The United States military is composed of several branches, each with its own reserve components. Two of the most well-known reserve components are the Army Reserve and the National Guard. While both organizations are part of the military, they have distinct differences in their mission, structure, and deployment policies. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals considering a career in the military, as well as for policymakers and the general public.
Introduction to the Army Reserve and National Guard

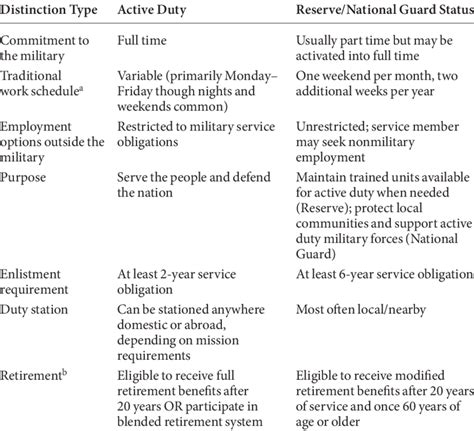
The Army Reserve is a federal force that provides support to the active-duty Army, while the National Guard is a dual-status force that can be called upon by both state and federal governments. The Army Reserve is composed of approximately 200,000 soldiers, with units located throughout the United States. The National Guard, on the other hand, has around 450,000 soldiers, with units in every state and territory.
Key Points
- The Army Reserve is a federal force that provides support to the active-duty Army.
- The National Guard is a dual-status force that can be called upon by both state and federal governments.
- The Army Reserve has approximately 200,000 soldiers, while the National Guard has around 450,000 soldiers.
- Deployment policies and training requirements differ between the two organizations.
- Both organizations offer opportunities for education, career advancement, and personal development.
Mission and Structure
The Army Reserve’s primary mission is to provide support to the active-duty Army during times of war or national emergency. The Army Reserve is organized into several commands, including the Army Reserve Command, the Army Reserve Personnel Command, and the Army Reserve Medical Command. In contrast, the National Guard has a dual mission: to provide support to the active-duty Army and to respond to state emergencies, such as natural disasters or civil disturbances. The National Guard is organized into two main components: the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard.
| Organization | Mission | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Army Reserve | Support active-duty Army | Federal force with several commands |
| National Guard | Support active-duty Army and respond to state emergencies | Dual-status force with Army and Air components |
Deployment Policies
Deployment policies differ significantly between the Army Reserve and the National Guard. Army Reserve soldiers can be deployed for up to 12 months at a time, with deployments typically occurring every 2-3 years. National Guard soldiers, on the other hand, can be deployed for up to 12 months, but deployments are typically less frequent, occurring every 5-6 years. Additionally, National Guard soldiers may be called upon to respond to state emergencies, which can result in shorter deployments.
Training Requirements
Training requirements also differ between the two organizations. Army Reserve soldiers typically attend drill weekends one weekend per month and annual training for two weeks per year. National Guard soldiers, on the other hand, attend drill weekends one weekend per month and annual training for 15-30 days per year. Both organizations require soldiers to complete basic training and advanced individual training, as well as attend periodic training exercises and drills.
Education and Career Advancement
Both the Army Reserve and the National Guard offer opportunities for education and career advancement. The Military Tuition Assistance Program provides financial assistance for soldiers pursuing higher education, while the GI Bill offers education benefits for soldiers who have completed their service. Additionally, both organizations offer training and certification programs in various fields, such as medicine, engineering, and logistics.
Conclusion

In conclusion, while both the Army Reserve and the National Guard are part of the military, they have distinct differences in their mission, structure, and deployment policies. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals considering a career in the military, as well as for policymakers and the general public. By providing opportunities for education, career advancement, and personal development, both organizations offer a rewarding and challenging experience for soldiers.
What is the main difference between the Army Reserve and the National Guard?
+The main difference is that the Army Reserve is a federal force that provides support to the active-duty Army, while the National Guard is a dual-status force that can be called upon by both state and federal governments.
How often can Army Reserve soldiers be deployed?
+Army Reserve soldiers can be deployed for up to 12 months at a time, with deployments typically occurring every 2-3 years.
What training requirements do National Guard soldiers have?
+National Guard soldiers attend drill weekends one weekend per month and annual training for 15-30 days per year, in addition to completing basic training and advanced individual training.


