outreach strategies.
- Technology, such as telehealth, can play a critical role in expanding access to preventive care services.
- Collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers is vital for addressing population health gaps through preventive care outreach.
Understanding Population Health Gaps
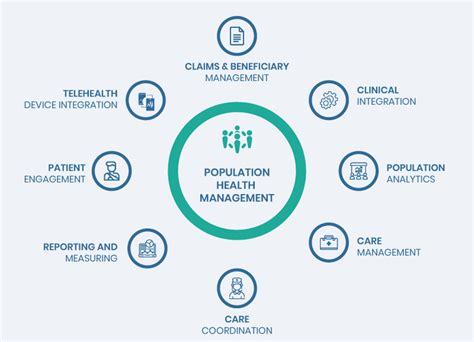
Population health gaps refer to the disparities in health outcomes and access to healthcare services among different population groups. These gaps can be attributed to various factors, including but not limited to, socioeconomic status, education level, employment status, and geographic location. The existence of these gaps underscores the need for targeted interventions, such as preventive care outreach programs, designed to address the unique needs of vulnerable populations.
Preventive care outreach programs are particularly effective in bridging these gaps by providing education, screenings, and interventions that promote healthy behaviors and early detection of diseases. For instance, programs focused on preventive care can offer vaccinations, cancer screenings, and health education, all of which are critical in preventing the onset of diseases or detecting them at an early stage when they are more treatable.
Role of Technology in Preventive Care Outreach
Technology has revolutionized the healthcare industry, and its impact on preventive care outreach is noteworthy. Telehealth, for example, has emerged as a powerful tool in expanding access to healthcare services, including preventive care. By leveraging telehealth, healthcare providers can reach a wider audience, including those in rural or underserved areas, reducing barriers to care and enhancing the delivery of preventive services.
Moreover, digital platforms and mobile applications can be utilized to disseminate health information, promote healthy lifestyles, and remind individuals about the importance of preventive care screenings and vaccinations. These technologies not only increase access to care but also empower individuals to take a more active role in their health management, fostering a culture of prevention rather than treatment.
| Preventive Care Service | Target Population | Delivery Method |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccinations | Children and Adults | Community Clinics, Telehealth |
| Cancer Screenings | Adults 40+ | Primary Care Settings, Mobile Health Units |
| Health Education | All Ages | Digital Platforms, Community Workshops |

Addressing Barriers to Preventive Care
Despite the advancements in healthcare technology and the acknowledged importance of preventive care, barriers to accessing these services persist. Financial constraints, lack of awareness about the benefits of preventive care, and systemic issues within the healthcare system itself can deter individuals from seeking preventive care services.
To address these barriers, a multifaceted approach is necessary. This includes policy interventions aimed at reducing healthcare costs and improving insurance coverage, public health campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of preventive care, and innovations in healthcare delivery that make preventive services more accessible and affordable.
Collaboration and Community Engagement
The success of preventive care outreach programs heavily depends on collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers. Community-based initiatives that engage local populations in health promotion activities can be particularly effective. These initiatives not only help in disseminating health information but also in building trust and fostering a sense of community ownership over health outcomes.
Furthermore, policymakers play a critical role in creating an environment that supports preventive care. This can be achieved through legislation that prioritizes preventive services, allocates resources for community health programs, and ensures that healthcare systems are equipped to deliver high-quality preventive care.
What is the primary goal of preventive care outreach programs?
+The primary goal of preventive care outreach programs is to prevent diseases and detect them early, thereby reducing the risk of complications and improving health outcomes.
How can technology enhance preventive care outreach?
+Technology, such as telehealth and digital platforms, can increase access to preventive care services, especially for underserved populations, and provide personalized health interventions.
Why is community engagement crucial for the success of preventive care outreach programs?
+Community engagement helps in building trust, disseminating health information, and fostering a sense of community ownership over health outcomes, which are essential for the effectiveness and sustainability of preventive care outreach programs.
In conclusion, preventive care outreach is a vital component of addressing population health gaps. By understanding the barriers to preventive care, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers, we can work towards a healthcare system that prioritizes prevention and promotes equitable access to health services for all. As we move forward, it’s essential to continue evaluating and refining our approaches to preventive care outreach, ensuring that they are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our populations and grounded in the latest evidence and best practices.