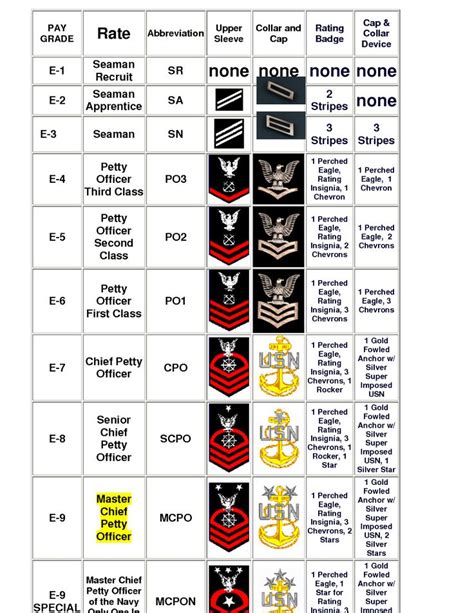
The United States Navy's enlisted rank structure is a hierarchical system that categorizes sailors based on their level of experience, training, and responsibility. The Navy's rank structure is designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize the achievements and contributions of its enlisted personnel. In this article, we will explore the different ranks within the Navy's enlisted rank structure, from the lowest to the highest, and discuss the responsibilities, requirements, and benefits associated with each rank.
Overview of the Navy’s Enlisted Rank Structure

The Navy’s enlisted rank structure is divided into nine pay grades, each with its own set of ranks and responsibilities. The ranks are further divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted. The junior enlisted category includes the lowest four pay grades, while the NCO category includes the middle three pay grades, and the senior enlisted category includes the highest two pay grades.
Key Points
- The Navy's enlisted rank structure consists of nine pay grades
- Junior enlisted category includes pay grades E-1 to E-4
- Non-commissioned officer (NCO) category includes pay grades E-5 to E-7
- Senior enlisted category includes pay grades E-8 and E-9
- Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits
Junior Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-4)
The junior enlisted ranks are the entry-level positions within the Navy. These ranks are typically held by new recruits and sailors who are still in the early stages of their careers. The junior enlisted ranks include:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The lowest rank in the Navy, typically held by new recruits during their initial training period.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): The second-lowest rank, typically held by sailors who have completed their initial training and are assigned to a ship or unit.
- Seaman (E-3): A junior enlisted rank that requires a minimum of 12 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): The first rank in the petty officer category, which requires a minimum of 24 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
| Rank | Pay Grade | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit | E-1 | Initial training, basic duties |
| Seaman Apprentice | E-2 | Assigned to ship or unit, basic duties |
| Seaman | E-3 | Completed "A" school, junior leadership roles |
| Petty Officer Third Class | E-4 | Leadership roles, specialized skills |
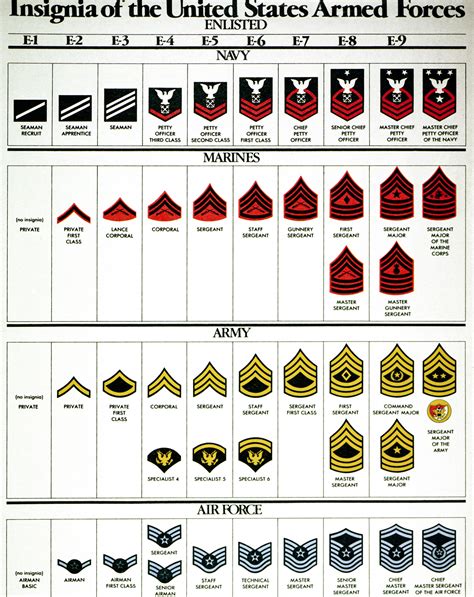
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks (E-5 to E-7)
The NCO ranks are the backbone of the Navy’s enlisted rank structure. These ranks are typically held by experienced sailors who have demonstrated leadership potential and have completed advanced training. The NCO ranks include:
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): A mid-level NCO rank that requires a minimum of 36 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): A senior NCO rank that requires a minimum of 48 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): The highest NCO rank, which requires a minimum of 60 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
Senior Enlisted Ranks (E-8 and E-9)
The senior enlisted ranks are the highest ranks within the Navy’s enlisted rank structure. These ranks are typically held by experienced sailors who have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills and have completed advanced training. The senior enlisted ranks include:
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): The second-highest rank in the Navy, which requires a minimum of 72 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): The highest rank in the Navy, which requires a minimum of 84 months of service and completion of a Navy “A” school.
In conclusion, the Navy's enlisted rank structure is a complex system that recognizes the achievements and contributions of its enlisted personnel. From the junior enlisted ranks to the senior enlisted ranks, each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits. By understanding the different ranks within the Navy's enlisted rank structure, sailors can better navigate their careers and achieve their goals.
What is the lowest rank in the Navy’s enlisted rank structure?
+The lowest rank in the Navy’s enlisted rank structure is Seaman Recruit (E-1).
What is the highest rank in the Navy’s enlisted rank structure?
+The highest rank in the Navy’s enlisted rank structure is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
How do sailors advance in rank within the Navy’s enlisted rank structure?
+Sailors can advance in rank by completing advanced training, demonstrating leadership potential, and meeting the requirements for each rank.