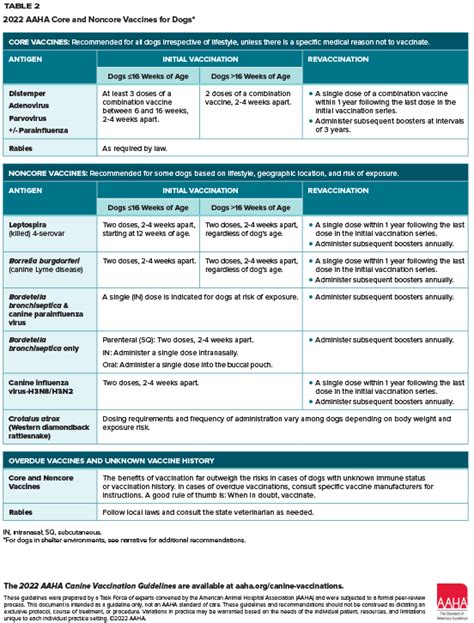
Vaccines have revolutionized the field of medicine, providing protection against a wide range of diseases. Among these, the Aaha vaccine, though not a standard medical term, could be considered in the context of diseases affecting animals, particularly the Aaha disease, which might be a colloquial or less commonly used term. However, for the purpose of this article, we'll focus on vaccine tips that could be universally applied, considering the primary intent might be related to animal health or a specific disease. Understanding vaccines and their administration is crucial for both humans and animals. Here are some essential tips related to vaccines, which can be applied broadly.
Understanding Vaccines

Vaccines are biological preparations that provide active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. They can be prophylactic (to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by a natural or “wild” pathogen) or therapeutic (e.g., to stimulate the body’s immune system against disease). The administration of vaccines is based on the principle that the body’s immune system can recognize and fight pathogens like viruses or bacteria more effectively if it has been pre-exposed to a harmless piece of a pathogen (antigen) or to a weakened pathogen.
Key Points
- Vaccine Types: Vaccines can be classified into several types, including inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, conjugate vaccines, and subunit vaccines, among others.
- Administration: The method of administering a vaccine depends on the type of vaccine. Common methods include injection (intramuscular or subcutaneous), oral, and intranasal.
- Immune Response: Vaccines stimulate the body's immune system to recognize and fight pathogens without causing the disease itself.
- Safety and Efficacy: Vaccines undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before they are approved for use.
- Importance of Booster Shots: Some vaccines require booster shots to maintain immunity over time.
Vaccine Development and Approval Process
The development of a vaccine is a complex, multi-stage process that involves several years of research, testing, and regulatory approvals. It begins with exploratory research where scientists identify natural or synthetic antigens that might be used as vaccine components. This is followed by preclinical testing, where the vaccine is tested in the laboratory and on animals. If successful, the vaccine proceeds to clinical trials in humans, which are conducted in three phases. Phase 1 trials assess the safety of the vaccine in a small group of volunteers. Phase 2 trials evaluate the vaccine’s ability to generate an immune response and its safety in a larger group of people. Phase 3 trials compare the vaccinated group with a placebo group to assess the vaccine’s efficacy and monitor for side effects. After the completion of these phases, the vaccine is submitted for approval to regulatory bodies like the FDA in the United States.
| Vaccine Development Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Exploratory Research | Identification of potential vaccine antigens. |
| Preclinical Testing | Laboratory and animal testing for safety and efficacy. |
| Clinical Trials - Phase 1 | Assessment of safety in a small group of humans. |
| Clinical Trials - Phase 2 | Evaluation of immune response and safety in a larger group. |
| Clinical Trials - Phase 3 | Comparison of vaccinated vs. placebo groups for efficacy and side effects. |
| Regulatory Approval | Submission and approval by regulatory bodies. |

Vaccine Safety and Monitoring
Vaccine safety is a top priority in the development and distribution of vaccines. Even after a vaccine is approved and licensed, its safety continues to be monitored through various systems and studies. This ongoing surveillance helps to quickly identify any potential safety issues and ensures that the benefits of vaccination continue to outweigh the risks. It’s also crucial for maintaining public trust in vaccines and vaccination programs.
Common Misconceptions About Vaccines
There are several misconceptions about vaccines that can lead to confusion and skepticism among the public. For example, the myth that vaccines can cause autism has been thoroughly debunked by scientific research. Similarly, the idea that vaccines overload the immune system is not supported by evidence. Understanding these misconceptions and addressing them with accurate, evidence-based information is vital for promoting vaccine confidence and ensuring high vaccination rates.
What are the benefits of getting vaccinated?
+Vaccination protects not only the individual who receives the vaccine but also helps prevent the spread of disease in the community, thereby protecting those who are not vaccinated, such as young children or people with certain medical conditions.
How are vaccines tested for safety and efficacy?
+Vaccines undergo rigorous testing through preclinical studies and three phases of clinical trials before they are approved for use. Even after approval, vaccines are continuously monitored for safety and efficacy.
Can vaccines cause side effects?
+Like any medication, vaccines can cause side effects, but they are generally mild and temporary, such as soreness at the injection site or a mild fever. Serious side effects are extremely rare.
In conclusion, vaccines play a critical role in public health by providing immunity against infectious diseases. Understanding how vaccines work, their safety profile, and addressing misconceptions are key to maintaining high vaccination rates and protecting communities from outbreaks. As medical science continues to evolve, so does our understanding and development of vaccines, leading to better health outcomes for individuals and populations worldwide.