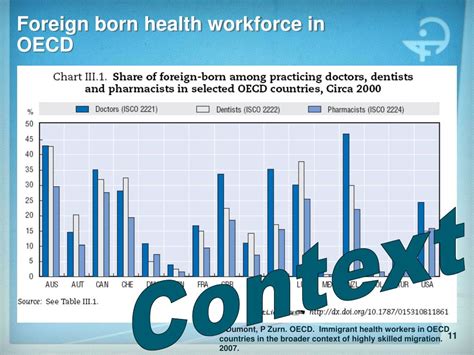
The foreign-born healthcare workforce has become an integral part of the global healthcare system, with many countries relying on international migration to address shortages in their healthcare professions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are over 1.3 million foreign-born healthcare workers worldwide, making up approximately 12% of the global healthcare workforce. In the United States alone, it is estimated that over 28% of physicians and 15% of registered nurses are foreign-born, highlighting the significant contribution of international healthcare professionals to the country's healthcare system.
The influx of foreign-born healthcare workers has been driven by a combination of factors, including aging populations, increased healthcare demands, and shortages of domestically trained healthcare professionals. Many countries have implemented policies to attract and retain international healthcare workers, such as streamlined visa processes, language proficiency testing, and cultural adaptation programs. However, the integration of foreign-born healthcare workers into host countries' healthcare systems can be complex, with challenges including language barriers, cultural differences, and varying standards of education and training.
Key Points
- The foreign-born healthcare workforce makes up approximately 12% of the global healthcare workforce, with over 1.3 million international healthcare workers worldwide.
- In the United States, over 28% of physicians and 15% of registered nurses are foreign-born, highlighting the significant contribution of international healthcare professionals to the country's healthcare system.
- The integration of foreign-born healthcare workers into host countries' healthcare systems can be complex, with challenges including language barriers, cultural differences, and varying standards of education and training.
- Many countries have implemented policies to attract and retain international healthcare workers, such as streamlined visa processes, language proficiency testing, and cultural adaptation programs.
- Foreign-born healthcare workers play a critical role in addressing healthcare workforce shortages, particularly in rural and underserved areas where domestic healthcare professionals may be less likely to practice.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Foreign-Born Healthcare Workforce

The integration of foreign-born healthcare workers into host countries’ healthcare systems presents both challenges and opportunities. One of the primary challenges is ensuring that international healthcare workers meet the necessary standards of education, training, and licensure. This can be a complex process, as educational and training requirements vary significantly between countries. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can create challenges for foreign-born healthcare workers to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues, potentially impacting the quality of care provided.
Despite these challenges, the foreign-born healthcare workforce also presents opportunities for improving the quality and diversity of healthcare services. International healthcare workers bring unique perspectives and experiences to the healthcare system, which can enhance cultural competency and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, foreign-born healthcare workers can help address healthcare workforce shortages, particularly in rural and underserved areas where domestic healthcare professionals may be less likely to practice. According to a study by the National Center for Health Workforce Analysis, foreign-born healthcare workers are more likely to practice in underserved areas, highlighting their critical role in ensuring access to healthcare services for vulnerable populations.
Cultural Competency and Language Proficiency in the Foreign-Born Healthcare Workforce
Cultural competency and language proficiency are essential components of effective healthcare delivery, particularly in diverse healthcare settings. Foreign-born healthcare workers must be able to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues from diverse cultural backgrounds, which can be a significant challenge. To address this challenge, many healthcare organizations and educational institutions offer cultural competency training and language proficiency programs for international healthcare workers. These programs aim to enhance the cultural awareness and language skills of foreign-born healthcare workers, enabling them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care that meets the unique needs of diverse patient populations.
| Country | Percentage of Foreign-Born Healthcare Workers |
|---|---|
| United States | 28% (physicians), 15% (registered nurses) |
| Canada | 23% (physicians), 12% (registered nurses) |
| Australia | 25% (physicians), 18% (registered nurses) |
| United Kingdom | 30% (physicians), 20% (registered nurses) |
Policy Implications and Future Directions for the Foreign-Born Healthcare Workforce

The foreign-born healthcare workforce has significant implications for healthcare policy and planning, both domestically and internationally. Governments, healthcare organizations, and educational institutions must work together to develop policies and programs that support the integration of international healthcare workers into host countries’ healthcare systems. This includes streamlining visa processes, providing cultural adaptation programs, and ensuring that foreign-born healthcare workers meet the necessary standards of education, training, and licensure.
Looking to the future, the foreign-born healthcare workforce is likely to play an increasingly critical role in addressing healthcare workforce shortages and improving the quality of care. As the global healthcare system continues to evolve, it is essential that policymakers and healthcare leaders prioritize the development of effective strategies to attract, retain, and support international healthcare workers. This includes investing in language proficiency programs, cultural competency training, and professional development opportunities that enable foreign-born healthcare workers to thrive in diverse healthcare settings.
What is the significance of the foreign-born healthcare workforce in addressing healthcare workforce shortages?
+The foreign-born healthcare workforce plays a critical role in addressing healthcare workforce shortages, particularly in rural and underserved areas where domestic healthcare professionals may be less likely to practice. International healthcare workers can help fill gaps in the healthcare workforce, ensuring that patients have access to high-quality care.
What challenges do foreign-born healthcare workers face in integrating into host countries’ healthcare systems?
+Foreign-born healthcare workers may face challenges including language barriers, cultural differences, and varying standards of education and training. These challenges can impact their ability to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues, potentially affecting the quality of care provided.
How can policymakers and healthcare leaders support the integration of foreign-born healthcare workers into host countries’ healthcare systems?
+Policymakers and healthcare leaders can support the integration of foreign-born healthcare workers by streamlining visa processes, providing cultural adaptation programs, and ensuring that international healthcare workers meet the necessary standards of education, training, and licensure. Additionally, investing in language proficiency programs and cultural competency training can help foreign-born healthcare workers thrive in diverse healthcare settings.