The role of an Air Traffic Control Manager is a critical one, requiring a unique blend of technical expertise, leadership skills, and the ability to perform under pressure. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the importance of effective air traffic control management has never been more pronounced. With the global air traffic control market projected to reach $12.3 billion by 2025, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2020 to 2025, the demand for skilled and experienced air traffic control managers is on the rise.
Air Traffic Control Managers are responsible for overseeing the daily operations of air traffic control facilities, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the National Airspace System (NAS). This involves coordinating with air traffic controllers, pilots, and other stakeholders to minimize delays, prevent accidents, and optimize air traffic flow. According to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), there were over 16.4 million flights in the NAS in 2020, highlighting the complexity and scale of air traffic control operations.
Key Points
- The air traffic control market is projected to reach $12.3 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 4.5% from 2020 to 2025.
- Air Traffic Control Managers oversee the daily operations of air traffic control facilities, ensuring safe and efficient aircraft movement.
- Effective air traffic control management requires technical expertise, leadership skills, and the ability to perform under pressure.
- The FAA reports over 16.4 million flights in the NAS in 2020, highlighting the complexity of air traffic control operations.
- Air Traffic Control Managers must stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and procedures to ensure the safe and efficient movement of aircraft.
Air Traffic Control Operations

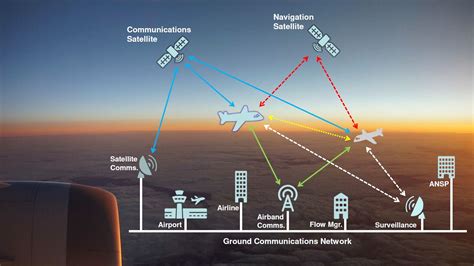
Air traffic control operations involve a range of activities, from coordinating flight plans and clearances to managing air traffic flow and responding to emergencies. Air Traffic Control Managers must have a deep understanding of air traffic control procedures, as well as the technical systems and equipment used to support these operations. This includes radar systems, communication networks, and air traffic control software. For example, the FAA’s Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system, which provides real-time aircraft position and velocity data, has improved air traffic control efficiency and safety.
Air Traffic Control Technologies
The air traffic control industry is undergoing significant technological advancements, with the introduction of new systems and equipment designed to improve efficiency, safety, and capacity. Air Traffic Control Managers must stay up-to-date with these developments, including the implementation of NextGen air traffic control systems, which leverage advanced technologies such as automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) and performance-based navigation (PBN). A study by the FAA found that the implementation of NextGen systems has resulted in a 35% reduction in flight delays and a 25% reduction in fuel consumption.
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) | Provides real-time aircraft position and velocity data |
| Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) | Enables aircraft to fly more precise routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions |
| NextGen Air Traffic Control Systems | Leverages advanced technologies to improve efficiency, safety, and capacity |

Leadership and Management

Air Traffic Control Managers must possess strong leadership and management skills, as they are responsible for supervising teams of air traffic controllers and other support staff. This involves providing guidance, training, and feedback, as well as making strategic decisions about air traffic control operations and resource allocation. Effective communication and collaboration are critical, as air traffic control managers must work closely with pilots, airlines, and other stakeholders to ensure the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. For instance, the use of Crew Resource Management (CRM) techniques has been shown to improve teamwork and communication among air traffic control teams, resulting in improved safety and efficiency.
Strategic Planning and Decision-Making
Air Traffic Control Managers must be able to think strategically, making informed decisions about air traffic control operations and resource allocation. This involves analyzing data and trends, identifying areas for improvement, and developing strategies to optimize air traffic flow and minimize delays. A study by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) found that the implementation of strategic planning and decision-making frameworks has resulted in a 20% reduction in air traffic control costs and a 15% improvement in on-time performance.
In conclusion, the role of an Air Traffic Control Manager is complex and demanding, requiring a unique blend of technical expertise, leadership skills, and the ability to perform under pressure. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the importance of effective air traffic control management will only continue to grow, highlighting the need for skilled and experienced air traffic control managers who can navigate the challenges of this critical role.
What are the primary responsibilities of an Air Traffic Control Manager?
+Air Traffic Control Managers are responsible for overseeing the daily operations of air traffic control facilities, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the National Airspace System (NAS). This involves coordinating with air traffic controllers, pilots, and other stakeholders to minimize delays, prevent accidents, and optimize air traffic flow.
What technologies are being used to improve air traffic control operations?
+The air traffic control industry is undergoing significant technological advancements, with the introduction of new systems and equipment designed to improve efficiency, safety, and capacity. These include automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B), performance-based navigation (PBN), and NextGen air traffic control systems.
What skills are required to be a successful Air Traffic Control Manager?
+Air Traffic Control Managers must possess strong leadership and management skills, as well as technical expertise in air traffic control operations and procedures. Effective communication and collaboration are critical, as air traffic control managers must work closely with pilots, airlines, and other stakeholders to ensure the safe and efficient movement of aircraft.