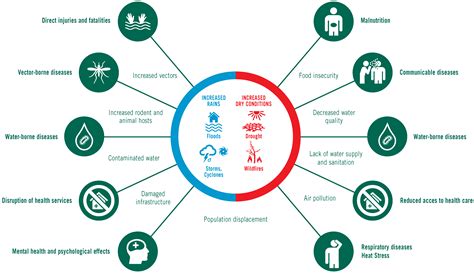
El Niño, a complex weather phenomenon characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific, has far-reaching consequences on global climate patterns. This phenomenon, which occurs every 2-7 years, not only impacts environmental conditions but also has significant effects on human health. The relationship between El Niño and health is multifaceted, involving changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events that can exacerbate existing health issues and create new ones.
Understanding El Niño’s Impact on Health
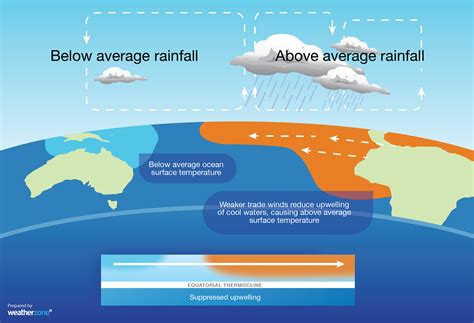
El Niño’s influence on health is primarily indirect, resulting from its effects on ecosystems, agriculture, and water resources. The increased temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to droughts in some areas and floods in others, affecting the distribution and prevalence of disease vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks. Furthermore, changes in weather patterns can influence the quality of air and water, impacting respiratory and gastrointestinal health.
Disease Outbreaks and El Niño
One of the most significant health concerns associated with El Niño is the increased risk of disease outbreaks. The altered environmental conditions can lead to an explosion in mosquito populations, which are vectors for diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. For example, during the 1997-1998 El Niño event, the number of malaria cases in Colombia increased by 50%, highlighting the potential for El Niño to exacerbate malaria transmission. Similarly, the 2015-2016 El Niño event was linked to an increase in Zika virus cases in South America, underscoring the need for enhanced surveillance and control measures during such events.
| Disease | El Niño Impact |
|---|---|
| Malaria | Increased mosquito populations, 50% increase in cases in Colombia during 1997-1998 El Niño |
| Dengue Fever | Altered precipitation patterns leading to increased mosquito breeding sites |
| Zika Virus | Linked to increased cases in South America during 2015-2016 El Niño |

Water and Food Security

El Niño can also have significant impacts on water and food security, which are critical for maintaining public health. Droughts can lead to water scarcity, affecting both human consumption and agricultural production. This can result in malnutrition, as the availability of nutritious food decreases. On the other hand, floods can contaminate water sources, leading to outbreaks of waterborne diseases such as cholera and typhoid fever. For instance, the 2015-2016 El Niño event led to severe droughts in Ethiopia, resulting in food insecurity and malnutrition among vulnerable populations.
Mental Health Implications
Beyond the physical health impacts, El Niño can also have profound effects on mental health. The stress and trauma associated with extreme weather events, such as losing homes or livelihoods, can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The indirect effects of El Niño, such as food and water insecurity, can further exacerbate these mental health challenges. It is essential to consider these psychological impacts in disaster response and recovery efforts, ensuring that mental health support is integrated into relief initiatives.
Key Points
- El Niño's health impacts are primarily indirect, resulting from changes in ecosystems, agriculture, and water resources.
- The phenomenon can lead to increased disease outbreaks, particularly those transmitted by vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks.
- Water and food security are significantly affected, leading to malnutrition and waterborne diseases.
- Mental health implications, including anxiety, depression, and PTSD, are critical considerations in response and recovery efforts.
- Understanding the complex relationship between El Niño and health is essential for developing effective public health strategies and interventions.
Preparing for and Responding to El Niño-Related Health Challenges
Given the significant health impacts associated with El Niño, it is crucial for public health professionals, policymakers, and communities to be prepared. This includes enhancing surveillance for disease outbreaks, improving water and food security, and developing strategies to mitigate the mental health implications of extreme weather events. Early warning systems, public education campaigns, and community-based initiatives can play vital roles in reducing the health burdens of El Niño. Furthermore, investing in public health infrastructure, including healthcare facilities and emergency response systems, is essential for an effective response to El Niño-related health challenges.
As the world continues to experience the impacts of climate change, understanding and addressing the health effects of El Niño will become increasingly important. By acknowledging the complexity of these issues and working towards comprehensive and inclusive solutions, we can better protect human health and well-being in the face of environmental challenges.
What are the primary health concerns associated with El Niño?
+The primary health concerns include increased risk of disease outbreaks such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus, as well as issues related to water and food security, and mental health implications.
How can communities prepare for the health impacts of El Niño?
+Communities can prepare by enhancing disease surveillance, improving water and food security, developing strategies to mitigate mental health implications, and investing in public health infrastructure and emergency response systems.
What role can public health professionals play in addressing El Niño-related health challenges?
+Public health professionals can play a critical role in developing and implementing effective public health strategies, conducting research to better understand the health impacts of El Niño, and advocating for policies and practices that protect human health and well-being.