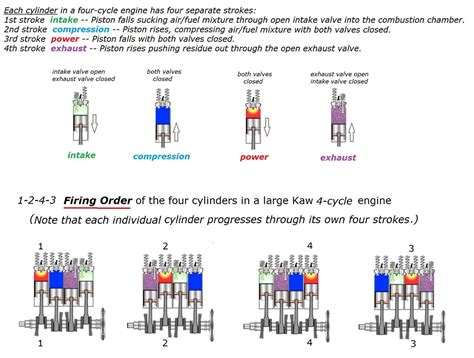
The diesel engine firing order is a critical aspect of diesel engine operation, as it directly affects the engine's performance, efficiency, and overall longevity. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines do not use spark plugs to ignite the fuel; instead, they rely on the heat generated by the compression of air in the cylinders to ignite the fuel. This process is known as compression ignition. The firing order, in this context, refers to the sequence in which the fuel is injected into the cylinders and the order in which the cylinders fire.
To understand the diesel engine firing order, it's essential to first grasp the basic principles of diesel engine operation. Diesel engines typically operate on a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. The firing order is usually represented by a series of numbers, with each number corresponding to a cylinder. For example, a common firing order for a 6-cylinder diesel engine might be 1-5-3-6-2-4. This sequence indicates that cylinder 1 fires first, followed by cylinder 5, then cylinder 3, and so on.
Key Points
- The diesel engine firing order is crucial for the engine's performance and efficiency.
- Diesel engines operate on a compression ignition principle, where the heat from air compression ignites the fuel.
- The firing order is typically represented by a sequence of numbers corresponding to the cylinders.
- Understanding the firing order is essential for diagnosing and repairing diesel engine issues.
- The firing order can vary depending on the engine manufacturer and the specific engine model.
Diesel Engine Firing Order Principles
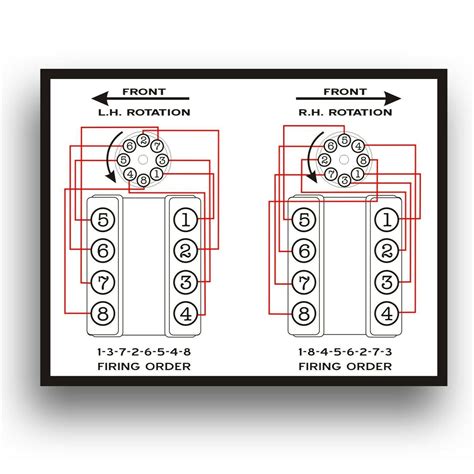
The firing order in a diesel engine is designed to balance the engine’s operation, ensuring that the forces generated by the firing of the cylinders are evenly distributed. This balance is critical for minimizing vibrations and ensuring the longevity of the engine. The principles behind the firing order involve considering the engine’s configuration, such as the number of cylinders and their arrangement (inline, V, or boxer), as well as the engine’s intended application (e.g., automotive, marine, or industrial).
Firing Order Patterns
There are various firing order patterns used in diesel engines, each tailored to the specific engine design and application. For instance, a 4-cylinder diesel engine might have a firing order of 1-3-4-2, while a 6-cylinder engine could follow the sequence 1-5-3-6-2-4, as mentioned earlier. The selection of a firing order is based on factors like the engine’s crankshaft design, the location of the valves and fuel injectors, and the desired engine performance characteristics.
| Engine Type | Firing Order Example |
|---|---|
| 4-Cylinder Inline | 1-3-4-2 |
| 6-Cylinder Inline | 1-5-3-6-2-4 |
| V8 Diesel | 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 |
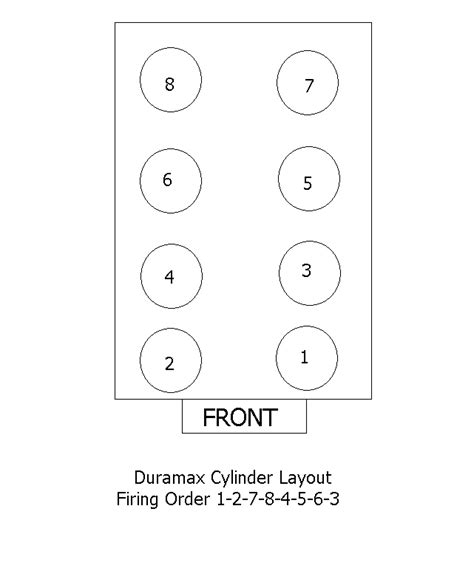
Importance of Firing Order in Diesel Engine Maintenance
Maintenance and repair of diesel engines often require an understanding of the firing order. When diagnosing issues, technicians may need to identify which cylinder is not firing properly, which can be done by following the firing order sequence. Additionally, during engine overhauls or when replacing critical components like fuel injectors or cylinder heads, knowledge of the firing order ensures that these parts are installed correctly, maintaining the engine’s designed performance and efficiency.
Common Issues Related to Firing Order
Issues related to the firing order can arise from various sources, including faulty fuel injectors, improper timing, or problems with the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU). A misfiring cylinder can lead to decreased engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and potentially cause damage to the catalytic converter or other emission control devices. In some cases, a faulty firing order can also lead to increased emissions, contributing to environmental pollution and potentially resulting in the engine failing emissions tests.
In conclusion, the diesel engine firing order is a fundamental aspect of diesel engine operation and maintenance. Understanding the firing order is essential for both the proper functioning of the engine and for diagnosing and repairing issues that may arise. As diesel engines continue to evolve with advancements in technology, the principles behind the firing order remain a critical component of their design and operation.
What is the significance of the firing order in diesel engines?
+The firing order is crucial for the balanced operation of the engine, ensuring that the forces generated by the firing of the cylinders are evenly distributed. This balance is key to minimizing vibrations and ensuring the longevity of the engine.
How does the firing order affect diesel engine performance?
+The firing order directly affects the engine’s performance, efficiency, and overall longevity. A properly sequenced firing order ensures optimal engine operation, while any deviation can lead to decreased performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential engine damage.
Can the firing order be adjusted or modified in diesel engines?
+While the firing order is typically fixed by the engine’s design, some modern diesel engines with advanced electronic control units (ECUs) may allow for adjustments to the firing sequence under certain conditions. However, any modifications should be made with caution and typically require specialized knowledge and equipment.