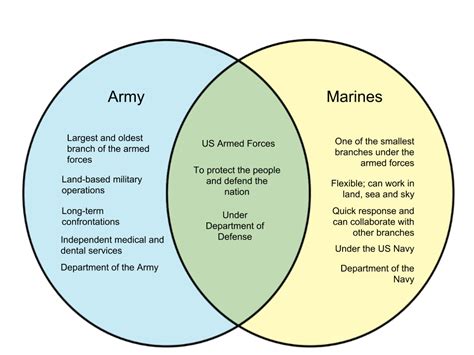
The United States Armed Forces are comprised of several branches, each with its unique mission, responsibilities, and culture. Two of the most prominent branches are the Marine Corps and the Army. While both are integral to the country’s defense, they have distinct differences in their roles, training, and operations. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the complexity and strength of the U.S. military.
The Marine Corps, also known as the Marines, is a branch of the military that specializes in expeditionary and amphibious operations. They are known for their elite fighting force and their ability to deploy rapidly and conduct a wide range of missions, from humanitarian assistance to combat operations. The Marines are often the first to enter a conflict zone, and their primary role is to seize and secure key terrain, such as beaches, ports, and airfields. This allows other branches of the military to follow and establish a more permanent presence.
On the other hand, the Army is the largest branch of the U.S. military and is responsible for land-based military operations. The Army’s primary role is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land. They are trained to conduct a wide range of missions, from counterinsurgency and counterterrorism to disaster relief and humanitarian assistance. The Army is also responsible for occupying and securing territory, as well as conducting peacekeeping and stability operations.
One of the main differences between the Marines and the Army is their training and culture. The Marines are known for their rigorous boot camp, which is considered one of the toughest in the world. Marine recruits undergo 13 weeks of intense training, which includes physical conditioning, combat skills, and leadership development. The Marines also have a strong emphasis on teamwork, discipline, and esprit de corps, which is reflected in their motto, “The Few, The Proud.”
In contrast, the Army’s basic training is also challenging, but it is more focused on teaching recruits the skills they need to perform their specific job, known as a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS). The Army’s training is also more specialized, with recruits learning specific skills such as infantry, artillery, or engineering. The Army’s culture is also more diverse, with a wider range of units and specialties, each with its own unique traditions and customs.
Another significant difference between the Marines and the Army is their equipment and weaponry. The Marines are known for their lightweight and mobile equipment, which allows them to deploy quickly and conduct operations in a variety of environments. The Marines also have a strong emphasis on amphibious operations, with a fleet of ships and landing craft that enable them to launch attacks from the sea. In contrast, the Army has a wider range of equipment, including tanks, artillery, and aircraft, which allows them to conduct a wider range of missions, from heavy armor battles to air assault operations.
Key Points
- The Marine Corps specializes in expeditionary and amphibious operations, while the Army is responsible for land-based military operations.
- The Marines have a more rigorous boot camp and a stronger emphasis on teamwork and discipline.
- The Army's training is more specialized, with recruits learning specific skills such as infantry, artillery, or engineering.
- The Marines have lightweight and mobile equipment, while the Army has a wider range of equipment, including tanks, artillery, and aircraft.
- The Marines are known for their elite fighting force and their ability to deploy rapidly, while the Army is responsible for occupying and securing territory.
In terms of operations, the Marines and the Army have different areas of focus. The Marines are often deployed in smaller units, such as battalions or regiments, and are tasked with conducting specific missions, such as securing a beachhead or conducting a raid. The Army, on the other hand, is often deployed in larger units, such as brigades or divisions, and is tasked with conducting more complex operations, such as occupying a city or securing a border.
The Marines and the Army also have different command structures and organizational cultures. The Marines are organized into three main components: the operating forces, the supporting establishment, and the reserve. The operating forces are responsible for conducting military operations, while the supporting establishment provides administrative and logistical support. The reserve is a part-time force that can be called upon to augment the active-duty force in times of war or crisis.
In contrast, the Army is organized into several different components, including the active component, the reserve, and the National Guard. The active component is the full-time force that conducts military operations, while the reserve and National Guard are part-time forces that can be called upon to augment the active component in times of war or crisis.
Marine Corps vs Army: A Comparison of Roles and Responsibilities
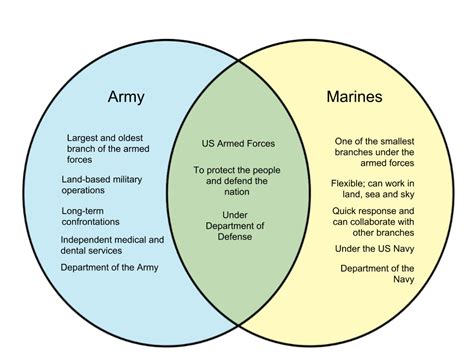
The Marine Corps and the Army have distinct roles and responsibilities, reflecting their different missions and areas of focus. The Marines are specialized in expeditionary and amphibious operations, while the Army is responsible for land-based military operations. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the complexity and strength of the U.S. military.
Expeditionary Operations
The Marines are trained to conduct expeditionary operations, which involve deploying rapidly and conducting missions in a variety of environments. This includes amphibious assaults, raids, and other types of operations that require a high degree of mobility and flexibility. The Marines’ expeditionary mindset is reflected in their equipment and training, which emphasizes speed, agility, and adaptability.
Land-Based Operations
The Army, on the other hand, is responsible for land-based military operations, which involve occupying and securing territory, as well as conducting peacekeeping and stability operations. The Army’s training and equipment are focused on supporting these types of operations, with an emphasis on firepower, maneuverability, and logistics.
| Branch | Mission | Training | Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Corps | Expeditionary and amphibious operations | Rigorous boot camp, emphasis on teamwork and discipline | Lightweight and mobile equipment |
| Army | Land-based military operations | Specialized training, emphasis on specific skills | Wider range of equipment, including tanks, artillery, and aircraft |

In conclusion, the Marine Corps and the Army are two distinct branches of the U.S. military, each with its unique mission, responsibilities, and culture. While both are integral to the country’s defense, they have different areas of focus and expertise. The Marines are specialized in expeditionary and amphibious operations, while the Army is responsible for land-based military operations. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the complexity and strength of the U.S. military.
What is the main difference between the Marine Corps and the Army?
+The main difference between the Marine Corps and the Army is their mission and area of focus. The Marine Corps is specialized in expeditionary and amphibious operations, while the Army is responsible for land-based military operations.
What type of training do Marine Corps recruits undergo?
+Marine Corps recruits undergo 13 weeks of intense training, which includes physical conditioning, combat skills, and leadership development. The training is designed to prepare recruits for the rigors of military life and to instill the values and traditions of the Marine Corps.
What is the Army’s role in U.S. military operations?
+The Army’s role in U.S. military operations is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land. The Army is responsible for occupying and securing territory, as well as conducting peacekeeping and stability operations.