When an individual is arrested, they are typically charged with a specific crime or offense, which can range from a misdemeanor to a felony. Understanding the nuances of arrest charge information is crucial for navigating the complex legal system. The process of being charged involves the issuance of a complaint or indictment, which outlines the alleged offense and the corresponding penalties. In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of arrest charge information, exploring the different types of charges, the charging process, and the potential consequences of a conviction.
Types of Arrest Charges

Arrest charges can be broadly categorized into two main types: misdemeanors and felonies. Misdemeanors are generally considered less serious offenses, punishable by fines, probation, or short-term imprisonment. Examples of misdemeanors include disorderly conduct, petty theft, and traffic violations. Felonies, on the other hand, are more serious crimes that can result in significant prison time, fines, and long-term consequences. Felonies can include offenses such as burglary, assault, and drug trafficking. It is essential to note that the specific classification of a charge can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the circumstances surrounding the alleged offense.
Misdemeanor Charges
Misdemeanor charges are typically less severe than felony charges and often carry less stringent penalties. However, a misdemeanor conviction can still have significant consequences, including fines, community service, and a permanent record. Common examples of misdemeanor charges include:
- Disorderly conduct
- Petty theft
- Traffic violations
- Simple assault
- Public intoxication
Felony Charges
Felony charges are more serious and can result in substantial prison time, fines, and long-term consequences. Felonies can be further divided into different degrees, with first-degree felonies being the most severe. Examples of felony charges include:
- Burglary
- Assault
- Drug trafficking
- Robbery
- Manslaughter
| Charge Type | Penalty Range |
|---|---|
| Misdemeanor | Fines, probation, or short-term imprisonment (up to 1 year) |
| Felony | Significant prison time, fines, and long-term consequences (1-20 years or more) |
The Charging Process
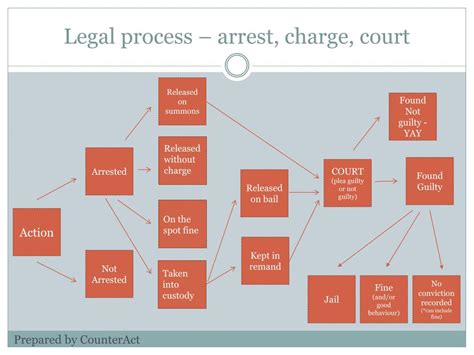
The charging process typically begins with an arrest, followed by the issuance of a complaint or indictment. The complaint or indictment outlines the alleged offense, the corresponding charges, and the potential penalties. The individual charged will then be scheduled for an arraignment, where they will be formally advised of the charges and given the opportunity to enter a plea. The charging process can be complex, and it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the procedures and timelines involved.
Complaint or Indictment
A complaint or indictment is a formal document that outlines the alleged offense and the corresponding charges. The complaint or indictment will typically include the following information:
- A description of the alleged offense
- The corresponding charges
- The potential penalties
- The names and contact information of the parties involved
Arraignment
An arraignment is a court hearing where the individual charged is formally advised of the charges and given the opportunity to enter a plea. During the arraignment, the judge will:
- Advise the individual of their rights
- Explain the charges and potential penalties
- Ask the individual to enter a plea (guilty, not guilty, or no contest)
- Set a bail amount or conditions for release
Key Points
- Understanding the nuances of arrest charge information is crucial for navigating the complex legal system.
- Arrest charges can be broadly categorized into two main types: misdemeanors and felonies.
- The charging process typically begins with an arrest, followed by the issuance of a complaint or indictment.
- The complaint or indictment outlines the alleged offense, the corresponding charges, and the potential penalties.
- An arraignment is a court hearing where the individual charged is formally advised of the charges and given the opportunity to enter a plea.
Consequences of a Conviction
A conviction can have significant consequences, including fines, probation, imprisonment, and a permanent record. The severity of the consequences will depend on the type of charge, the individual’s prior record, and the jurisdiction. It is essential to understand the potential consequences of a conviction and to seek the advice of a qualified attorney to navigate the complex legal system.
Short-Term Consequences
Short-term consequences of a conviction can include:
- Fines and court costs
- Probation or community service
- Short-term imprisonment
- Loss of driving privileges
Long-Term Consequences
Long-term consequences of a conviction can include:
- A permanent record
- Loss of employment opportunities
- Difficulty obtaining loans or credit
- Loss of professional licenses or certifications
What is the difference between a misdemeanor and a felony?
+A misdemeanor is generally considered a less serious offense, punishable by fines, probation, or short-term imprisonment. A felony, on the other hand, is a more serious crime that can result in significant prison time, fines, and long-term consequences.
What is the charging process?
+The charging process typically begins with an arrest, followed by the issuance of a complaint or indictment. The complaint or indictment outlines the alleged offense, the corresponding charges, and the potential penalties. The individual charged will then be scheduled for an arraignment, where they will be formally advised of the charges and given the opportunity to enter a plea.
What are the consequences of a conviction?
+A conviction can have significant consequences, including fines, probation, imprisonment, and a permanent record. The severity of the consequences will depend on the type of charge, the individual's prior record, and the jurisdiction.
Meta description suggestion: “Arrest charge information guide: Understand the different types of charges, the charging process, and the potential consequences of a conviction. Learn about the nuances of the legal system and how to navigate the complex process.” (145 characters)

