The healthcare industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging population, an increased focus on preventive care, and the adoption of digital technologies. As a result, the demand for data analysts in healthcare has skyrocketed, with these professionals playing a critical role in helping organizations make informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and reduce costs. In this article, we will delve into the world of data analyst jobs in healthcare, exploring the key responsibilities, required skills, and emerging trends in this exciting field.
Introduction to Data Analyst Jobs in Healthcare

Data analysts in healthcare are responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting complex data sets to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform business decisions, clinical practices, and policy developments. These professionals work with a range of data sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), claims data, and patient satisfaction surveys, to develop reports, dashboards, and visualizations that communicate key findings to stakeholders. With the healthcare industry generating vast amounts of data, data analysts are in high demand, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicting a 14% growth in employment opportunities for data analysts in the healthcare sector between 2020 and 2030.
Key Points
- The demand for data analysts in healthcare is driven by the industry's growth, digital transformation, and the need for data-driven decision-making.
- Data analysts in healthcare work with various data sources, including EHRs, claims data, and patient satisfaction surveys.
- Key responsibilities include data collection, analysis, and interpretation, as well as report development and stakeholder communication.
- Required skills include proficiency in data analysis tools, programming languages, and data visualization software, as well as strong analytical and communication skills.
- Emerging trends in healthcare data analysis include the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
Key Responsibilities and Required Skills
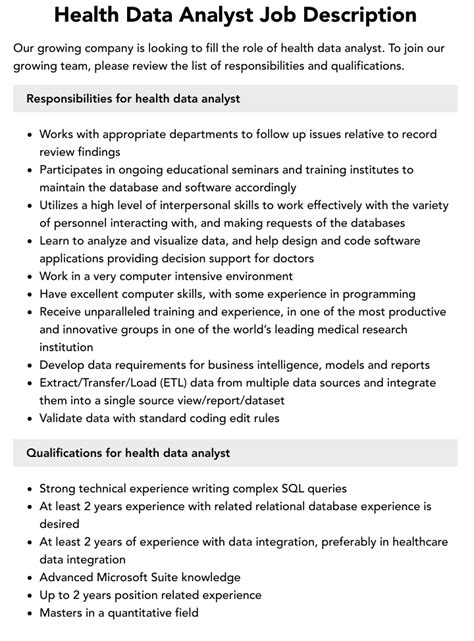
Data analysts in healthcare are responsible for a range of tasks, including data collection, data cleaning, and data analysis. They must also develop reports, dashboards, and visualizations to communicate key findings to stakeholders, including healthcare executives, clinicians, and policymakers. To perform these tasks effectively, data analysts in healthcare require a range of skills, including proficiency in data analysis tools, such as Excel, SQL, and Tableau, as well as programming languages, such as Python and R. Strong analytical and communication skills are also essential, as data analysts must be able to interpret complex data sets and communicate insights to non-technical stakeholders.
| Required Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Analysis Tools | Proficiency in tools like Excel, SQL, and Tableau |
| Programming Languages | Knowledge of languages like Python and R |
| Data Visualization | Ability to create reports, dashboards, and visualizations |
| Communication Skills | Strong analytical and communication skills |
| Domain Knowledge | Understanding of the healthcare industry and its trends |

Emerging Trends in Healthcare Data Analysis

The healthcare industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advances in digital technologies, changes in consumer behavior, and the need for more efficient and effective care delivery models. As a result, data analysts in healthcare are leveraging emerging trends, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP), to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of care. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to engage patients, provide personalized support, and improve medication adherence, while ML algorithms are being applied to predict patient risk, identify high-cost patients, and optimize treatment pathways.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Data analysts in healthcare are working on a range of exciting projects, from developing predictive models to identify high-risk patients to creating personalized treatment plans using genomics and precision medicine. For example, a leading healthcare organization used data analytics to reduce hospital readmissions by 25%, while another organization used ML algorithms to predict patient risk and identify high-cost patients, resulting in a 15% reduction in costs. These case studies demonstrate the power of data analytics in healthcare, highlighting the potential for data-driven insights to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of care.
In conclusion, data analyst jobs in healthcare offer a rewarding and challenging career path for professionals with a passion for data analysis, healthcare, and improving patient outcomes. With the demand for data analysts in healthcare expected to continue growing, individuals with the right skills, knowledge, and experience will be well-positioned to succeed in this exciting field. Whether you are just starting your career or looking to transition into a new role, the opportunities for data analysts in healthcare are vast and varied, offering a range of possibilities for professional growth and development.
What are the key responsibilities of a data analyst in healthcare?
+The key responsibilities of a data analyst in healthcare include data collection, data analysis, and report development, as well as stakeholder communication and insights presentation.
What skills are required to be a successful data analyst in healthcare?
+To be a successful data analyst in healthcare, you will need proficiency in data analysis tools, programming languages, and data visualization software, as well as strong analytical and communication skills.
What are some emerging trends in healthcare data analysis?
+Emerging trends in healthcare data analysis include the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of care.