The United States Air Force (USAF) is one of the most advanced and technologically sophisticated military branches in the world, with a wide range of career opportunities for both enlisted personnel and officers. When considering a career in the Air Force, one of the most significant decisions is whether to enlist or become an officer. In this article, we will explore the differences between enlisted and officer careers in the Air Force, including the roles, responsibilities, education requirements, and benefits associated with each path.
Key Points
- The Air Force offers a range of career opportunities for both enlisted personnel and officers, each with its own unique roles and responsibilities.
- Enlisted personnel typically enter the Air Force through basic training and technical school, while officers attend a four-year college or university and commission through the Air Force Academy, Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC), or Officer Training School (OTS).
- Officers are responsible for leading and managing teams, making strategic decisions, and overseeing operations, while enlisted personnel focus on specific technical skills and job specialties.
- Education requirements and opportunities vary significantly between enlisted and officer careers, with officers typically requiring a bachelor's degree and enlisted personnel having opportunities for on-the-job training and advanced education.
- Both enlisted and officer careers offer a range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance, as well as opportunities for advancement and professional growth.
Enlisted Careers in the Air Force
Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the Air Force, making up approximately 75% of the total force. They are responsible for performing specific technical skills and job specialties, such as aircraft maintenance, communications, and security. Enlisted personnel typically enter the Air Force through basic training and technical school, where they learn the skills and knowledge required for their specific job specialty.
There are several benefits to enlisting in the Air Force, including competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance. Enlisted personnel also have opportunities for advancement and professional growth, with the ability to earn promotions and take on leadership roles. Additionally, the Air Force offers a range of specialized training and education programs, including on-the-job training, apprenticeships, and advanced degree programs.
Some examples of enlisted careers in the Air Force include:
- Aircraft Maintenance: Enlisted personnel in this field are responsible for performing routine maintenance and repairs on aircraft, as well as troubleshooting and resolving technical issues.
- Communications: Enlisted personnel in this field are responsible for operating and maintaining communications equipment, including radios, computers, and networks.
- Security: Enlisted personnel in this field are responsible for providing security and protection for Air Force bases, personnel, and equipment.
Officer Careers in the Air Force
Officers in the Air Force are responsible for leading and managing teams, making strategic decisions, and overseeing operations. They are typically responsible for planning, organizing, and executing missions, as well as providing guidance and direction to enlisted personnel. Officers attend a four-year college or university and commission through the Air Force Academy, Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC), or Officer Training School (OTS).
There are several benefits to becoming an officer in the Air Force, including competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance. Officers also have opportunities for advancement and professional growth, with the ability to earn promotions and take on leadership roles. Additionally, the Air Force offers a range of specialized training and education programs, including flight training, advanced degree programs, and executive leadership development.
Some examples of officer careers in the Air Force include:
- Pilot: Officers in this field are responsible for flying and navigating aircraft, as well as planning and executing missions.
- Navigator: Officers in this field are responsible for planning and executing navigation and flight plans, as well as providing guidance and direction to pilots.
- Intelligence Officer: Officers in this field are responsible for analyzing and interpreting intelligence data, as well as providing strategic guidance and recommendations to senior leaders.
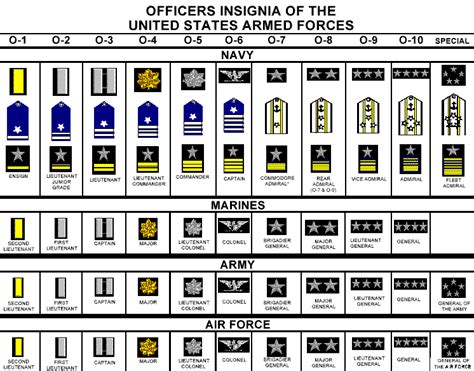
| Rank | Enlisted | Officer |
|---|---|---|
| E-1 | Airman Basic | Second Lieutenant |
| E-2 | Airman | First Lieutenant |
| E-3 | Airman First Class | Captain |
| E-4 | Senior Airman | Major |
| E-5 | Staff Sergeant | Lieutenant Colonel |

Education and Training
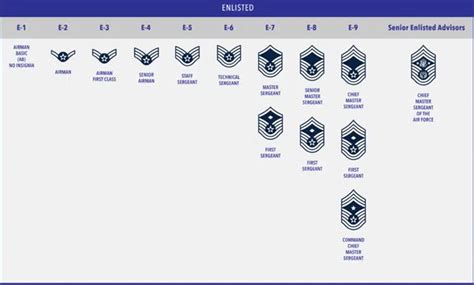
Education and training are critical components of any career in the Air Force, whether enlisted or officer. Enlisted personnel typically attend basic training and technical school, where they learn the skills and knowledge required for their specific job specialty. Officers, on the other hand, attend a four-year college or university and commission through the Air Force Academy, ROTC, or OTS.
In addition to initial training, the Air Force offers a range of specialized training and education programs, including on-the-job training, apprenticeships, and advanced degree programs. These programs provide enlisted personnel and officers with the skills and knowledge required to advance in their careers and take on leadership roles.
Advanced Education Opportunities
The Air Force offers a range of advanced education opportunities, including master’s and doctoral degree programs, as well as professional certifications and licenses. These programs provide enlisted personnel and officers with the skills and knowledge required to advance in their careers and take on leadership roles.
Some examples of advanced education opportunities in the Air Force include:
- Master’s Degree Programs: The Air Force offers a range of master’s degree programs, including business, engineering, and computer science.
- Doctoral Degree Programs: The Air Force offers a range of doctoral degree programs, including business, engineering, and computer science.
- Professional Certifications and Licenses: The Air Force offers a range of professional certifications and licenses, including pilot’s licenses, engineering certifications, and computer security certifications.
What are the primary differences between enlisted and officer careers in the Air Force?
+The primary differences between enlisted and officer careers in the Air Force are the levels of education, training, and responsibility. Enlisted personnel typically enter the Air Force through basic training and technical school, while officers attend a four-year college or university and commission through the Air Force Academy, ROTC, or OTS. Officers are responsible for leading and managing teams, making strategic decisions, and overseeing operations, while enlisted personnel focus on specific technical skills and job specialties.
What are the benefits of enlisting in the Air Force?
+The benefits of enlisting in the Air Force include competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance. Enlisted personnel also have opportunities for advancement and professional growth, with the ability to earn promotions and take on leadership roles. Additionally, the Air Force offers a range of specialized training and education programs, including on-the-job training, apprenticeships, and advanced degree programs.
What are the benefits of becoming an officer in the Air Force?
+The benefits of becoming an officer in the Air Force include competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance. Officers also have opportunities for advancement and professional growth, with the ability to earn promotions and take on leadership roles. Additionally, the Air Force offers a range of specialized training and education programs, including flight training, advanced degree programs, and executive leadership development.
In conclusion, the decision to enlist or become an officer in the Air Force is a personal one that depends on individual goals, interests, and career aspirations. Both paths offer a range of benefits and opportunities for advancement and professional growth, but they require different levels of education, training, and commitment. By understanding the differences between enlisted and officer careers, individuals can make informed decisions about their future and choose the path that best aligns with their goals and aspirations.