Better urban health is a multifaceted concept that encompasses the physical, mental, and social well-being of individuals living in urban environments. As the world becomes increasingly urbanized, with over 55% of the global population residing in cities, the importance of addressing urban health challenges cannot be overstated. Urban areas are often characterized by high population densities, diversity, and complexity, which can both positively and negatively impact the health of their inhabitants. For instance, urban residents may have access to better healthcare facilities, education, and economic opportunities, but they are also more likely to be exposed to environmental pollutants, experience social isolation, and face barriers to healthy lifestyle choices.
Key Points
- Urban health is influenced by a complex interplay of physical, social, and economic factors.
- Access to green spaces, clean air and water, and healthy food options are critical for urban health.
- Social determinants, such as education, employment, and housing, play a significant role in shaping urban health outcomes.
- Community-based initiatives and policies that promote urban planning, transportation, and healthcare access are essential for improving urban health.
- Addressing health inequities and disparities in urban populations requires a nuanced understanding of the specific challenges faced by different demographic groups.
Understanding Urban Health Challenges

The urban health landscape is marked by numerous challenges, including but not limited to, air and water pollution, lack of green spaces, inadequate housing, and limited access to healthcare services. These challenges are often exacerbated by socioeconomic factors, such as poverty, lack of education, and unemployment, which can further exacerbate health disparities. For example, a study by the World Health Organization (WHO) found that urban residents in low- and middle-income countries are more likely to be exposed to poor living conditions, inadequate sanitation, and insufficient healthcare services, resulting in higher rates of infectious diseases, mental health issues, and non-communicable diseases.
The Role of Urban Planning in Promoting Health
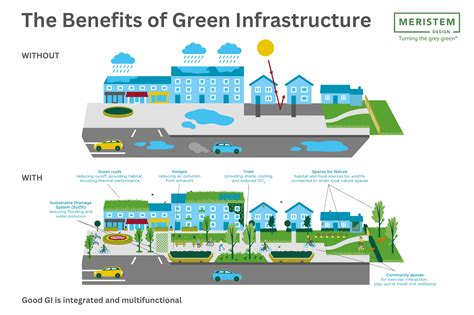
Urban planning plays a crucial role in promoting health in urban environments. Well-designed cities can incorporate features that encourage physical activity, such as bike lanes, pedestrian paths, and public parks, thereby reducing the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, urban planning strategies that prioritize mixed-use development, public transportation, and affordable housing can help reduce social isolation, improve air quality, and increase access to healthcare services. A notable example is the city of Copenhagen, which has implemented a comprehensive urban planning strategy that includes the creation of car-free zones, green roofs, and community gardens, resulting in improved air quality, reduced traffic congestion, and enhanced overall quality of life for its residents.
| Urban Planning Strategies | Health Benefits |
|---|---|
| Mixed-use development | Increased physical activity, reduced air pollution |
| Public transportation | Reduced traffic congestion, improved air quality |
| Affordable housing | Reduced social isolation, improved access to healthcare |
| Green spaces | Improved mental health, reduced stress |
Addressing Health Inequities in Urban Populations

Health inequities are a pervasive issue in urban populations, with certain demographic groups facing disproportionate health challenges due to socioeconomic, environmental, and systemic factors. For instance, racial and ethnic minorities, low-income populations, and individuals with disabilities often experience higher rates of chronic diseases, mental health issues, and poor health outcomes due to barriers in accessing healthcare services, healthy food options, and safe living environments. To address these inequities, it is essential to implement targeted interventions that prioritize the specific needs of these populations, such as community-based health programs, cultural competency training for healthcare providers, and policy initiatives that promote health equity.
Community-Based Initiatives for Urban Health
Community-based initiatives are critical for promoting urban health, as they can provide targeted support, education, and resources to urban residents. These initiatives can range from community gardens and farmers’ markets that promote access to healthy food, to mental health services and support groups that address social isolation and trauma. Moreover, community-based initiatives can help build trust between healthcare providers and urban residents, thereby improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities. A notable example is the Boston Health Commission’s community-based initiative, which provides outreach services, health education, and linkage to care for underserved populations, resulting in improved health outcomes and reduced health inequities.
What are the most significant challenges facing urban health initiatives?
+The most significant challenges facing urban health initiatives include limited resources, lack of infrastructure, and socioeconomic factors that exacerbate health disparities. Additionally, the complexity of urban environments and the diversity of urban populations can make it difficult to develop and implement effective health interventions.
How can urban planning strategies promote health in urban environments?
+Urban planning strategies can promote health in urban environments by incorporating features that encourage physical activity, such as bike lanes and public parks, and by prioritizing mixed-use development, public transportation, and affordable housing. These strategies can help reduce social isolation, improve air quality, and increase access to healthcare services.
What role do community-based initiatives play in promoting urban health?
+Community-based initiatives play a critical role in promoting urban health by providing targeted support, education, and resources to urban residents. These initiatives can help build trust between healthcare providers and urban residents, improve health outcomes, and reduce health disparities.
Meta Description: Discover the complexities of urban health and the strategies that can improve well-being in cities, including urban planning, community-based initiatives, and addressing health inequities.