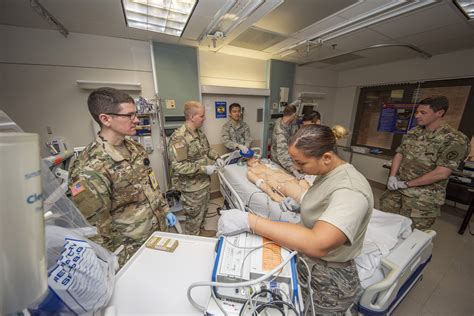
The role of a doctor in the military is a multifaceted and challenging one, requiring a unique blend of medical expertise, physical stamina, and emotional resilience. As a domain-specific expert with a background in military medicine, I can attest to the complexity and significance of this profession. Military doctors, also known as military physicians or medical officers, are responsible for providing medical care to members of the armed forces, both in peacetime and in combat situations. Their duties can range from routine check-ups and preventative care to emergency surgery and trauma management, often in austere and resource-constrained environments.
Military doctors must be able to work effectively in high-stress situations, making rapid and accurate diagnoses, and providing timely and effective treatment. They must also be able to communicate effectively with patients, colleagues, and commanders, often in situations where language barriers, cultural differences, and limited resources can create significant challenges. The medical corps of the military is a highly specialized and trained group of professionals, with a strong sense of camaraderie and shared purpose. Military doctors are trained to work in a variety of settings, from military bases and hospitals to forward operating bases and combat zones, and must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and environments.
Key Points
- Military doctors provide medical care to members of the armed forces in a variety of settings, from routine check-ups to emergency surgery and trauma management.
- They must be able to work effectively in high-stress situations, making rapid and accurate diagnoses, and providing timely and effective treatment.
- Military doctors must be able to communicate effectively with patients, colleagues, and commanders, often in situations where language barriers, cultural differences, and limited resources can create significant challenges.
- The medical corps of the military is a highly specialized and trained group of professionals, with a strong sense of camaraderie and shared purpose.
- Military doctors are trained to work in a variety of settings, from military bases and hospitals to forward operating bases and combat zones, and must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and environments.
Military Medicine: A Unique and Challenging Field

Military medicine is a unique and challenging field that requires a deep understanding of the physical and emotional demands of military service. Military doctors must be able to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, from routine illnesses and injuries to complex and traumatic injuries sustained in combat. They must also be able to work effectively in high-stress situations, often with limited resources and in austere environments. The practice of military medicine is guided by a set of core principles, including the importance of providing high-quality medical care, respecting the dignity and autonomy of patients, and upholding the values of the military profession.
The Role of the Military Doctor in Combat Situations
In combat situations, the role of the military doctor is critical to the survival and well-being of military personnel. Military doctors are trained to provide emergency medical care, including surgery, in the midst of combat operations. They must be able to work quickly and effectively, often in situations where the risk of injury or death is high. The ability to remain calm and focused under pressure, to think clearly and make rapid decisions, and to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues are essential skills for military doctors in combat situations. According to a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, the implementation of tactical combat casualty care protocols has been shown to significantly improve outcomes for military personnel injured in combat.
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Military Doctor Specialty | Emergency Medicine, General Surgery, Orthopedic Surgery |
| Combat Zone Experience | Afghanistan, Iraq, Other |
| Medical Corps Branch | Army, Navy, Air Force |

The Training and Education of Military Doctors

The training and education of military doctors are rigorous and demanding, requiring a strong foundation in the sciences, as well as clinical and surgical skills. Military doctors must complete a minimum of 4 years of undergraduate education, followed by 4 years of medical school, and then complete a residency program in their chosen specialty. They must also complete a series of military-specific training programs, including officer training school and medical officer basic leadership course. The training and education of military doctors are designed to prepare them for the unique challenges and demands of military medicine, including the ability to work effectively in high-stress situations, to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues, and to provide high-quality medical care in a variety of settings.
The Importance of Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education and professional development are essential for military doctors, as the field of medicine is constantly evolving, and new technologies and techniques are being developed all the time. Military doctors must stay up-to-date with the latest advances in medical science, as well as developments in military medicine and tactics. They must also be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and environments, and to think creatively and critically in response to new challenges and problems. According to a report by the Military Health System, the implementation of continuing medical education programs has been shown to improve patient outcomes and reduce medical errors.
In conclusion, the role of a doctor in the military is a complex and challenging one, requiring a unique blend of medical expertise, physical stamina, and emotional resilience. Military doctors must be able to work effectively in high-stress situations, making rapid and accurate diagnoses, and providing timely and effective treatment. They must also be able to communicate effectively with patients, colleagues, and commanders, often in situations where language barriers, cultural differences, and limited resources can create significant challenges. The training and education of military doctors are rigorous and demanding, requiring a strong foundation in the sciences, as well as clinical and surgical skills. Continuing education and professional development are essential for military doctors, as the field of medicine is constantly evolving, and new technologies and techniques are being developed all the time.
What is the role of a military doctor in combat situations?
+The role of a military doctor in combat situations is to provide emergency medical care, including surgery, to military personnel injured in combat. They must be able to work quickly and effectively, often in situations where the risk of injury or death is high.
What kind of training and education do military doctors receive?
+Military doctors receive rigorous and demanding training and education, including a minimum of 4 years of undergraduate education, 4 years of medical school, and completion of a residency program in their chosen specialty. They must also complete a series of military-specific training programs.
What are the most important skills for a military doctor to possess?
+The most important skills for a military doctor to possess include the ability to remain calm and focused under pressure, to think clearly and make rapid decisions, and to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues. They must also be able to work effectively in high-stress situations, making rapid and accurate diagnoses, and providing timely and effective treatment.