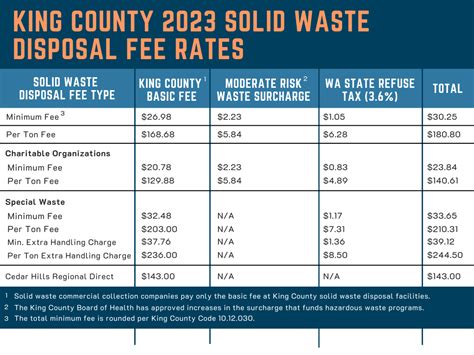
Disposal fees, also known as waste disposal fees or tipping fees, are charges levied on individuals or organizations for the disposal of waste at landfills or other waste management facilities. These fees are designed to cover the costs associated with the disposal of waste, including labor, equipment, and environmental protection measures. In this guide, we will delve into the world of disposal fees, exploring their significance, types, and implications for various stakeholders.
Key Points
- Disposal fees vary depending on the type and quantity of waste, as well as the location and regulatory requirements.
- The average cost of disposing of municipal solid waste in the United States is around $45 per ton.
- Disposal fees can be a significant expense for businesses and individuals, highlighting the importance of waste reduction and recycling strategies.
- Regulatory frameworks and environmental concerns are driving the development of more sustainable waste management practices.
- Technological innovations, such as waste-to-energy conversion and advanced recycling techniques, are transforming the waste management landscape.
Types of Disposal Fees

Disposal fees can be categorized into several types, each with its own set of characteristics and implications. The most common types of disposal fees include:
- Tipping fees: These are charges levied on waste generators for the disposal of waste at landfills or other waste management facilities.
- Gate fees: These fees are charged for the acceptance of waste at a waste management facility, regardless of whether the waste is disposed of or processed.
- Processing fees: These fees are associated with the processing of waste, such as sorting, recycling, or energy recovery.
Factors Influencing Disposal Fees
Disposal fees are influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Type and quantity of waste: The type and quantity of waste being disposed of can significantly impact disposal fees, with hazardous or specialty waste often attracting higher fees.
- Location and regulatory requirements: Disposal fees can vary depending on the location and regulatory requirements, with some regions imposing stricter environmental regulations and associated costs.
- Market conditions and competition: Market conditions and competition can also impact disposal fees, with prices fluctuating in response to changes in supply and demand.
| Waste Type | Average Disposal Fee (USD/ton) |
|---|---|
| Municipal Solid Waste | 45 |
| Construction and Demolition Waste | 30 |
| Hazardous Waste | 100 |
| Specialty Waste | 150 |

Implications of Disposal Fees
Disposal fees have significant implications for various stakeholders, including businesses, individuals, and the environment. Some of the key implications include:
- Cost savings: By adopting waste reduction and recycling strategies, organizations can minimize disposal costs and reduce their environmental impact.
- Regulatory compliance: Disposal fees can influence regulatory compliance, with organizations seeking to minimize costs and ensure adherence to environmental regulations.
- Environmental protection: Disposal fees can contribute to environmental protection by promoting sustainable waste management practices and reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Future of Disposal Fees
The future of disposal fees is likely to be shaped by technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and environmental concerns. Some of the key trends and developments include:
- Waste-to-energy conversion: The growth of waste-to-energy conversion technologies is expected to transform the waste management landscape, reducing disposal costs and promoting sustainable energy production.
- Advanced recycling techniques: The development of advanced recycling techniques, such as chemical recycling and biodegradation, is expected to increase recycling rates and reduce disposal costs.
- Circular economy principles: The adoption of circular economy principles, which prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and reuse, is expected to minimize disposal costs and promote sustainable waste management practices.
What are disposal fees, and how are they calculated?
+Disposal fees are charges levied on waste generators for the disposal of waste at landfills or other waste management facilities. The calculation of disposal fees depends on various factors, including the type and quantity of waste, location, and regulatory requirements.
How can businesses and individuals reduce disposal costs?
+Businesses and individuals can reduce disposal costs by adopting waste reduction and recycling strategies, such as minimizing waste generation, implementing recycling programs, and exploring alternative disposal methods.
What is the future of disposal fees, and how will they impact the waste management industry?
+The future of disposal fees is likely to be shaped by technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and environmental concerns. The growth of waste-to-energy conversion technologies, advanced recycling techniques, and circular economy principles is expected to transform the waste management landscape, reducing disposal costs and promoting sustainable waste management practices.