Involuntary acts, by their very nature, are actions that occur without the conscious intention or will of an individual. These acts can be categorized into various types, each with distinct characteristics and implications under the law. Understanding the nuances of involuntary acts is crucial for legal professionals, as it directly impacts how such actions are treated within the judicial system. This article delves into the concept of involuntary acts, exploring their definition, types, and the legal ramifications associated with them.
Definition and Scope of Involuntary Acts

Involuntary acts are defined as actions that an individual performs without their conscious will or intention. This lack of intent distinguishes involuntary acts from voluntary ones, where the person consciously decides to perform the action. The scope of involuntary acts encompasses a wide range of behaviors, from reflex actions to actions performed under duress or coercion, and even certain types of unconscious behavior. The legal system recognizes the difference between voluntary and involuntary acts, as the intention behind an action can significantly affect the legal consequences that follow.
Types of Involuntary Acts
There are several types of involuntary acts, each with its own set of circumstances and legal implications. These include:
- Reflex Actions: These are immediate, involuntary responses to certain stimuli. For example, withdrawing a hand when it touches something hot is a reflex action that occurs without conscious thought.
- Actions Under Duress: When an individual is forced to perform an action against their will due to a threat of harm to themselves or others, the act is considered to have been done under duress. The presence of duress can mitigate legal responsibility for the act.
- Unconscious Behavior: This refers to actions performed while the individual is unconscious or in a state of reduced consciousness, such as during sleepwalking. The legal treatment of such acts can vary, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances.
- Actions Due to Mental Incapacity: In cases where an individual lacks the mental capacity to understand the nature and consequences of their actions, those actions may be considered involuntary. Mental incapacity can stem from various conditions, including developmental disabilities, mental illnesses, or the influence of substances.
- Automatism: This is a state of unconsciousness or impaired consciousness, during which an individual may perform complex actions without being aware of what they are doing. Automatism can be caused by a variety of factors, including medical conditions, sleep deprivation, or the effects of drugs.
| Type of Involuntary Act | Legal Implication |
|---|---|
| Reflex Actions | Generally, not considered legally culpable as they are beyond the individual's control. |
| Actions Under Duress | May reduce or eliminate legal liability, depending on the circumstances and the jurisdiction's laws regarding duress. |
| Unconscious Behavior | Legal treatment varies; in some cases, the individual may not be held liable due to lack of intent or control. |
| Actions Due to Mental Incapacity | Often results in reduced or no legal liability, as the individual cannot form the requisite intent for a criminal act. |
| Automatism | Similar to unconscious behavior, the legal outcome depends on whether the automatism was deemed to be the result of a disease of the mind or an insane automatism, or a non-insane automatism. |
Key Points
- Involuntary acts are performed without conscious intention or will, distinguishing them from voluntary actions.
- The legal system recognizes various types of involuntary acts, including reflex actions, actions under duress, unconscious behavior, actions due to mental incapacity, and automatism.
- The legal implications of involuntary acts can vary significantly, with factors such as intent, control, and mental capacity playing critical roles in determining liability.
- Understanding involuntary acts requires a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating insights from law, psychology, and medicine to accurately assess the circumstances surrounding an action.
- The treatment of involuntary acts under the law aims to balance justice with compassion, acknowledging that not all actions are within an individual's control.
Legal Ramifications and Considerations
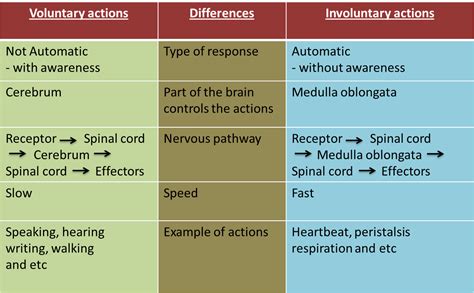
The legal ramifications of involuntary acts are complex and multifaceted. In many jurisdictions, the presence of involuntary action can significantly mitigate or even eliminate criminal liability, as the act is not considered to be a product of the individual’s free will. However, the determination of whether an act was involuntary can be challenging and often requires detailed psychological and medical assessments. The legal system must balance the need to hold individuals accountable for their actions with the recognition that true involuntary acts are beyond the individual’s control.
Evidence and Evaluation
Evaluating the involuntariness of an act involves a thorough examination of the circumstances surrounding the action, including any evidence of duress, mental incapacity, or automatism. Expert testimony from psychologists, psychiatrists, and other relevant professionals is often crucial in helping the court understand the nature of the act and the individual’s state of mind at the time. The legal process must carefully consider all relevant factors to make an informed decision about the individual’s liability.
What distinguishes involuntary acts from voluntary ones in legal terms?
+The primary distinction lies in the presence or absence of intent. Involuntary acts are those performed without the individual's conscious will or intention, whereas voluntary acts are consciously chosen and intended.
How do reflex actions impact legal liability?
+Reflex actions, being involuntary and immediate responses to stimuli, generally do not incur legal liability as they are considered beyond the individual's control.
Can actions performed under duress be considered involuntary?
+Yes, actions performed under duress can be considered involuntary, as the individual is forced to act against their will due to a threat of harm. The presence of duress can mitigate or eliminate legal liability.
In conclusion, involuntary acts present a complex and nuanced challenge within the legal system. The distinction between voluntary and involuntary actions is fundamental, and understanding the various types of involuntary acts and their legal implications is essential for ensuring justice and fairness. As legal principles and societal attitudes evolve, the treatment of involuntary acts under the law will continue to be refined, reflecting a deeper understanding of human behavior, psychology, and the intricacies of intent and control.



