Combat medics, also known as field medics or military medics, play a crucial role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers in combat zones. While their primary responsibility is to provide medical aid, the question of whether combat medics fight is a complex one. The answer lies in the nuances of their role and the circumstances in which they operate.
Role of Combat Medics
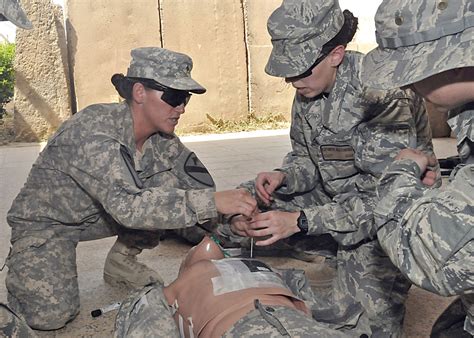
Combat medics are trained to provide emergency medical care in high-stress, dynamic environments. Their primary function is to treat wounded soldiers, stabilize their conditions, and evacuate them to medical facilities for further treatment. In addition to their medical responsibilities, combat medics are also expected to be proficient in basic combat skills, such as first aid, self-defense, and weapons handling.
However, combat medics are not typically expected to engage in combat as their primary role. Their focus is on providing medical care, not on fighting. In fact, the Geneva Conventions, which govern the conduct of war, grant medical personnel, including combat medics, protection from attack and persecution. This protection is based on the principle of neutrality, which recognizes the importance of medical care in conflict zones and seeks to ensure that medical personnel can perform their duties without fear of harm.
Combat Medic Training
Combat medics undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat zones. This training includes instruction in advanced first aid, trauma care, and evacuation procedures. Additionally, combat medics learn basic combat skills, such as marksmanship, self-defense, and tactical movement. While this training enables them to defend themselves if necessary, it is not intended to prepare them for a primary role in combat.
For example, the US Army's Combat Medic Specialist (68W) training program includes instruction in subjects such as patient assessment, trauma care, and medical evacuation procedures. The program also includes training in combat skills, such as marksmanship and self-defense, but these skills are secondary to the medic's primary role as a medical care provider.
| Combat Medic Training Topics | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient Assessment | Assessing patients' conditions and determining the best course of treatment |
| Trauma Care | Providing emergency medical care for traumatic injuries |
| Medical Evacuation Procedures | Evacuating patients to medical facilities for further treatment |
| Marksmanship | Basic training in firearms handling and marksmanship |
| Self-Defense | Training in self-defense techniques to protect oneself in hostile environments |
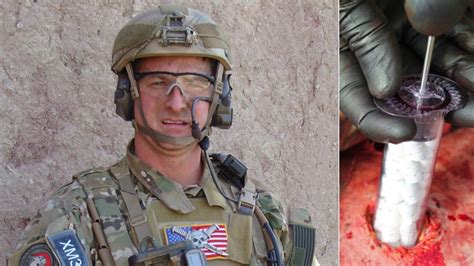
Combat Medics in Combat Zones

In combat zones, combat medics often find themselves in situations where they must balance their medical responsibilities with the need to defend themselves and their patients. While they may not be expected to engage in combat as their primary role, they may be required to use their combat skills to protect themselves and their patients from harm.
For example, during the Iraq War, US combat medics were often embedded with infantry units, providing medical care to wounded soldiers in the midst of combat. In these situations, medics might be required to use their combat skills to defend themselves and their patients, while also providing medical care to those in need.
It's worth noting that the line between providing medical care and engaging in combat can become blurred in high-stress, dynamic environments. Combat medics must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.
Key Points
- Combat medics are trained to provide medical care in high-stress, dynamic environments
- While they are not typically expected to engage in combat, they may be required to use their combat skills to defend themselves and their patients
- Combat medics undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat zones
- Their primary focus is always on providing medical care, not on fighting
- Combat medics must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death
Conclusion
In conclusion, while combat medics are not typically expected to engage in combat as their primary role, they may be required to use their combat skills to defend themselves and their patients in high-stress, dynamic environments. Their primary focus is always on providing medical care, and they undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat zones.
As the nature of warfare continues to evolve, the role of combat medics will likely continue to adapt, requiring them to balance their medical responsibilities with the need to defend themselves and their patients in increasingly complex and dynamic environments.
What is the primary role of a combat medic?
+The primary role of a combat medic is to provide medical care to wounded soldiers in combat zones.
Do combat medics undergo combat training?
+Yes, combat medics undergo training in basic combat skills, such as marksmanship and self-defense, to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat zones.
Are combat medics expected to engage in combat?
+No, combat medics are not typically expected to engage in combat as their primary role. However, they may be required to use their combat skills to defend themselves and their patients in high-stress, dynamic environments.
Meta Description: Learn about the role of combat medics in the military and whether they are expected to fight. Discover the challenges they face and the training they receive to prepare them for combat zones. (147 characters)


