The concept of caregiver healthcare is intricately linked with the broader social and environmental factors that influence an individual's well-being. Urie Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex interplay between caregivers, their environment, and the healthcare system. This theory posits that human development is shaped by multiple, nested systems, ranging from the microsystem (immediate environment) to the macrosystem (broader societal context). In the context of caregiver healthcare, Bronfenbrenner's theory highlights the need for a holistic approach that considers the various systems influencing caregiver well-being.
At the microsystem level, caregivers are directly influenced by their immediate environment, including family members, healthcare providers, and social support networks. The quality of relationships within this system can significantly impact caregiver stress, emotional well-being, and ability to provide effective care. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Gerontology found that caregivers who received emotional support from family members and friends reported lower levels of depression and anxiety. In contrast, caregivers with limited social support networks are more likely to experience burnout and decreased physical health.
Ecological Systems Theory and Caregiver Healthcare
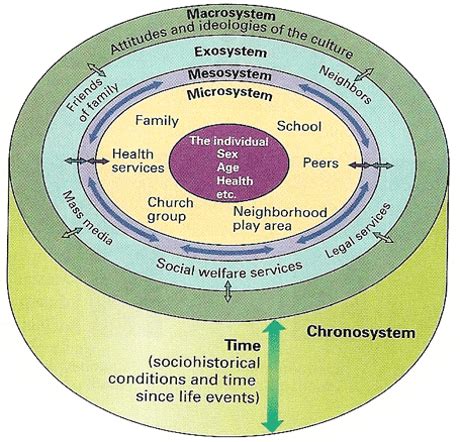
Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of multiple systems influencing caregiver healthcare. The mesosystem, which encompasses the interactions between different microsystems, plays a crucial role in shaping caregiver experiences. For example, the relationship between caregivers and healthcare providers can significantly impact the quality of care provided. A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that caregivers who reported positive interactions with healthcare providers were more likely to adhere to treatment plans and report improved caregiver well-being.
Mesosystem Influences on Caregiver Healthcare
The exosystem, which includes external factors such as healthcare policies, socioeconomic status, and access to resources, also exerts a significant influence on caregiver healthcare. Caregivers from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face increased barriers to accessing healthcare services, including lack of health insurance, transportation difficulties, and limited access to respite care. According to data from the National Alliance for Caregiving, caregivers with annual incomes below $50,000 are more likely to report financial strain and decreased ability to provide care.
| System Level | Influence on Caregiver Healthcare |
|---|---|
| Microsystem | Immediate environment, social support networks, and relationships with healthcare providers |
| Mesosystem | Interactions between microsystems, including relationships between caregivers and healthcare providers |
| Exosystem | External factors, such as healthcare policies, socioeconomic status, and access to resources |
| Macrosystem | Broad societal context, including cultural values, social norms, and economic conditions |
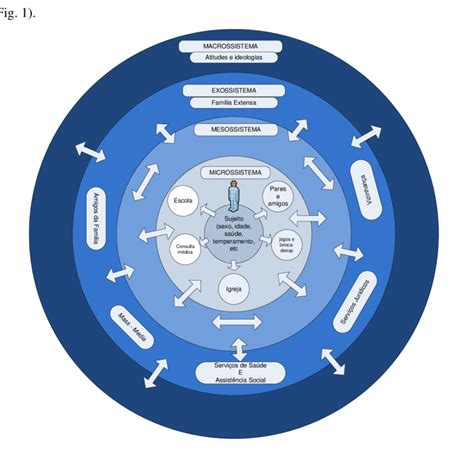
The macrosystem, which encompasses the broader societal context, also plays a critical role in shaping caregiver healthcare. Cultural values, social norms, and economic conditions can influence caregiver expectations, responsibilities, and access to resources. For example, a study published in the Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology found that caregivers from collectivist cultures reported higher levels of caregiver burden and stress due to strong family obligations and limited access to formal support services.
Key Points
- The ecological systems theory provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex interplay between caregivers, their environment, and the healthcare system.
- The microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, and macrosystem all exert significant influences on caregiver healthcare, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to supporting caregiver well-being.
- Caregivers from lower socioeconomic backgrounds face increased barriers to accessing healthcare services, including lack of health insurance, transportation difficulties, and limited access to respite care.
- The relationship between caregivers and healthcare providers plays a critical role in shaping caregiver experiences and healthcare outcomes.
- Cultural values, social norms, and economic conditions influence caregiver expectations, responsibilities, and access to resources, emphasizing the need for culturally sensitive interventions.
In conclusion, the concept of caregiver healthcare is deeply intertwined with the broader social and environmental factors that influence an individual's well-being. By applying Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory, healthcare providers can develop a nuanced understanding of the complex interplay between caregivers, their environment, and the healthcare system. This knowledge can inform targeted interventions to support caregiver well-being, improve healthcare outcomes, and address the unique challenges faced by caregivers from diverse backgrounds.
What is the ecological systems theory, and how does it relate to caregiver healthcare?
+The ecological systems theory, developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex interplay between individuals, their environment, and the broader societal context. In the context of caregiver healthcare, this theory highlights the need for a holistic approach that considers the various systems influencing caregiver well-being, including the microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, and macrosystem.
How do socioeconomic factors influence caregiver healthcare?
+Caregivers from lower socioeconomic backgrounds face increased barriers to accessing healthcare services, including lack of health insurance, transportation difficulties, and limited access to respite care. These factors can exacerbate caregiver burden, stress, and decreased physical health, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to address socioeconomic disparities in caregiver healthcare.
What role do cultural values and social norms play in shaping caregiver healthcare?
+Cultural values, social norms, and economic conditions influence caregiver expectations, responsibilities, and access to resources. For example, caregivers from collectivist cultures may report higher levels of caregiver burden and stress due to strong family obligations and limited access to formal support services. Culturally sensitive interventions are essential to addressing the unique challenges faced by caregivers from diverse backgrounds.



