When an individual visits a primary care (PC) physician with concerns about their mental health, the diagnosis process can be complex and nuanced. The primary care setting is often the first point of contact for individuals seeking mental health care, and it is essential for PC physicians to be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to accurately diagnose and manage mental health conditions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 30% of primary care patients have a mental health disorder, with depression and anxiety being the most common conditions.
A study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine found that primary care physicians correctly diagnose mental health conditions about 50% of the time. This highlights the need for improved training and education in mental health diagnosis and management for primary care physicians. The diagnosis process typically begins with a comprehensive clinical interview, during which the physician will ask the patient about their symptoms, medical history, and social and environmental factors that may be contributing to their mental health concerns.
Key Points
- Primary care physicians are often the first point of contact for individuals seeking mental health care.
- The diagnosis process for mental health conditions in primary care settings can be complex and nuanced.
- A comprehensive clinical interview is a crucial component of the diagnosis process.
- Primary care physicians should be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to accurately diagnose and manage mental health conditions.
- Improved training and education in mental health diagnosis and management are necessary for primary care physicians.
Diagnosis Process
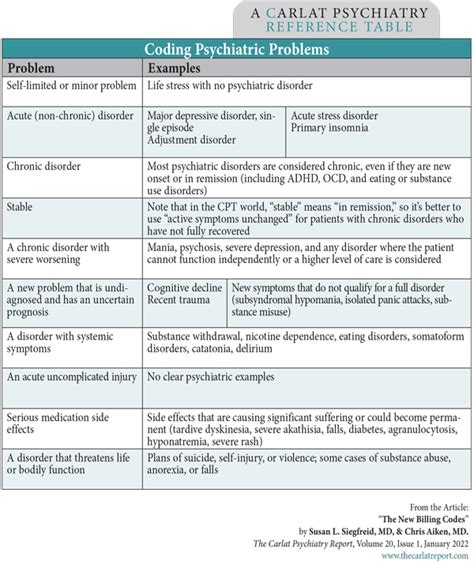
The diagnosis process for mental health conditions in primary care settings typically involves a combination of clinical interviews, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. The primary care physician will use the information gathered during the clinical interview to identify potential mental health conditions and develop a differential diagnosis. The physician may also use standardized assessment tools, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7) for anxiety, to help inform the diagnosis.
Standardized Assessment Tools
Standardized assessment tools can be useful in primary care settings to help diagnose and monitor mental health conditions. These tools can provide a quick and efficient way to assess symptoms and identify potential mental health conditions. For example, the PHQ-9 is a 9-item questionnaire that assesses symptoms of depression, such as feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. The GAD-7 is a 7-item questionnaire that assesses symptoms of anxiety, such as feelings of worry, nervousness, or fear.
| Mental Health Condition | Standardized Assessment Tool |
|---|---|
| Depression | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) |
| Anxiety | Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7) |
| Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | PTSD Checklist (PCL-5) |

Treatment and Management

Once a mental health condition has been diagnosed, the primary care physician will work with the patient to develop a treatment plan. This may involve medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. The primary care physician may also refer the patient to a mental health specialist, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, for further evaluation and treatment. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology, patients who receive collaborative care, which involves a team of healthcare providers working together to provide comprehensive care, have better outcomes than those who receive usual care.
Collaborative Care
Collaborative care is an effective approach to managing mental health conditions in primary care settings. This approach involves a team of healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, mental health specialists, and care managers, working together to provide comprehensive care. Collaborative care has been shown to improve patient outcomes, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that patients who received collaborative care had a 50% reduction in depressive symptoms compared to those who received usual care.
In conclusion, the diagnosis and management of mental health conditions in primary care settings require a comprehensive and nuanced approach. Primary care physicians must be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to accurately diagnose and manage mental health conditions, and standardized assessment tools can be useful in informing diagnoses. Collaborative care is an effective approach to managing mental health conditions, and primary care physicians should work with mental health specialists and other healthcare providers to provide comprehensive care.
What is the most common mental health condition diagnosed in primary care settings?
+Depression is the most common mental health condition diagnosed in primary care settings, affecting approximately 10% of adults in the United States.
What is the purpose of using standardized assessment tools in primary care settings?
+The purpose of using standardized assessment tools is to help diagnose and monitor mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, and to inform treatment plans.
What is collaborative care, and how does it improve patient outcomes?
+Collaborative care is an approach to managing mental health conditions that involves a team of healthcare providers working together to provide comprehensive care. Collaborative care has been shown to improve patient outcomes, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life by providing coordinated and patient-centered care.



