The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is a supersonic, twin-engine, variable sweep wing fighter aircraft that played a crucial role in the United States Navy's fleet defense for over three decades. With its unique design and capabilities, the F-14 Tomcat has become an iconic symbol of naval aviation. The Tomcat's development began in the 1960s as a replacement for the F-4 Phantom II, with the first prototype making its maiden flight on December 21, 1970. The F-14 entered service with the US Navy in 1974 and was eventually retired in 2006.
Design and Development

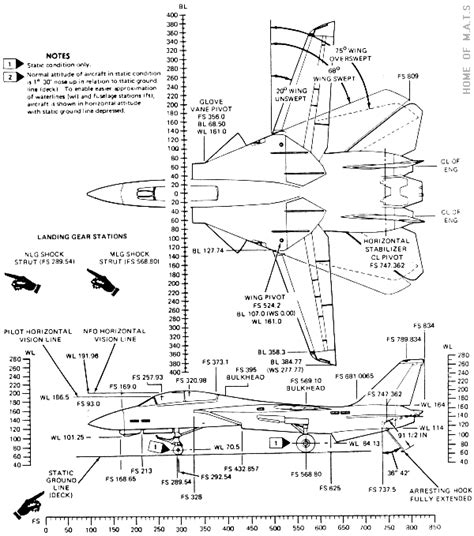
The F-14 Tomcat was designed to be a multi-role fighter, capable of air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance missions. Its variable sweep wing design, which allows the wings to move from 20 to 68 degrees, enables the aircraft to adapt to different flight regimes. The Tomcat’s airframe is constructed primarily of titanium and stainless steel, with a radar-absorbing material (RAM) coating to reduce its radar cross-section. The F-14 is powered by two General Electric F110-GE-400 turbofan engines, each producing 27,000 pounds of thrust.
Aerodynamic Characteristics
The F-14 Tomcat’s aerodynamic design features a number of innovative elements, including its variable sweep wing and a unique “glove” section on the fuselage. The glove section, which houses the Tomcat’s radar and avionics systems, is designed to reduce drag and improve the aircraft’s overall aerodynamic performance. The F-14’s wing is also equipped with a number of high-lift devices, including slats and flaps, which enable the aircraft to take off and land from the short decks of aircraft carriers.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Length | 62 feet 9 inches (19.1 meters) |
| Wingspan (swept) | 38 feet 2 inches (11.6 meters) |
| Wingspan (unswept) | 64 feet 1 inch (19.5 meters) |
| Height | 16 feet 1 inch (4.9 meters) |
| Empty Weight | 43,735 pounds (19,838 kilograms) |
| Maximum Takeoff Weight | 74,350 pounds (33,720 kilograms) |
| Engine | 2 x General Electric F110-GE-400 turbofans |
| Thrust | 54,000 pounds (240 kN) |

Operational History

The F-14 Tomcat saw extensive service with the US Navy, participating in a number of conflicts and operations around the world. The Tomcat’s first combat deployment was in 1975, during the Mayaguez incident, and it went on to see action in the Gulf of Sidra, the Iran-Iraq War, and the Gulf War. The F-14 was also used for reconnaissance and strike missions, and was capable of carrying a variety of air-to-ground munitions, including bombs, rockets, and missiles.
Upgrades and Modernization
Throughout its service life, the F-14 Tomcat underwent a number of upgrades and modernization programs, aimed at improving its avionics, radar, and weapon systems. The Tomcat’s AN/AWG-9 radar system, which was capable of detecting and tracking multiple targets at long range, was upgraded to the AN/AWG-9B system, which added improved air-to-ground modes and enhanced electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) capabilities. The F-14 was also equipped with the AIM-54 Phoenix missile, a long-range, air-to-air missile that was capable of engaging targets at ranges of up to 100 miles.
Key Points
- The F-14 Tomcat is a supersonic, twin-engine, variable sweep wing fighter aircraft that played a crucial role in the US Navy's fleet defense.
- The Tomcat's variable sweep wing design allows it to achieve a wide range of speeds, from low-speed carrier landings to high-speed intercepts.
- The F-14 is powered by two General Electric F110-GE-400 turbofan engines, each producing 27,000 pounds of thrust.
- The Tomcat's AN/AWG-9 radar system is capable of detecting and tracking multiple targets at long range, and was upgraded to the AN/AWG-9B system to add improved air-to-ground modes and ECCM capabilities.
- The F-14 was equipped with the AIM-54 Phoenix missile, a long-range, air-to-air missile that was capable of engaging targets at ranges of up to 100 miles.
Technical Specifications
The F-14 Tomcat’s technical specifications are a testament to its impressive performance and capabilities. The Tomcat’s maximum speed is over Mach 2.3, and it is capable of climbing to altitudes of over 50,000 feet. The F-14’s range is approximately 500 miles, and it can carry a payload of up to 14,500 pounds.
Avionics and Electronics
The F-14 Tomcat’s avionics and electronics systems are highly advanced, and include a number of innovative features such as a digital central computer, a data link system, and a tactical display system. The Tomcat’s AN/AWG-9 radar system is capable of detecting and tracking multiple targets at long range, and is integrated with the aircraft’s fire control system to provide a high degree of accuracy and effectiveness.
| System | Description |
|---|---|
| Radar | AN/AWG-9 pulse-Doppler radar |
| Fire Control | AN/ASW-25 fire control system |
| Communications | AN/ARC-159 UHF radio |
| Navigations | AN/ASN-92 inertial navigation system |
| Electronic Countermeasures | AN/ALQ-100 electronic countermeasures system |
What is the F-14 Tomcat's top speed?
+The F-14 Tomcat's top speed is over Mach 2.3, which is approximately 1,485 miles per hour.
What is the range of the F-14 Tomcat?
+The F-14 Tomcat's range is approximately 500 miles, although this can vary depending on the specific mission and payload.
What is the F-14 Tomcat's service ceiling?
+The F-14 Tomcat's service ceiling is over 50,000 feet, making it capable of operating at high altitudes.
The F-14 Tomcat is a highly advanced and capable fighter aircraft that played a crucial role in the US Navy’s fleet defense for over three decades. Its unique design features, including its variable sweep wing and advanced avionics, make it an iconic symbol of naval aviation. Despite its retirement from service, the F-14 Tomcat remains a popular and respected aircraft, and its legacy continues to inspire new generations of pilots and aviation enthusiasts.