Global health rheumatology is an increasingly important field of study, as rheumatic diseases affect millions of people worldwide, causing significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burden. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 1 in 5 people globally suffer from a rheumatic condition, with the prevalence expected to rise due to aging populations and increased life expectancy. As a result, there is a growing need for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and researchers to understand the complexities of rheumatic diseases and develop effective strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and management.
The field of global health rheumatology encompasses a broad range of topics, including the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations of rheumatic diseases, as well as the social, economic, and cultural factors that influence healthcare access and outcomes. Rheumatic diseases are a heterogeneous group of conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, and gout, among others. These conditions can cause significant pain, disability, and decreased quality of life, making them a major public health concern.
Key Points
- Rheumatic diseases affect approximately 1 in 5 people worldwide, with the prevalence expected to rise due to aging populations and increased life expectancy.
- The field of global health rheumatology encompasses a broad range of topics, including the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations of rheumatic diseases.
- Rheumatic diseases are a heterogeneous group of conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, and gout.
- Effective strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and management of rheumatic diseases are critical to reducing the global burden of these conditions.
- Cultural and socioeconomic factors can significantly influence healthcare access and outcomes for individuals with rheumatic diseases.
Epidemiology and Burden of Rheumatic Diseases
The epidemiology of rheumatic diseases varies widely depending on the specific condition, geographic region, and population being studied. For example, rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women and tends to peak in incidence between the ages of 35 and 55, while osteoarthritis is more common in older adults and is often associated with obesity and joint trauma. The global burden of rheumatic diseases is substantial, with an estimated 3.8% of the global population affected by rheumatoid arthritis alone.
The economic burden of rheumatic diseases is also significant, with estimated annual costs ranging from $10,000 to $30,000 per patient in the United States. In addition to direct medical costs, rheumatic diseases can also result in significant indirect costs, including lost productivity, disability, and caregiver burden. Furthermore, the social and emotional impacts of rheumatic diseases should not be underestimated, as these conditions can cause significant pain, disability, and decreased quality of life.
Global Disparities in Healthcare Access and Outcomes
Global disparities in healthcare access and outcomes are a significant concern in the field of global health rheumatology. In low- and middle-income countries, access to healthcare services, including rheumatology care, is often limited due to lack of resources, infrastructure, and trained healthcare professionals. This can result in delayed diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and poor health outcomes for individuals with rheumatic diseases.
Cultural and socioeconomic factors can also significantly influence healthcare access and outcomes for individuals with rheumatic diseases. For example, in some cultures, traditional or alternative therapies may be preferred over conventional Western medicine, while in other cases, lack of health insurance or high out-of-pocket costs may limit access to necessary care. Understanding these factors is critical to developing effective strategies for improving healthcare access and outcomes for individuals with rheumatic diseases worldwide.
| Rheumatic Disease | Global Prevalence | Estimated Annual Costs (US) |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | 3.8% | $10,000 - $30,000 |
| Osteoarthritis | 9.6% | $5,000 - $15,000 |
| Lupus | 0.2% | $5,000 - $10,000 |
| Gout | 1.4% | $2,000 - $5,000 |

Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Rheumatic Diseases

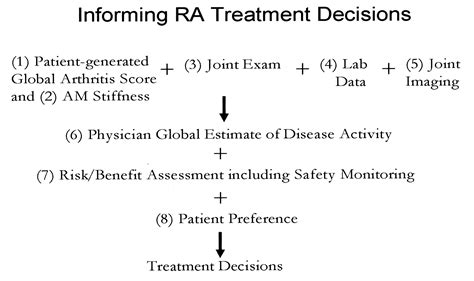
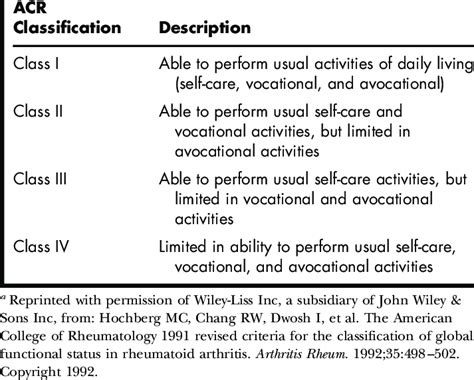
Prevention, diagnosis, and management of rheumatic diseases are critical to reducing the global burden of these conditions. While there are no proven strategies for preventing rheumatic diseases, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve health outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. Diagnosis of rheumatic diseases typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and imaging studies, such as X-rays and ultrasound.
Management of rheumatic diseases often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. For example, medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics can help to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression in rheumatoid arthritis, while physical therapy and exercise can help to improve joint mobility and reduce pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in Global Health Rheumatology
Emerging trends and technologies are transforming the field of global health rheumatology, offering new opportunities for improving healthcare access and outcomes for individuals with rheumatic diseases. For example, telemedicine and digital health technologies can help to increase access to rheumatology care, particularly in rural or underserved areas. Additionally, advances in genomics and precision medicine may help to identify new targets for treatment and improve personalized care for individuals with rheumatic diseases.
Other emerging trends in global health rheumatology include the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve diagnosis and treatment outcomes, as well as the development of new medications and therapies, such as biosimilars and gene therapies. As these trends and technologies continue to evolve, it is essential to ensure that they are accessible and effective for diverse populations worldwide.
What is the global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis?
+The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis is estimated to be approximately 3.8%.
What are the most common rheumatic diseases worldwide?
+The most common rheumatic diseases worldwide include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, and gout.
What are the estimated annual costs of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States?
+The estimated annual costs of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States range from 10,000 to 30,000 per patient.