The DIP joint, also known as the distal interphalangeal joint, is a complex and highly specialized joint that plays a crucial role in the movement and flexibility of the fingers and toes. Located between the distal and middle phalanges of the fingers and toes, the DIP joint is a hinge-type joint that allows for flexion and extension movements. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the DIP joint, as well as explore the various conditions that can affect this joint.
Anatomy of the DIP Joint
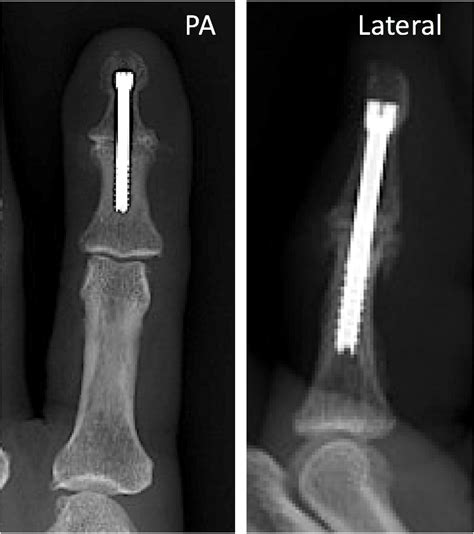
The DIP joint is a synovial joint that consists of the distal end of the middle phalanx and the proximal end of the distal phalanx. The joint is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that provides stability and support, and is reinforced by collateral ligaments that connect the bones on either side of the joint. The joint also contains a synovial membrane that produces synovial fluid, which helps to reduce friction and promote smooth movement. The DIP joint is also surrounded by a number of muscles and tendons that work together to control movement and provide stability.
Function of the DIP Joint
The primary function of the DIP joint is to allow for flexion and extension movements of the fingers and toes. The joint is capable of producing a wide range of movements, from slight flexion to full extension, and is essential for activities such as grasping, gripping, and manipulating objects. The DIP joint also plays a critical role in the transmission of forces from the fingers and toes to the rest of the hand and foot, and is important for maintaining balance and stability.
| Joint Movement | Range of Motion |
|---|---|
| Flexion | 0-60 degrees |
| Extension | 0-30 degrees |
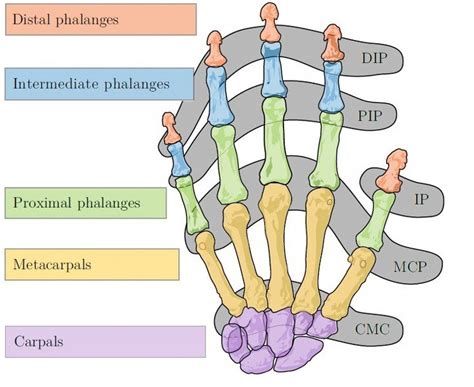
Key Points
- The DIP joint is a hinge-type joint that allows for flexion and extension movements.
- The joint is surrounded by a fibrous capsule and reinforced by collateral ligaments.
- The DIP joint is essential for activities such as grasping, gripping, and manipulating objects.
- The joint plays a critical role in the transmission of forces from the fingers and toes to the rest of the hand and foot.
- The DIP joint is susceptible to a number of conditions, including arthritis, injuries, and infections.
Clinical Significance of the DIP Joint
The DIP joint is susceptible to a number of conditions, including arthritis, injuries, and infections. One of the most common conditions affecting the DIP joint is osteoarthritis, which can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. The joint can also be affected by rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions. Injuries to the DIP joint can occur as a result of trauma, overuse, or repetitive strain, and can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Infections, such as septic arthritis, can also affect the DIP joint and require prompt medical attention.
Conditions Affecting the DIP Joint
There are a number of conditions that can affect the DIP joint, including:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Injuries, such as sprains and strains
- Infections, such as septic arthritis
Treatment and Management of DIP Joint Conditions
Treatment and management of DIP joint conditions depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Conservative management options, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), can be effective for mild to moderate conditions. Physical therapy can also be beneficial for improving range of motion, strength, and function. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged joint.
Surgical Options for DIP Joint Conditions
Surgical options for DIP joint conditions include:
- Joint replacement
- Joint fusion
- Tendon repair
- Ligament reconstruction
What is the most common condition affecting the DIP joint?
+Osteoarthritis is the most common condition affecting the DIP joint, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
How is the DIP joint treated?
+Treatment of the DIP joint depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, and can include conservative management options, physical therapy, and surgical intervention.
What are the potential complications of DIP joint conditions?
+Potential complications of DIP joint conditions include chronic pain, limited mobility, and decreased quality of life, as well as increased risk of falls and injuries.
Meta Description: The DIP joint is a complex and highly specialized joint that plays a crucial role in the movement and flexibility of the fingers and toes. Learn about the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the DIP joint, as well as the various conditions that can affect this joint.



