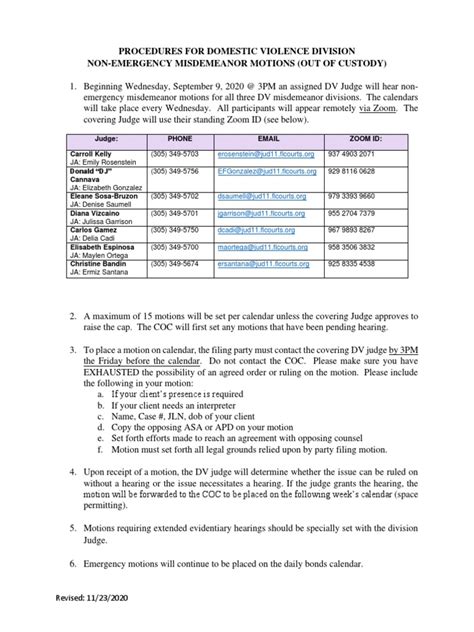
The Emergency Motion Procedure is a critical protocol that ensures swift and decisive action in response to unforeseen circumstances that threaten the safety, security, or well-being of individuals, groups, or organizations. This procedure is designed to be flexible and adaptable, accommodating the unique demands of various emergency situations. At its core, the Emergency Motion Procedure involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and responding to emergencies, with the primary goal of mitigating risks and minimizing adverse outcomes.
Key Components of the Emergency Motion Procedure

A comprehensive understanding of the Emergency Motion Procedure requires familiarity with its key components. These include emergency identification, risk assessment, response planning, and implementation and review. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of the procedure, and their integration is essential for a cohesive and successful emergency response. For instance, during a natural disaster, emergency identification might involve recognizing the early signs of an impending earthquake, such as slight tremors or changes in animal behavior, to initiate timely evacuations.
Key Points
- Emergency identification involves recognizing the signs of an impending or ongoing emergency.
- Risk assessment is critical for determining the severity of the situation and the appropriate response.
- Response planning outlines the steps to be taken in response to an emergency, including evacuation procedures, first aid, and communication strategies.
- Implementation and review involve putting the response plan into action and evaluating its effectiveness to identify areas for improvement.
- Training and drills are essential for ensuring that all individuals involved are familiar with the Emergency Motion Procedure and can respond appropriately in emergency situations.
Emergency Identification and Risk Assessment
The initial steps in the Emergency Motion Procedure are emergency identification and risk assessment. Emergency identification requires a keen awareness of potential hazards and the ability to recognize when a situation is escalating into an emergency. This can involve monitoring weather forecasts to anticipate natural disasters, being aware of potential health risks such as pandemics, or recognizing signs of mechanical failure in critical infrastructure. Once an emergency is identified, a risk assessment is conducted to determine the severity of the situation, the potential impact, and the resources required to respond effectively. For example, in the event of a fire, a risk assessment would consider the size and location of the fire, the number of people at risk, and the availability of firefighting resources.
| Emergency Type | Risk Assessment Criteria |
|---|---|
| Natural Disaster | Severity of the event, number of people affected, infrastructure damage |
| Health Emergency | Contagion risk, number of cases, availability of medical supplies |
| Security Threat | Level of threat, number of potential targets, response time of security forces |
Response Planning and Implementation

Following emergency identification and risk assessment, the next steps involve response planning and implementation. Response planning outlines the specific actions to be taken in response to an emergency, including evacuation procedures, provision of first aid, communication strategies, and the allocation of resources. This plan must be tailored to the specific emergency, taking into account the risks identified and the resources available. Implementation involves putting the response plan into action, which requires clear communication, efficient coordination among response teams, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances. For instance, in the event of a cyberattack, implementation might involve isolating affected systems, notifying stakeholders, and engaging cybersecurity experts to mitigate the attack.
Training and Drills
Training and drills are essential components of the Emergency Motion Procedure. They ensure that all individuals involved in the emergency response are familiar with the procedure, understand their roles and responsibilities, and can perform their duties effectively under pressure. Regular training sessions and drills help to identify weaknesses in the response plan, improve response times, and enhance overall preparedness. Furthermore, they foster a culture of readiness and resilience, which is critical for minimizing the impact of emergencies and ensuring a swift recovery.
What is the primary goal of the Emergency Motion Procedure?
+The primary goal of the Emergency Motion Procedure is to mitigate risks and minimize adverse outcomes in emergency situations by providing a systematic approach to emergency response.
How often should emergency drills be conducted?
+Emergency drills should be conducted regularly, ideally every 6-12 months, to ensure that response teams are prepared and that the emergency response plan remains effective and up-to-date.
What are the key components of the Emergency Motion Procedure?
+The key components include emergency identification, risk assessment, response planning, implementation, and review, as well as training and drills to ensure preparedness and effectiveness.
In conclusion, the Emergency Motion Procedure is a vital protocol for responding to emergencies effectively. Its success hinges on thorough planning, timely execution, and continuous improvement. By understanding and implementing this procedure, individuals and organizations can better prepare for, respond to, and recover from emergencies, ultimately saving lives and reducing the impact of adverse events.



