The company chain of command refers to the hierarchical structure of an organization, outlining the lines of authority, responsibility, and communication. It is a crucial aspect of any company, as it helps to ensure that decisions are made efficiently, tasks are delegated effectively, and employees understand their roles and expectations. In this article, we will delve into the concept of company chain of command, its importance, and the different types of organizational structures that companies can adopt.
Understanding the Chain of Command
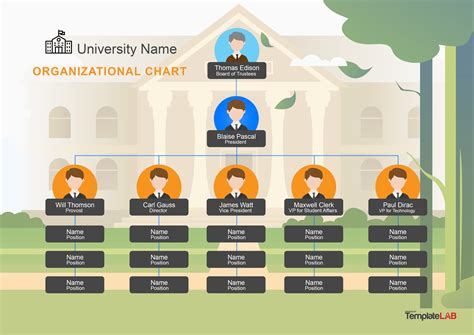
The chain of command is a linear structure that outlines the reporting relationships between employees, from the highest level of management to the lowest level of staff. It is typically depicted as a pyramid, with the CEO or Managing Director at the top, followed by senior managers, middle managers, team leaders, and finally, frontline staff. Each level of the hierarchy has its own set of responsibilities, authorities, and accountabilities, which are defined by the company’s policies, procedures, and job descriptions.
Key Components of the Chain of Command
There are several key components that make up the chain of command, including:
- Line Authority: The direct line of authority from one level of management to the next, which enables decision-making and task delegation.
- Staff Authority: The advisory role of staff members, such as human resources or finance, who provide support and guidance to line managers.
- Functional Authority: The authority granted to specific departments or teams, such as marketing or sales, to make decisions and take actions within their area of expertise.
| Level of Management | Responsibilities | Authorities |
|---|---|---|
| CEO/Managing Director | Overall strategy, direction, and decision-making | Ultimate authority, final decision-maker |
| Senior Managers | Departmental management, goal-setting, and resource allocation | Significant authority, decision-making within department |
| Middle Managers | Team management, task delegation, and performance monitoring | Authority to delegate tasks, monitor performance |
| Team Leaders | Day-to-day team management, task allocation, and support | Authority to allocate tasks, provide guidance and support |
| Frontline Staff | Task execution, customer service, and data collection | Authority to perform tasks, report to team leader |

Types of Organizational Structures

Companies can adopt various types of organizational structures, depending on their size, industry, and goals. Some common types of structures include:
- Functional Structure: A hierarchical structure where departments are organized by function, such as marketing, sales, and finance.
- Divisional Structure: A structure where departments are organized by product, customer, or geographic region.
- Matrix Structure: A structure where employees report to multiple managers, often used in project-based organizations.
- Flat Structure: A structure with few levels of management, often used in small or agile organizations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Structures
Each type of organizational structure has its advantages and disadvantages. For example:
- Functional Structure: Advantages include clear lines of authority, efficient use of resources, and specialized expertise. Disadvantages include slow decision-making, lack of flexibility, and potential for departmental silos.
- Divisional Structure: Advantages include increased autonomy, faster decision-making, and better customer focus. Disadvantages include duplication of resources, potential for conflict between divisions, and increased complexity.
Key Points
- The company chain of command is a hierarchical structure that outlines the lines of authority, responsibility, and communication within an organization.
- A well-defined chain of command is essential for effective communication, decision-making, and problem-solving.
- Companies can adopt various types of organizational structures, depending on their size, industry, and goals.
- Each type of structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of structure depends on the company's specific needs and objectives.
- A flat structure can be beneficial for small or agile organizations, while a functional structure may be more suitable for larger or more complex organizations.
In conclusion, the company chain of command is a critical aspect of any organization, as it helps to ensure that decisions are made efficiently, tasks are delegated effectively, and employees understand their roles and expectations. By understanding the different types of organizational structures and their advantages and disadvantages, companies can choose the best structure to suit their needs and objectives.
What is the purpose of the company chain of command?
+The purpose of the company chain of command is to outline the lines of authority, responsibility, and communication within an organization, ensuring that decisions are made efficiently, tasks are delegated effectively, and employees understand their roles and expectations.
What are the different types of organizational structures?
+Common types of organizational structures include functional, divisional, matrix, and flat structures. Each type of structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of structure depends on the company’s specific needs and objectives.
How does the company chain of command affect communication and decision-making?
+A well-defined chain of command can improve communication and decision-making by ensuring that employees understand their roles and responsibilities, and that tasks are delegated efficiently and effectively. It can also help to reduce confusion, errors, and delays, and improve overall organizational performance.



