The rabies vaccine is a crucial component in the prevention and treatment of rabies, a viral disease that affects the nervous system of mammals, including humans. While the vaccine is highly effective in preventing the disease, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Understanding these side effects is essential for healthcare providers and individuals who are considering vaccination. In this article, we will delve into the common side effects of the rabies vaccine, exploring their causes, symptoms, and implications for public health.
Key Points
- The rabies vaccine can cause local and systemic side effects, ranging from mild to severe.
- Common side effects include pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, as well as fever, headache, and fatigue.
- Severe side effects, such as anaphylaxis and neurological disorders, are rare but can be life-threatening.
- The risk of side effects can be minimized by using modern vaccine formulations and following proper vaccination protocols.
- Reporting side effects to healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring vaccine safety and efficacy.
Common Side Effects of the Rabies Vaccine
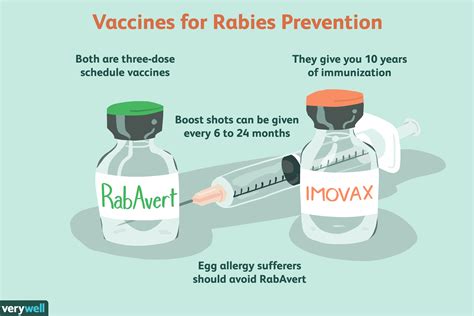
The rabies vaccine can cause a range of side effects, which can be classified into two main categories: local and systemic. Local side effects occur at the site of injection and are usually mild, while systemic side effects affect the entire body and can be more severe. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most common side effects of the rabies vaccine include:
- Pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site (occurring in up to 25% of vaccine recipients)
- Fever (occurring in up to 15% of vaccine recipients)
- Headache (occurring in up to 10% of vaccine recipients)
- Fatigue (occurring in up to 10% of vaccine recipients)
These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days. However, in some cases, they can be more severe and require medical attention.
Severe Side Effects of the Rabies Vaccine
While rare, severe side effects of the rabies vaccine can be life-threatening. These include:
- Anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that can cause difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure (occurring in less than 1% of vaccine recipients)
- Neurological disorders, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, which can cause muscle weakness, numbness, and paralysis (occurring in less than 1% of vaccine recipients)
- Seizures and convulsions (occurring in less than 1% of vaccine recipients)
These severe side effects require immediate medical attention and can have long-term consequences for the individual’s health and well-being.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site | Up to 25% | Pain, redness, swelling, and warmth at the injection site |
| Fever | Up to 15% | Increased body temperature, chills, and sweating |
| Headache | Up to 10% | Pain or discomfort in the head, neck, or shoulders |
| Fatigue | Up to 10% | Feeling tired, weak, or lacking energy |
| Anaphylaxis | Less than 1% | Difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, drop in blood pressure, and skin rash or hives |
| Neurological disorders | Less than 1% | Muscle weakness, numbness, paralysis, seizures, and convulsions |
Minimizing the Risk of Side Effects

To minimize the risk of side effects from the rabies vaccine, it is essential to use modern vaccine formulations and follow proper vaccination protocols. This includes:
- Using vaccines that are manufactured and distributed by reputable companies
- Following the recommended vaccination schedule and dosage
- Monitoring the individual’s health and medical history before vaccination
- Providing clear instructions and guidance on vaccine administration and post-vaccination care
By taking these steps, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of side effects and ensure that the rabies vaccine is administered safely and effectively.
Reporting Side Effects
Reporting side effects to healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring vaccine safety and efficacy. This includes:
- Notifying the healthcare provider of any side effects that occur after vaccination
- Providing detailed information about the side effects, including their severity and duration
- Participating in follow-up evaluations and assessments to monitor the individual’s health and well-being
By reporting side effects, individuals can help healthcare providers identify potential issues and take steps to prevent them in the future.
What are the common side effects of the rabies vaccine?
+The common side effects of the rabies vaccine include pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, as well as fever, headache, and fatigue.
What are the severe side effects of the rabies vaccine?
+The severe side effects of the rabies vaccine include anaphylaxis, neurological disorders, and seizures and convulsions.
How can the risk of side effects from the rabies vaccine be minimized?
+The risk of side effects from the rabies vaccine can be minimized by using modern vaccine formulations and following proper vaccination protocols.
Why is reporting side effects important?
+Reporting side effects is crucial for monitoring vaccine safety and efficacy, and can help healthcare providers identify potential issues and take steps to prevent them in the future.
What should I do if I experience side effects after receiving the rabies vaccine?
+If you experience side effects after receiving the rabies vaccine, you should notify your healthcare provider and provide detailed information about the side effects, including their severity and duration.
In conclusion, while the rabies vaccine can cause side effects, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks. By understanding the common and severe side effects of the rabies vaccine, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Additionally, by reporting side effects and following proper vaccination protocols, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of side effects and ensure that the rabies vaccine is administered safely and effectively.

