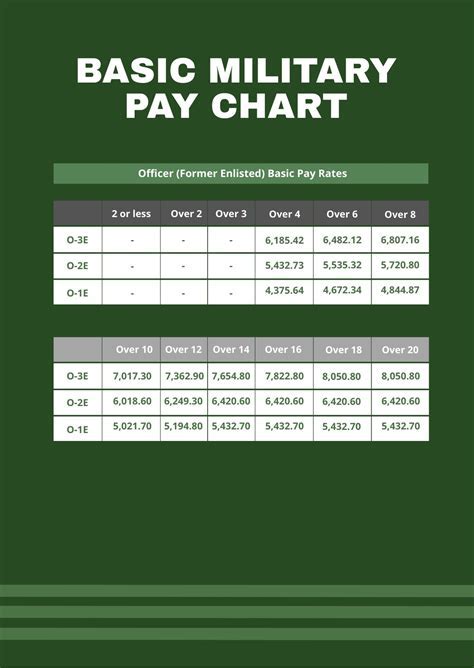
The United States military is comprised of several branches, each with its unique mission, responsibilities, and requirements. Two of the most notable branches are the National Guard and the Air Force. While both branches play critical roles in defending the nation, they have distinct differences in terms of their mission, organization, and membership requirements. In this article, we will delve into the differences between the National Guard and the Air Force, exploring their history, mission, and the benefits and challenges of serving in each branch.
Key Points
- The National Guard is a reserve component of the US military with both federal and state missions.
- The Air Force is a branch of the US military responsible for air and space operations.
- Membership requirements, training, and benefits differ between the National Guard and the Air Force.
- Both branches offer opportunities for education, career advancement, and personal growth.
- The choice between the National Guard and the Air Force depends on individual goals, preferences, and circumstances.
History and Mission of the National Guard

The National Guard is the oldest branch of the US military, with its roots dating back to 1636. It is a reserve component of the military, meaning that its members typically serve part-time, with the option to be called to full-time service in times of war or national emergency. The National Guard has both federal and state missions, with members serving in their home states and responding to local emergencies, such as natural disasters, while also being available for deployment overseas. The National Guard is divided into two main components: the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard.
Army National Guard
The Army National Guard is the land-based component of the National Guard, with members serving in a variety of roles, including infantry, armor, artillery, and engineering. Army National Guard members typically serve one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with the option to attend additional training and deployments. The Army National Guard is often called upon to respond to domestic emergencies, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, and may also be deployed overseas in support of US military operations.
Air National Guard
The Air National Guard is the air-based component of the National Guard, with members serving in roles such as pilots, navigators, and maintenance personnel. Air National Guard members typically serve one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with the option to attend additional training and deployments. The Air National Guard is responsible for providing air support to the US military and may be deployed overseas in support of US military operations.
History and Mission of the Air Force

The Air Force is the youngest branch of the US military, established in 1947. It is responsible for air and space operations, with a mission to “fly, fight, and win in air, space, and cyberspace.” The Air Force is a full-time military branch, with members serving on active duty for a specified period, typically 4-6 years. The Air Force is divided into several main components, including the active duty Air Force, the Air Force Reserve, and the Air National Guard.
Air Force Components
The Air Force has several components, each with its own unique mission and responsibilities. The active duty Air Force is the full-time component of the Air Force, with members serving on bases around the world. The Air Force Reserve is a part-time component, with members serving one weekend per month and two weeks per year. The Air National Guard is a reserve component of the Air Force, with members serving in their home states and responding to local emergencies, while also being available for deployment overseas.
| Branch | Membership Requirements | Training | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Guard | Age 17-35, US citizen, high school diploma | Basic training, advanced individual training | Education benefits, healthcare, retirement benefits |
| Air Force | Age 17-39, US citizen, high school diploma | Basic training, technical training | Education benefits, healthcare, retirement benefits, housing allowance |
Benefits and Challenges of Serving in the National Guard and the Air Force
Serving in the National Guard or the Air Force can be a rewarding and challenging experience. Both branches offer opportunities for education, career advancement, and personal growth, as well as a sense of camaraderie and purpose. However, serving in the military also comes with its own set of challenges, including deployment, time away from family and friends, and the risk of injury or death. Members of the National Guard and the Air Force must be prepared to make sacrifices and face challenges head-on, while also taking advantage of the benefits and opportunities available to them.
Education Benefits
Both the National Guard and the Air Force offer education benefits to their members, including tuition assistance, scholarships, and loan repayment programs. The National Guard’s Education Assistance Program provides up to 4,500 per year in tuition assistance, while the Air Force's Tuition Assistance Program provides up to 4,500 per year in tuition assistance. Additionally, members of both branches may be eligible for the GI Bill, which provides up to $1,920 per month in education benefits.
Healthcare Benefits
Members of the National Guard and the Air Force are eligible for healthcare benefits, including medical, dental, and vision coverage. The National Guard’s TRICARE program provides medical coverage to members and their families, while the Air Force’s TRICARE program provides medical, dental, and vision coverage to members and their families.
Retirement Benefits
Members of the National Guard and the Air Force are eligible for retirement benefits, including a pension and healthcare coverage. The National Guard’s retirement program provides a pension to members who serve for 20 years or more, while the Air Force’s retirement program provides a pension to members who serve for 20 years or more.
What is the main difference between the National Guard and the Air Force?
+The main difference between the National Guard and the Air Force is their mission and organization. The National Guard is a reserve component of the US military with both federal and state missions, while the Air Force is a full-time military branch responsible for air and space operations.
What are the membership requirements for the National Guard and the Air Force?
+The membership requirements for the National Guard and the Air Force vary, but generally include being a US citizen, having a high school diploma, and meeting age and physical fitness requirements. The National Guard requires members to be between the ages of 17 and 35, while the Air Force requires members to be between the ages of 17 and 39.
What are the benefits of serving in the National Guard and the Air Force?
+The benefits of serving in the National Guard and the Air Force include education benefits, healthcare benefits, retirement benefits, and a sense of camaraderie and purpose. Members of both branches may also be eligible for housing allowances, food allowances, and other benefits.
In conclusion, the National Guard and the Air Force are two distinct branches of the US military, each with its own unique mission, organization, and benefits. While both branches offer opportunities for education, career advancement, and personal growth, they also come with their own set of challenges and requirements. Ultimately, the choice between the National Guard and the Air Force depends on individual goals, preferences, and circumstances. By understanding the differences between these two branches, individuals can make informed decisions about their military service and take advantage of the benefits and opportunities available to them.