The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a complex natural climate phenomenon that affects global climate patterns, leading to significant impacts on human health. El Niño, in particular, has been associated with various health-related consequences, ranging from increased risk of infectious diseases to mental health concerns. Understanding the relationship between El Niño and health is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its adverse effects.
Introduction to El Niño and Health Impacts
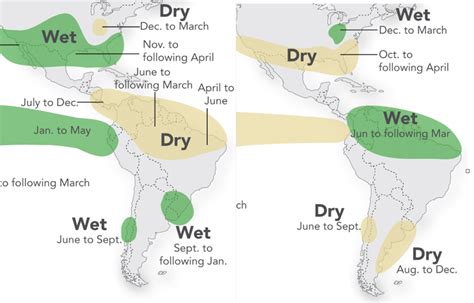
El Niño events are characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, near the equator. This warming of ocean water can have far-reaching consequences, including changes in precipitation patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and altered ecosystems. These environmental changes, in turn, can affect human health in various ways. For instance, warmer temperatures and changed precipitation patterns can facilitate the spread of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, leading to outbreaks of diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease.
Key Points
- El Niño events are associated with increased risk of infectious diseases due to changed environmental conditions.
- Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to mental health concerns, including stress and anxiety.
- El Niño-related disasters, such as floods and landslides, can result in injuries, fatalities, and displacement of populations.
- Food insecurity and malnutrition are potential consequences of El Niño-induced droughts and crop failures.
- Understanding the health impacts of El Niño is essential for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
El Niño and Infectious Diseases
The relationship between El Niño and infectious diseases is complex and influenced by various factors, including the intensity and duration of the El Niño event, as well as the effectiveness of local public health infrastructure. Increased rainfall and flooding can lead to the proliferation of disease vectors, while droughts can concentrate animal and human populations, increasing the risk of disease transmission. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), El Niño events have been linked to outbreaks of diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and Rift Valley fever.
| Disease | El Niño-Related Factors |
|---|---|
| Malaria | Warmer temperatures, increased rainfall, and flooding |
| Dengue fever | Warmer temperatures, increased rainfall, and urbanization |
| Cholera | Flooding, contamination of water sources, and poor sanitation |
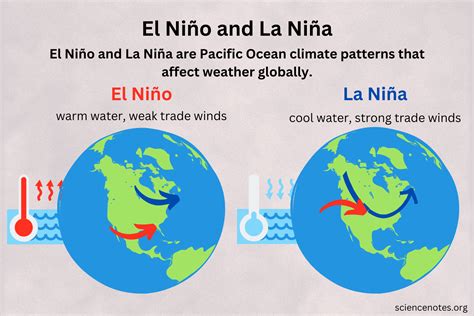
Mental Health and El Niño

The psychological toll of El Niño-related events should not be underestimated. Disasters such as floods, landslides, and droughts can lead to stress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in affected populations. Furthermore, the economic impacts of El Niño, including loss of income and livelihoods, can exacerbate mental health concerns. It is essential to integrate mental health support into disaster response and recovery efforts to mitigate the long-term effects of El Niño on mental well-being.
Food Security and El Niño
El Niño events can have significant impacts on food security, particularly in regions that are heavily reliant on agriculture. Droughts and crop failures can lead to food shortages, increased food prices, and malnutrition. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, El Niño events have been associated with significant declines in crop yields, particularly for staple crops such as maize, wheat, and rice.
In conclusion, the health impacts of El Niño are multifaceted and far-reaching. Understanding the complex relationships between El Niño, environment, and human health is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its adverse effects. By integrating health considerations into El Niño preparedness and response efforts, we can reduce the risks associated with this complex climate phenomenon and promote resilience in vulnerable populations.
What are the primary health impacts of El Niño events?
+The primary health impacts of El Niño events include increased risk of infectious diseases, mental health concerns, and food insecurity. El Niño-related disasters, such as floods and landslides, can also result in injuries, fatalities, and displacement of populations.
How can the health impacts of El Niño be mitigated?
+The health impacts of El Niño can be mitigated through effective preparedness and response efforts, including early warning systems, disease surveillance, and public health infrastructure strengthening. Integrating health considerations into El Niño preparedness and response efforts is crucial for reducing the risks associated with this complex climate phenomenon.
What is the role of mental health support in El Niño response efforts?
+Mental health support is essential in El Niño response efforts, as the phenomenon can lead to significant psychological toll, including stress, anxiety, and PTSD. Integrating mental health support into disaster response and recovery efforts can help mitigate the long-term effects of El Niño on mental well-being.



