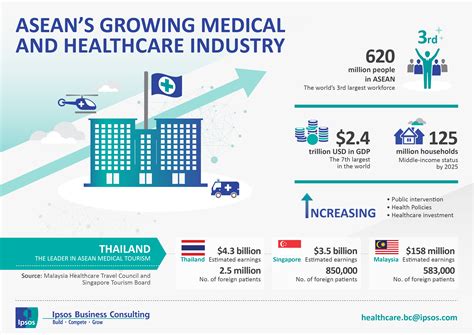
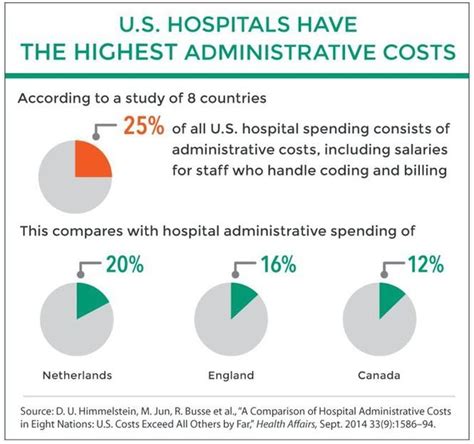
The healthcare sector in New South Wales (NSW) has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by an aging population, an increase in chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology. As the most populous state in Australia, NSW is home to a diverse range of healthcare services, including public and private hospitals, medical research institutions, and healthcare technology companies. In this article, we will explore the key drivers of healthcare growth in NSW, the current state of the sector, and the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
Key Points
- The healthcare sector in NSW is expected to grow by 3.5% per annum from 2023 to 2028, driven by an aging population and an increase in chronic diseases.
- The NSW Government has committed to investing $10.7 billion in healthcare infrastructure over the next four years, including the construction of new hospitals and the expansion of existing facilities.
- Medical research is a significant contributor to the NSW economy, with the state being home to several world-renowned research institutions, including the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre.
- The adoption of digital health technologies, such as telehealth and electronic health records, is becoming increasingly prevalent in NSW, with the state government investing $100 million in digital health initiatives over the next two years.
- The healthcare workforce in NSW is facing significant challenges, including staffing shortages and an aging workforce, with the state government implementing a range of initiatives to address these issues.
Drivers of Healthcare Growth in NSW

The healthcare sector in NSW is driven by a range of factors, including an aging population, an increase in chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology. The state’s population is projected to grow by 1.5% per annum from 2023 to 2028, with the proportion of people aged 65 and over expected to increase from 15.3% to 17.1% over the same period. This demographic shift will drive demand for healthcare services, particularly in the areas of aged care and gerontology.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, are a significant burden on the healthcare system in NSW. According to the NSW Ministry of Health, the prevalence of chronic diseases in the state is increasing, with 1 in 5 people living with a chronic disease. The adoption of healthy lifestyles, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help to prevent or manage chronic diseases, and the NSW Government has implemented a range of initiatives to promote healthy behaviors and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
| Chronic Disease | Prevalence in NSW |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | 6.4% of the population |
| Cardiovascular disease | 4.5% of the population |
| Cancer | 3.8% of the population |
Current State of the Healthcare Sector in NSW

The healthcare sector in NSW is a significant contributor to the state’s economy, with the sector generating $43.8 billion in output in 2020-21. The sector employs over 340,000 people, making it one of the largest employers in the state. The NSW Government is the largest provider of healthcare services in the state, with a range of public hospitals, community health centers, and other healthcare facilities.
Medical Research
Medical research is a significant contributor to the NSW economy, with the state being home to several world-renowned research institutions, including the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre. These institutions are involved in a range of research activities, including basic research, clinical trials, and translational research, and are helping to drive innovation and growth in the healthcare sector.
Opportunities and Challenges
The healthcare sector in NSW is facing a range of opportunities and challenges, including the adoption of digital health technologies, the need for workforce reform, and the increasing burden of chronic diseases. The adoption of digital health technologies, such as telehealth and electronic health records, is becoming increasingly prevalent in NSW, with the state government investing $100 million in digital health initiatives over the next two years.
Workforce Challenges
The healthcare workforce in NSW is facing significant challenges, including staffing shortages and an aging workforce. The NSW Government has implemented a range of initiatives to address these issues, including the creation of new training programs and the introduction of flexible work arrangements. However, more needs to be done to address the workforce challenges facing the healthcare sector, and to ensure that the sector has the skilled and diverse workforce it needs to meet the growing demand for healthcare services.
What is the current state of the healthcare sector in NSW?
+The healthcare sector in NSW is a significant contributor to the state's economy, with the sector generating $43.8 billion in output in 2020-21. The sector employs over 340,000 people, making it one of the largest employers in the state.
What are the key drivers of healthcare growth in NSW?
+The key drivers of healthcare growth in NSW include an aging population, an increase in chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology. The state's population is projected to grow by 1.5% per annum from 2023 to 2028, with the proportion of people aged 65 and over expected to increase from 15.3% to 17.1% over the same period.
What initiatives is the NSW Government implementing to address the workforce challenges facing the healthcare sector?
+The NSW Government has implemented a range of initiatives to address the workforce challenges facing the healthcare sector, including the creation of new training programs and the introduction of flexible work arrangements. The government is also investing in digital health technologies, such as telehealth and electronic health records, to help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services.
The healthcare sector in NSW is a significant contributor to the state's economy, and is expected to continue to grow and evolve in the coming years. The adoption of digital health technologies, the need for workforce reform, and the increasing burden of chronic diseases are just a few of the opportunities and challenges facing the sector. As the population of NSW continues to grow and age, it is essential that the healthcare sector is equipped to meet the growing demand for healthcare services, and that the sector has the skilled and diverse workforce it needs to provide high-quality, patient-centered care.